Question: help fix it Question 5: value equality We ask you to write the value_equality method. Given the two expressions e and f, first compute the
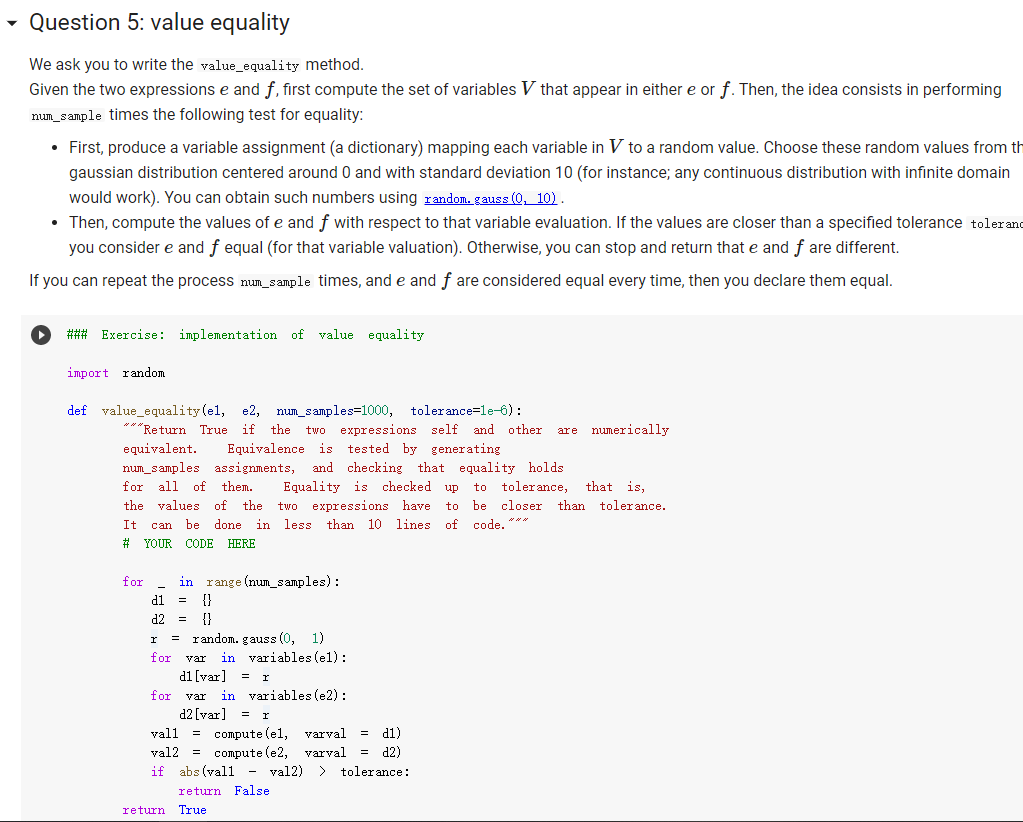

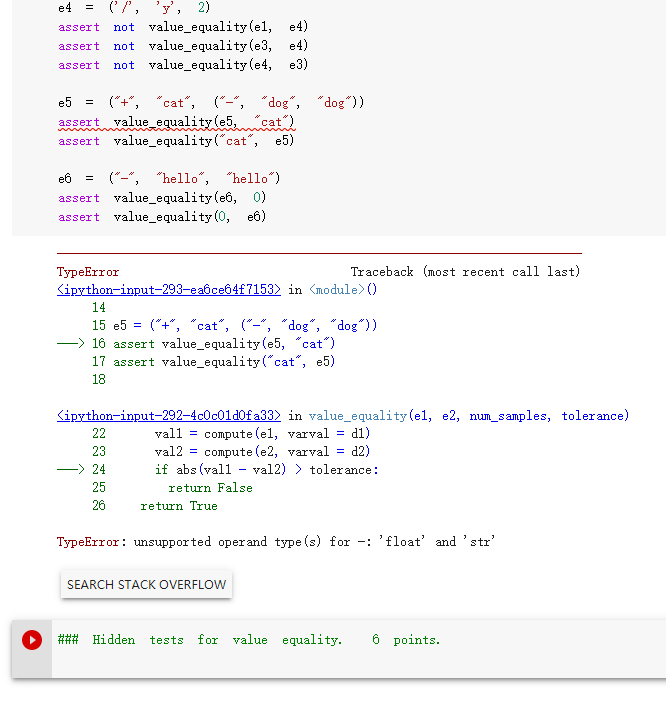
help fix it
Question 5: value equality We ask you to write the value_equality method. Given the two expressions e and f, first compute the set of variables V that appear in either e or f. Then, the idea consists in performing num_sample times the following test for equality: First, produce a variable assignment (a dictionary) mapping each variable in V to a random value. Choose these random values from th gaussian distribution centered around 0 and with standard deviation 10 (for instance; any continuous distribution with infinite domain would work). You can obtain such numbers using random. gauss (0, 10). Then, compute the values of e and f with respect to that variable evaluation. If the values are closer than a specified tolerance toleran you consider e and f equal (for that variable valuation). Otherwise, you can stop and return that e and f are different. If you can repeat the process num_sample times, and e and f are considered equal every time, then you declare them equal. ### Exercise: implementation of value equality import random def value_equalityel, e2, num_samples=1000, tolerance=le-6): ***Return True if the two expressions self and other are numerically equivalent. Equivalence is tested by generating num_samples assignments, and checking that equality holds for all of them. Equality is checked up to tolerance, that is, the values of the two expressions have to be closer than tolerance. It can be done in less than 10 lines of code. *** # YOUR CODE HERE = = in for - in range (num_samples): d1 ] d2 1) r = random. gauss (0, 1) for var variables (el): di (var] = 1 for var in variables (e2): d2 [var] = 1 vall = compute(el, varval di) val2 compute(e2, varval d2) if abs (vall - val2) > tolerance: return False return True = = [292] = r = d1 {} d2 1} random. gauss (0, 1) for var in variables (el): d1 var) r for var in variables (e2): d2 [var) vali compute (el, varval di) val2 compute (e2, varval = d2) if abs (vall val2) > tolerance: return false return True = 1 ### Tests for value equality. 