Question: help with c and d please 2. Non-covalent interactions. Structures of biological macromolecules, such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), are determined by combinations of covalent and
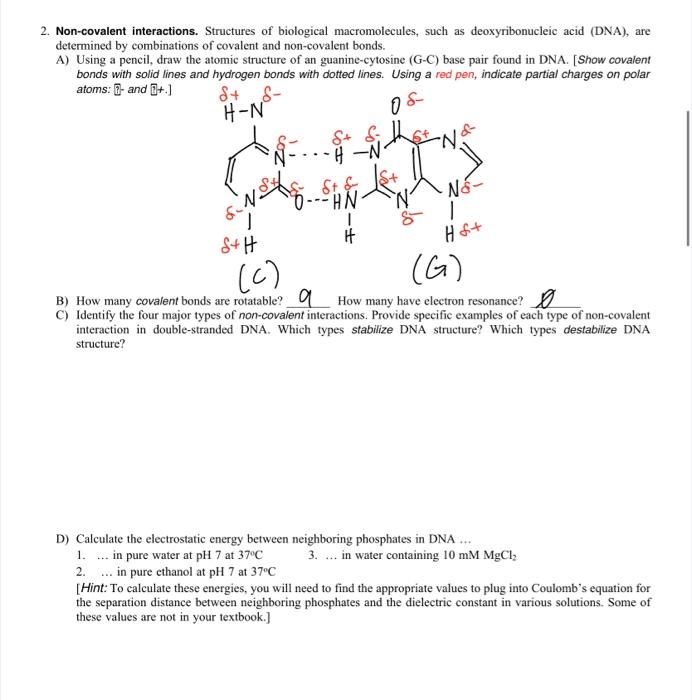
2. Non-covalent interactions. Structures of biological macromolecules, such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), are determined by combinations of covalent and non-covalent bonds. A) Using a pencil, draw the atomic structure of an guanine-cytosine (G-C) base pair found in DNA. [Show covalent bonds with solid lines and hydrogen bonds with dotted lines. Using a red pen, indicate partial charges on polar atoms: ?3. and [8+.] B) How many covalent bonds are rotatable? O( How many have electron resonance? C) Identify the four major types of non-covalent interactions. Provide specific examples of each type of non-covalent interaction in double-stranded DNA. Which types stabilize DNA structure? Which types destabilize DNA structure? D) Calculate the electrostatic energy between neighboring phosphates in DNA ... 1. ... in pure water at pH7 at 37C 3. ... in water containing 10mMMgCl 2. in pure ethanol at pH7 at 37C [Hint: To calculate these energies, you will need to find the appropriate values to plug into Coulomb's equation for the separation distance between neighboring phosphates and the dielectric constant in various solutions. Some of these values are not in your textbook.]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


