Question: :Help me answer please. 15-3 Compatibility Microsoft and a smaller rival often have to select from one of two competing technologies. The rival always prefers
:Help me answer please.
15-3 Compatibility
Microsoft and a smaller rival often have to select from one of two competing technologies. The rival always prefers to the same technology as Microsoft , while Microsoft always wants to select a different technology from its rival. Describe the compatibility of this game.
Microsoft and a smaller rival often have to select from one of two competing technologies. The rival always prefers to select the same technology as Microsoft , while Microsoft always wants to select a different technology from its rival.
Describe the equilibrium of this game.

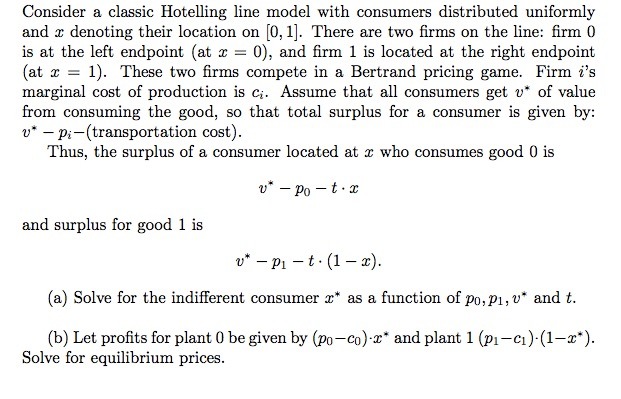
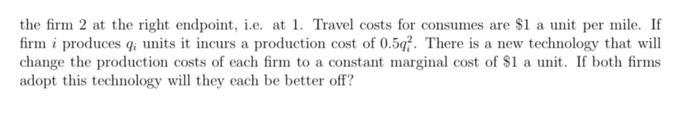
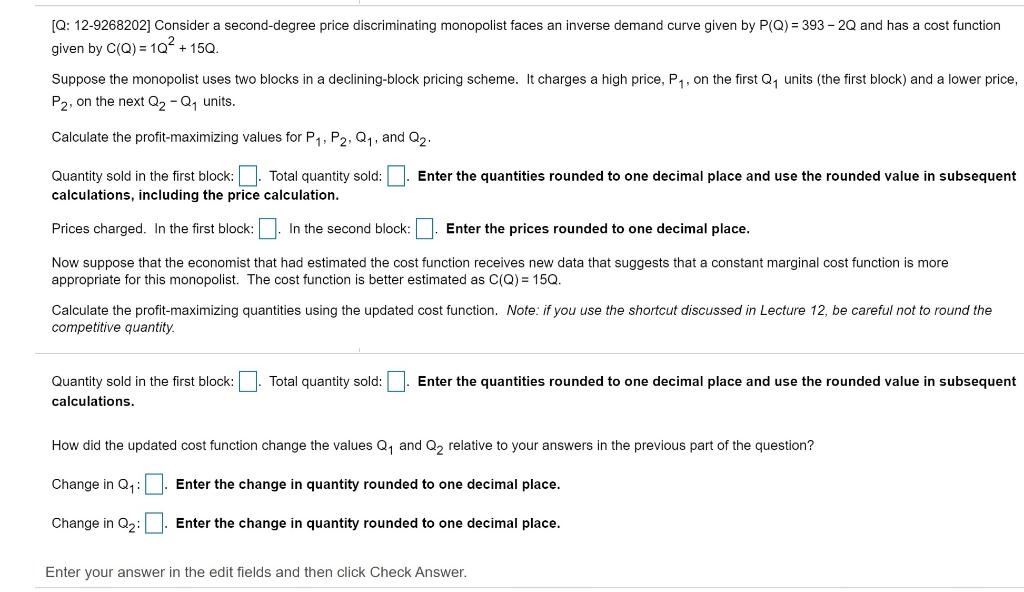
4. Suppose two friends-Jon and Sam-live in a deserted fortress in the bitter cold North. They need to produce swords and axes in order to defend themselves from wild animals. Jon has to work for 2 hours to produce a sword and for 5 hours to produce an axe. Sam needs 10 hours to produce a sword, but only 1 hour to produce an axe. Every day, each friend devotes 20 hours to the production of the two weapons. Use this information to answer the following questions. a. How many hours does Jon need to produce 5 swords? How many hours does Sam need to produce 5 swords? b. How many axes can Jon produce in 1 hour? How many axes can Jon produce in 10 hours? C. Assuming Jon only works on swords, how many swords can he produce in 20 hours? Assuming Jon only works on axes, how many axes can he produce in 20 hours? d. Assuming Sam only works on swords, how many swords can he produce in 20 hours? Assuming Sam only works on axes, how many axes can he produce in 20 hours? e. Fill out the following table: Opportunity cost of 1 sword Opportunity cost of 1 axe (in terms of axes) (in terms of swords) Jon Sam f. Who has the absolute advantage in producing swords? Who has the absolute advantage in producing axes? g. Who has the comparative advantage in producing swords? Who has the comparative advantage in producing axes? 5. Another pair of friends-Kat and Peet-live in an isolated forest. They can only feed themselves by hunting deer and gathering berries. The following table shows how many hours each friend needs to catch one deer or gather a pound of berries. Assume Kat and Peet each have 12 hours every day to hunt and gather. Hours of labor needed to Hours of labor needed to catch one deer gather one pound of berries Ka 1 hour of labor 2 hours of labor Peet 3 hours of labor 4 hours of labor a. Using the above information, draw the production possibilities frontier (PPF) of each friend on two separate graphs. Make sure to label your axes, putting deer on the x- axis and berries on the y-axis. b. Who has the absolute advantage in hunting deer? Who has the absolute advantage in gathering berries? C. Who has the comparative advantage in hunting deer? Who has the absolute advantage in gathering berries? d. What is the acceptable range of trading prices for 1 deer in terms of pounds of berries? Would both sides agree