Question: Help please 11.8. ATMOSPHERIC 002 NONLINEAR DATA FITTING 99 11.8 Atmospheric 002 Nonlinear Data Fitting It may come as a surprise that we can use
Help please
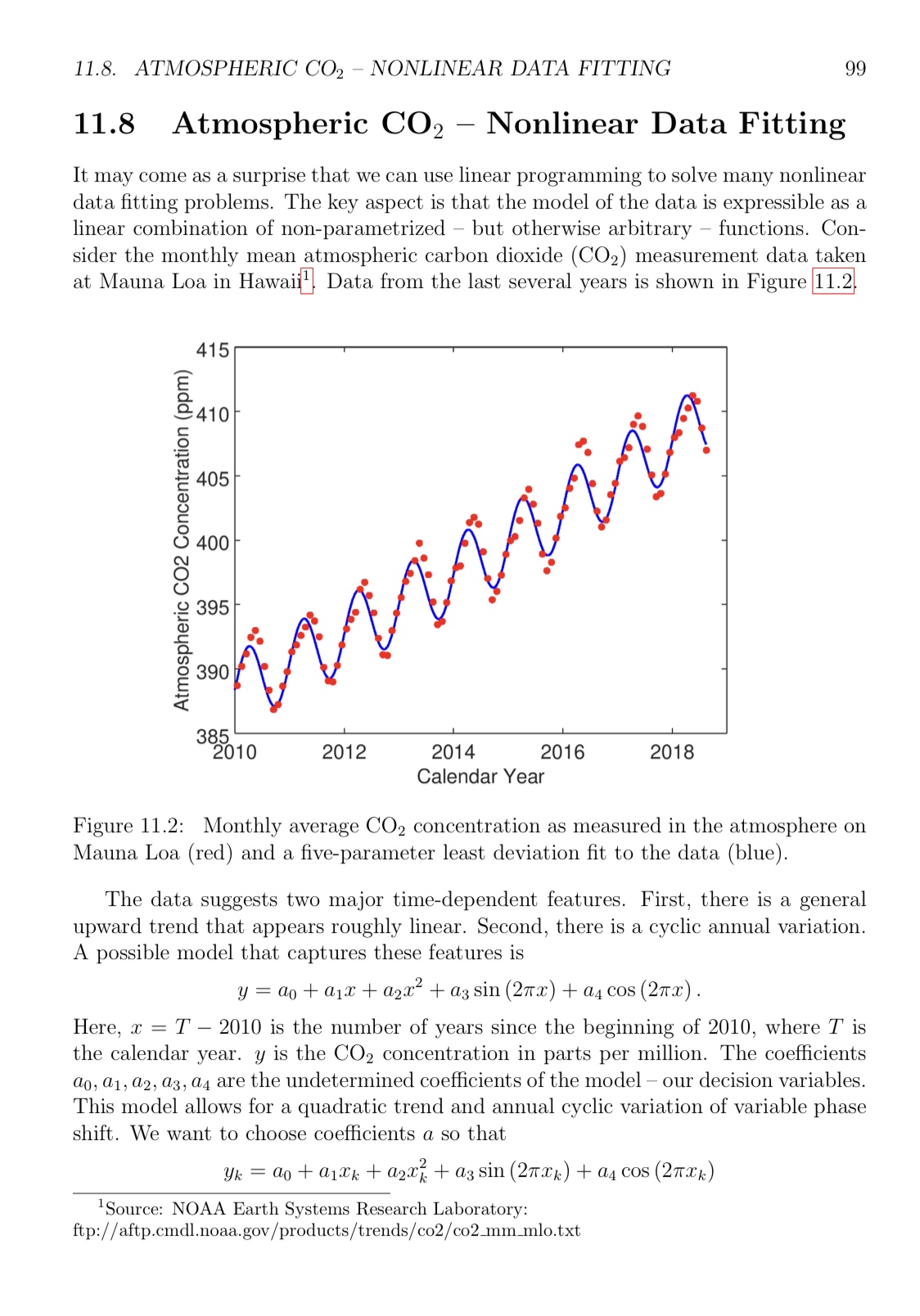



11.8. ATMOSPHERIC 002 NONLINEAR DATA FITTING 99 11.8 Atmospheric 002 Nonlinear Data Fitting It may come as a surprise that we can use linear programming to solve many nonlinear data tting problems. The key aspect is that the model of the data is expressible as a linear combination of non-parametrized but otherwise arbitrary functions. Con sider the monthly mean atmospheric carbon dioxide (002) measurement data taken at Mauna Loa in Hawaii Data from the last several years is shown in Figure m 415 3 o 4:. CI (J1 Atmospheric CO2 Concentration (ppm) .15. O O 8 2010 2012 2014 2016 2018 Calendar Year Figure 11.2: Monthly average 002 concentration as measured in the atmosphere on Mauna Loa (red) and a ve-parameter least deviation t to the data (blue). The data suggests two major timedependent features. First, there is a general upward trend that appears roughly linear. Second, there is a cyclic annual variation. A possible model that captures these features is y = on + 0.12: + 0.22:2 + a3 sin (2m) + (14 cos (27m). Here, :1: = T ~ 2010 is the number of years since the beginning of 2010, where T is the calendar year. y is the CO; concentration in parts per million. The coeicients a0, a1, a2, (t3, (:4 are the undetermined coefcients of the model our decision variables. This model allows for a quadratic trend and annual cyclic variation of variable phase shift. We want to choose coefcients a. so that ye = a0 + alrk + (1217: + a3 sin (21mm) + (14 cos (271ka) 1Source: NOAA Earth Systems Research Laboratory: ftp: / / aftp.cmd1 . noaa. gov / products / trends / {302 / co2_rnm_mlo.txt 8. Based on the ve-parameter model t to the Mauna Loa CO: data1 suggest a different model with no more than seven parameters that may more accurately represent the data set. Carefully justify your model. You do not need to solve this new problem. 