Question: Help Save & Exit $ 2,700, eee 2,025, eee 50 Saved Year ended December 31, 2016 Sales (45,000 tires at $68 each) Less: Variable costs
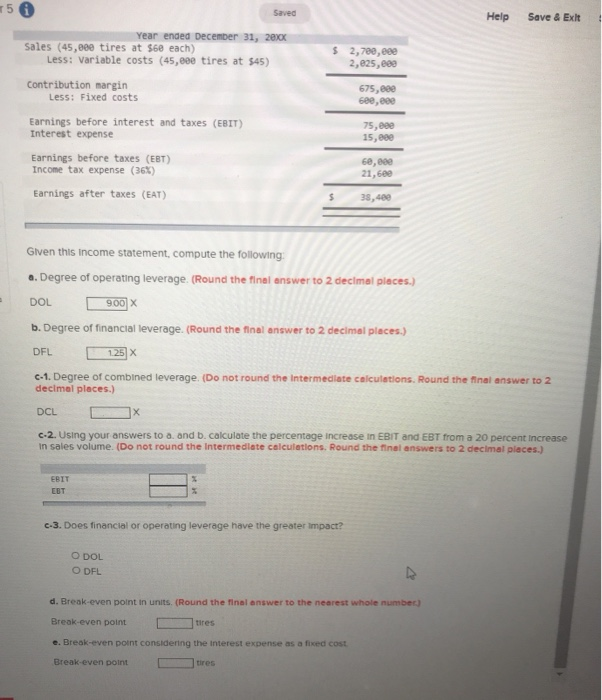
Help Save & Exit $ 2,700, eee 2,025, eee 50 Saved Year ended December 31, 2016 Sales (45,000 tires at $68 each) Less: Variable costs (45,000 tires at $45) Contribution margin Less: Fixed costs Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) Interest expense 675,000 see, eee 75, 15, eee Earnings before taxes (EBT) Income tax expense (36%) 60,000 21,600 Earnings after taxes (EAT) $ 38,400 Given this income statement, compute the following: a. Degree of operating leverage (Round the final answer to 2 decimal places.) DOL 900 b. Degree of financial leverage. (Round the final answer to 2 decimal places.) DFL 125 X c-1. Degree of combined leverage. (Do not round the intermediate calculations. Round the final answer to 2 decimal places.) DCL c-2. Using your answers to a. and b. calculate the percentage increase in EBIT and EBT from a 20 percent increase in sales volume. (Do not round the Intermediate calculations. Round the final answers to 2 decimal places.) EBIT EBT c-3. Does financial or operating leverage have the greater Impact? O DOL O DFL d. Break-even point in units. (Round the final answer to the nearest whole number) Break-even point tires e. Break-even point considering the interest expense as a fixed cost Break-even point tires
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


