Question: Help, I don't know how they're getting these numbers You have been asked to evaluate the economic implications of various methods for cooling condenser effluents

 Help, I don't know how they're getting these numbers
Help, I don't know how they're getting these numbers
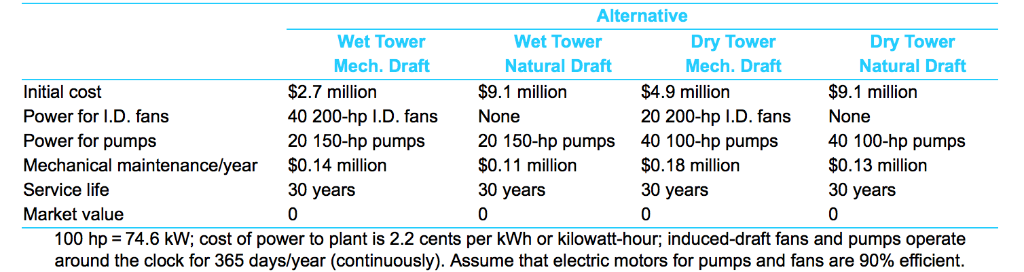
You have been asked to evaluate the economic implications of various methods for cooling condenser effluents from a 200-MW steamelectric plant. There are two basic types of cooling towers: wet and dry. Furthermore, heat may be removed from condenser water by (1) forcing (mechanically) air through the tower or (2) allowing heat transfer to occur by making use of natural draft. Consequently, there are four basic cooling tower designs that could be considered. Assuming that the cost of capital to the utilty co of per year, your job is to recommend the best alternative (i.e., the least expensive during the service life). Further, assume that each alternative is capable of satisfactorily removing waste heat from the condensers of a 200-MW power plant. What noneconomic factors can you identify that might also any is 10% play a role in the decision-making process? EEB Click the icon to view the alternatives description Click the icon to view the interest and annuity table for discrete compounding when i= 10% per year. The AW of Wet Tower, Mechanical Draft is -2,183,648. (Round to the nearest dollar.) 1,554,740. (Round to the nearest dollar.) The AW of Wet Tower, Natural Draft is The AW of Dry Tower, Mechanical Draft is $ (Round to the nearest dollar.) Alternative Wet Tower Dry Tower Dry Tower Wet Tower Natural Draft Mech. Draft Natural Draft Mech. Draft Initial cost $4.9 million $2.7 million $9.1 million $9.1 million 40 200-hp I.D. fans 20 150-hp pumps Power for I.D. fans None 20 200-hp I.D. fans 40 100-hp pumps $0.18 million None Power for pumps 20 150-hp pumps 40 100-hp pumps Mechanical maintenance/year $0.14 million $0.11 million $0.13 million 30 years 30 years 30 years 30 years Service life Market value 0 C 100 hp 74.6 kW; cost of power to plant is 2.2 cents per kWh or kilowatt-hour; induced-draft fans and pumps operate around the clock for 365 days/year (continuously). Assume that electric motors for pumps and fans are 90% efficient. You have been asked to evaluate the economic implications of various methods for cooling condenser effluents from a 200-MW steamelectric plant. There are two basic types of cooling towers: wet and dry. Furthermore, heat may be removed from condenser water by (1) forcing (mechanically) air through the tower or (2) allowing heat transfer to occur by making use of natural draft. Consequently, there are four basic cooling tower designs that could be considered. Assuming that the cost of capital to the utilty co of per year, your job is to recommend the best alternative (i.e., the least expensive during the service life). Further, assume that each alternative is capable of satisfactorily removing waste heat from the condensers of a 200-MW power plant. What noneconomic factors can you identify that might also any is 10% play a role in the decision-making process? EEB Click the icon to view the alternatives description Click the icon to view the interest and annuity table for discrete compounding when i= 10% per year. The AW of Wet Tower, Mechanical Draft is -2,183,648. (Round to the nearest dollar.) 1,554,740. (Round to the nearest dollar.) The AW of Wet Tower, Natural Draft is The AW of Dry Tower, Mechanical Draft is $ (Round to the nearest dollar.) Alternative Wet Tower Dry Tower Dry Tower Wet Tower Natural Draft Mech. Draft Natural Draft Mech. Draft Initial cost $4.9 million $2.7 million $9.1 million $9.1 million 40 200-hp I.D. fans 20 150-hp pumps Power for I.D. fans None 20 200-hp I.D. fans 40 100-hp pumps $0.18 million None Power for pumps 20 150-hp pumps 40 100-hp pumps Mechanical maintenance/year $0.14 million $0.11 million $0.13 million 30 years 30 years 30 years 30 years Service life Market value 0 C 100 hp 74.6 kW; cost of power to plant is 2.2 cents per kWh or kilowatt-hour; induced-draft fans and pumps operate around the clock for 365 days/year (continuously). Assume that electric motors for pumps and fans are 90% efficient
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