11.9. EXABYTE NETWORKING 101 where IN is the column vector of N ones1 IN is the N X N identity matrix, X is the column vector of squared :1: values, 5' and C are the column vectors of values sin(27r:1:) and cos(27r:1:), respectively. The following Octave code solves the CO2 data tting problem (assuming vectors a: and y are dened. N=length(x); c=[zeros(5,1);ones(N,1)]; w=ones(N,1); X=x.\"2; S=sin(2*pi*x); C=cos(2*pi*x); A=[w x -X S -C eye(N) ; w x X S C eye(N)]; B=[- ; y]; lb=-inf(N+5,1); ub= ; ct=repmat("L",1,2*N); vt=repmat("C",1,N+5); sense=1; [xstar,zstar]=glpk(c,A,B,lb,ub,ct,vt,sense); The optimal model parameters are of\" = [ 388.6 2.114 0.0314 2.976 0.840 ] . We can interpret these values as follows. I The seasonally adjusted CO2 level at the beginning of year 2010 was 389 ppm. I The annual increase in CO2 level is 2.11 ppm at the beginning of year 2010. I The annual increase in CO2 level is 2.36 ppm at year 2018 ((11 + 202(8) = 2.36). I The phase of annual variation is close to zero, most of the amplitude being in the sine term. I The seasonal variation in CO2 concentration has amplitude 3.09 ppm (3.09 = 142.976)2 + (0.840)?) 100 CHAPTER 11. MODELING EXAMPLES for all data points (Xk, yk). Using the method of least deviation, we have the opti- mization problem N min a z = > do + allk + a2xx + a3 sin (2Xk) + a4 cos (2mack) - yk k=1 and the equivalent linear formulation min a,o 2 = ) Ok k = 1 s.t. ok _ tao + allk + azz + a3 sin (24Xk) + 04 cos (24Xk) - yk k = 1,2, ..., N ok 2 -do - allk - a2x2 - a3 sin (27Xk) - a4 COS (2Xk) + yk k = 1,2, ..., N. Upon some rearrangement of terms, we have min 2 a,6 k = 1 s.t. -do - allk - Q2xk - a3 sin (27Xk) - 14 COS (27Xk) + 6k 2 -yk k = 1, 2, ..., N tao + al k + a2xx + a3 sin (27XCk) + 04 cos (2nack) + 0k 2 +yk k = 1,2, ..., N. which we can write in matrix form min z = cow s.t. Aw > B W > 0 WERN+5 w = do a1 a2 a3 a4 61 62 ... ON c = 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 ... A = -IN -x -X -S -C IN +IN +x +X +S +C IN B = -y ty
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