4 points. el ('+', ('*', 'x', 1), ('*', 'y', 0)) e2 'x' assert value_equality(el, e2) = ('*', 'x', 1)) e3 ('/', ('*', 'x', 'x'), assert value_equality(el, e3) e4 = ('' assert 2) not value_equality(el, e4) not value_equality(e3, e4) not value_equality (e4, e3) assert assert = ("+", e5 "cat", ("-", "dog", "dog")) assert value-equality(e5.cat) assert value_equality("cat", e5) e6 ("-", "hello", "hello") assert value_equality (eb, 0) assert value_equality, e6) TypeError Traceback (most recent call last) Kipython-input-293-ea6ce64f7153> in 0 14 15 e5 = ("+", "cat", ("-", "dog", "dog')) 16 assert value_equality(e5, "cat") 17 assert value_equality("cat", e5) 18 = ('/', 'y', 2) assert not value_equality(el, e4) not value_equality (e3, e4) assert not value_equality(e4, e3) assert e5 ("+", "cat", ("-", "dog", "dog")) assert value_equality(e5,"cat") assert value_equality("cat", e5) e6 ("-", "hello", "hello) assert value_equality (e6, 0) assert value_equality(0, e6) TypeError Traceback (most recent call last) Kipython-input-293-ea6ce64f7153> in 0 14 15 e5 ("+", "cat", ("-", "dog", "dog")) 16 assert value_equality(e5, "cat") 17 assert value_equality("cat", e5) 18 Kipython-input-292-4c0c01d0fa33) in value_equality(el, e2, num_samples, tolerance) 22 vall = compute (el, varval 01) 23 val2 = compute(e2, varval = d2) 24 if abs (vall val2) > tolerance: 25 return false 26 return True TypeError: unsupported operand type (s) for -: 'float' and 'str' SEARCH STACK OVERFLOW ### Hidden tests for value equality. 6 points. Question 5: value equality We ask you to write the value_equality method. Given the two expressions e and f, first compute the set of variables V that appear in either e or f. Then, the idea consists in performing num_sample times the following test for equality: First, produce a variable assignment (a dictionary) mapping each variable in V to a random value. Choose these random values from th gaussian distribution centered around 0 and with standard deviation 10 (for instance; any continuous distribution with infinite domain would work). You can obtain such numbers using random. gauss (0, 10). Then, compute the values of e and f with respect to that variable evaluation. If the values are closer than a specified tolerance toleran you consider e and f equal (for that variable valuation). Otherwise, you can stop and return that e and f are different. If you can repeat the process num_sample times, and e and f are considered equal every time, then you declare them equal. ### Exercise: implementation of value equality import random def value_equalityel, e2, num_samples=1000, tolerance=le-6): ***Return