Question: Help please I need to know if this is correct I need this in by tonight 7. Determine the value of y. 8. Determine the
 Help please I need to know if this is correct I need this in by tonight
Help please I need to know if this is correct I need this in by tonight
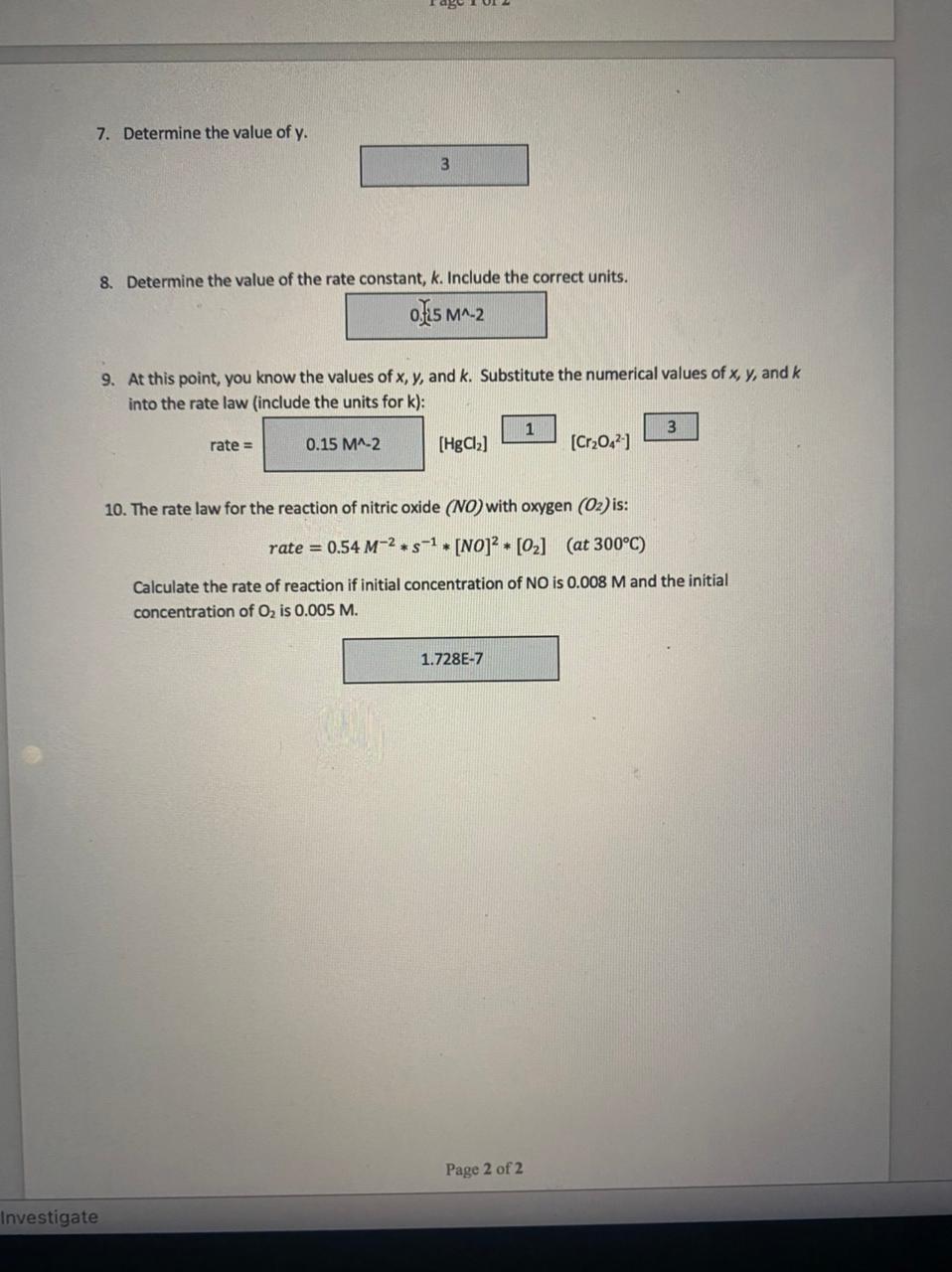
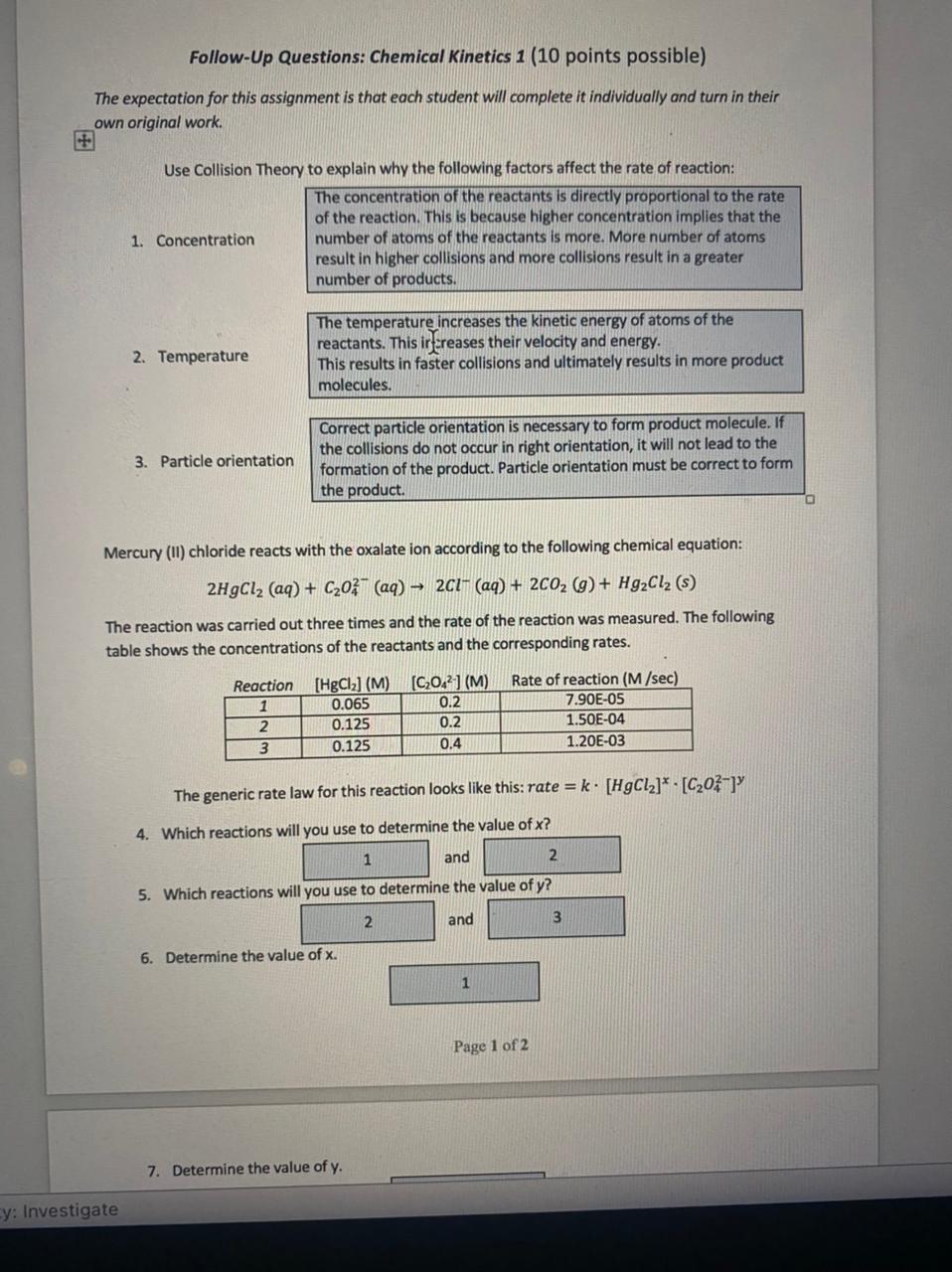
7. Determine the value of y. 8. Determine the value of the rate constant, k. Include the correct units. 9. At this point, you know the values of x,y, and k. Substitute the numerical values of x,y, and k into the rate law (include the units for k ): rate= [HgCl2] [Cr2O42] 10. The rate law for the reaction of nitric oxide (NO) with oxygen (O2) is: rate=0.54M2s1[NO]2[O2](at300C) Calculate the rate of reaction if initial concentration of NO is 0.008M and the initial concentration of O2 is 0.005M. Follow-Up Questions: Chemical Kinetics 1 (10 points possible) The expectation for this assignment is that each student will complete it individually and turn in their own original work. Use Collision Theory to explain why the following factors affect the rate of reaction: The concentration of the reactants is directly proportional to the rate of the reaction. This is because higher concentration implies that the 1. Concentration number of atoms of the reactants is more. More number of atoms result in higher collisions and more collisions result in a greater number of products. The temperature increases the kinetic energy of atoms of the reactants. This irfereases their velocity and energy. 2. Temperature This results in faster collisions and ultimately results in more product molecules. Correct particle orientation is necessary to form product molecule. If the collisions do not occur in right orientation, it will not lead to the 3. Particle orientation formation of the product. Particle orientation must be correct to form the product. Mercury (II) chloride reacts with the oxalate ion according to the following chemical equation: 2HgCl2(aq)+C2O42(aq)2Cl(aq)+2CO2(g)+Hg2Cl2(s) The reaction was carried out three times and the rate of the reaction was measured. The following table shows the concentrations of the reactants and the corresponding rates. The generic rate law for this reaction looks like this: rate =k[HgCl2]x[C2O42]y 4. Which reactions will you use to determine the value of x ? and 5. Which reactions will you use to determine the value of y ? and 6. Determine the value of x
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