to trade if the price is 1 pound of berries for 1 deer? e. What is the acceptable range of trading prices for 1 pound of berries in terms of deer? Would both sides agree to trade if the price is 1/2 deer for 1 pound of berries? f. On a third graph, draw the joint PPF of Kat and Peet-that is, their PPF if they decide to specialize and combine their production.Consider a classic Hotelling line model with consumers distributed uniformly and a: denoting their location on [i], 1]. There are two rms on the line: rm {I is at the left endpoint (at :r: = ), and rm 1 is located at the right endpoint {at a: = 1}. These two rms compete in a Bertrand pricing game. Firm f's marginal cost of production is c,. Assume that all consumers get 13* of 1value from consuming the good, so that total surplus for a oonsumer is given by: 13* m[transportation cost]. Thus, the surplus of a oonsumer located at 2: who oonsumes good I] is 1.!" pa t + :i: and surplus for good 1 is 19* p1 t+[1:r:). {a} Solve for the indifferent oonsumer is\" as a function of pg, pl, 11* and t. (h) Let prots for plant [1 be given by {pgcg)-r* and plant 1 (p1 c1}-{1:c*}. Solve for equilibrimn prices. the firm 2 at the right endpoint, i.e. at 1. Travel costs for consumes are $1 a unit per mile. If firm i produces q; units it incurs a production cost of 0.57. There is a new technology that will change the production costs of each firm to a constant marginal cost of $1 a unit. If both firms adopt this technology will they each be better off?[Q: 12-9268202] Consider a second-degree price discriminating monopolist faces an inverse demand curve given by P(Q) = 393 - 2Q and has a cost function given by C(Q) = 1Q~ + 15Q. Suppose the monopolist uses two blocks in a declining-block pricing scheme. It charges a high price, P, , on the first Q, units (the first block) and a lower price, P2, on the next Q2 - Q, units. Calculate the profit-maximizing values for P, , P2, Q1 , and Q2. Quantity sold in the first block: . Total quantity sold: . Enter the quantities rounded to one decimal place and use the rounded value in subsequent calculations, including the price calculation. Prices charged. In the first block: . In the second block: . Enter the prices rounded to one decimal place. Now suppose that the economist that had estimated the cost function receives new data that suggests that a constant marginal cost function is more appropriate for this monopolist. The cost function is better estimated as C(Q) = 15Q. Calculate the profit-maximizing quantities using the updated cost function. Note: if you use the shortcut discussed in Lecture 12, be careful not to round the competitive quantity. Quantity sold in the first block: . Total quantity sold: . Enter the quantities rounded to one decimal place and use the rounded value in subsequent calculations. How did the updated cost function change the values Q, and Q2 relative to your answers in the previous part of the question? Change in Q1:]. Enter the change in quantity rounded to one decimal place. Change in Q2: . Enter the change in quantity rounded to one decimal place. Enter your answer in the edit fields and then click Check
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