True if the two expressions self and other are numerically equivalent. Equivalence is tested by generating num_samples assignments, and checking that equality holds for all of them. Equality is checked up to tolerance, that is, the values of the two expressions have to be closer than tolerance. It can be done in less than 10 lines of code. *** # YOUR CODE HERE = = in for - in range (num_samples): d1 ] d2 1) r = random. gauss (0, 1) for var variables (el): di (var] = 1 for var in variables (e2): d2 [var] = 1 vall = compute(el, varval di) val2 compute(e2, varval d2) if abs (vall - val2) > tolerance: return False return True = = [292] = r = d1 {} d2 1} random. gauss (0, 1) for var in variables (el): d1 var) r for var in variables (e2): d2 [var) vali compute (el, varval di) val2 compute (e2, varval = d2) if abs (vall val2) > tolerance: return false return True = 1 ### Tests for value equality. 4 points. el ('+', ('*', 'x', 1), ('*', 'y', 0)) e2 'x' assert value_equality(el, e2) = ('*', 'x', 1)) e3 ('/', ('*', 'x', 'x'), assert value_equality(el, e3) e4 = ('' assert 2) not value_equality(el, e4) not value_equality(e3, e4) not value_equality (e4, e3) assert assert = ("+", e5 "cat", ("-", "dog", "dog")) assert value-equality(e5.cat) assert value_equality("cat", e5) e6 ("-", "hello", "hello") assert value_equality (eb, 0) assert value_equality, e6) TypeError Traceback (most recent call last) Kipython-input-293-ea6ce64f7153> in 0 14 15 e5 = ("+", "cat", ("-", "dog", "dog')) 16 assert value_equality(e5, "cat") 17 assert value_equality("cat", e5) 18 = ('/', 'y', 2) assert not value_equality(el, e4) not value_equality (e3, e4) assert not value_equality(e4, e3) assert e5 ("+", "cat", ("-", "dog", "dog")) assert value_equality(e5,"cat") assert value_equality("cat", e5) e6 ("-", "hello", "hello) assert value_equality (e6, 0) assert value_equality(0, e6) TypeError Traceback (most recent call last) Kipython-input-293-ea6ce64f7153> in 0 14 15 e5 ("+", "cat", ("-", "dog", "dog")) 16 assert value_equality(e5, "cat") 17 assert value_equality("cat", e5) 18 Kipython-input-292-4c0c01d0fa33) in value_equality(el, e2, num_samples, tolerance) 22 vall = compute (el, varval 01) 23 val2 = compute(e2, varval = d2) 24 if abs (vall val2) > tolerance: 25 return false 26 return True TypeError: unsupported operand type (s) for -: 'float' and 'str' SEARCH STACK OVERFLOW ### Hidden tests for value equality. 6 points






