Question: Help with this MatLab code gets thumbs up and thanks, all helper functions should be in main CP3LastnameFirstname.m function. Create a MATLAB m file named
Help with this MatLab code gets thumbs up and thanks, all helper functions should be in main CP3LastnameFirstname.m function.
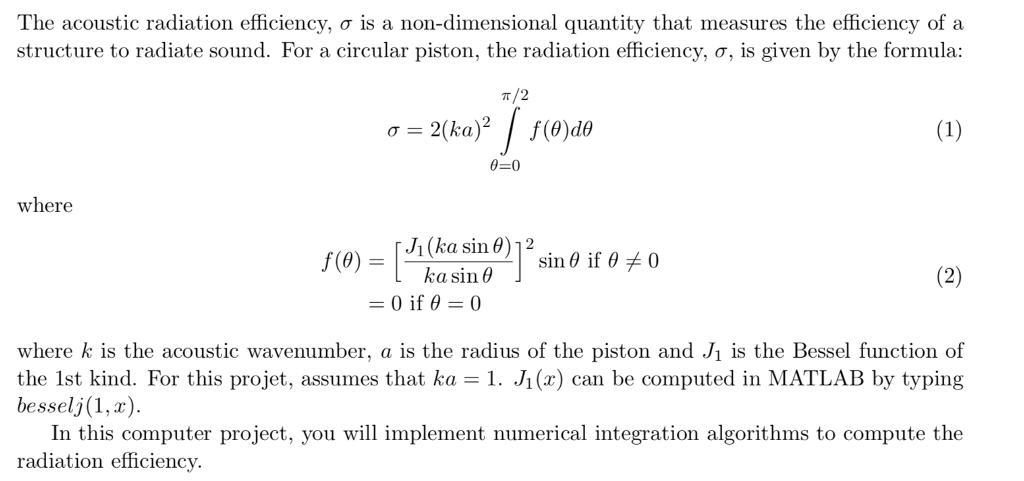

Create a MATLAB m file named CP3LastnameFirstname.m, where Lastname is your last name and Firstname is your first name. This m file should include 5 functions: CP3LastnameFirstname, f, compositeSimp13, Simp38 and SimpInt.
Write the function f defined by Eq. 2. The function should take a variable x as an input and return f(x).
In your LastnameFirstnameCP3.m, call the function f and plot in Figure 1 f() vs for varying from 0 to /2.
where
[J1(kasin)]2 kasin sin if = 0 (2)
f() = = 0 if = 0
1
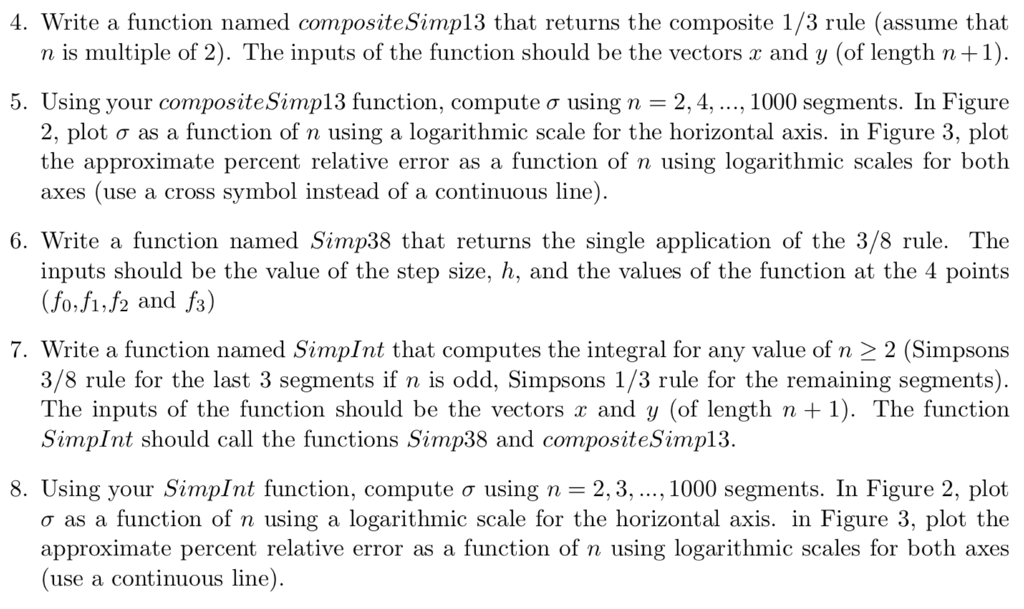
Write a function named compositeSimp13 that returns the composite 1/3 rule (assume that n is multiple of 2). The inputs of the function should be the vectors x and y (of length n+1).
Using your compositeSimp13 function, compute using n = 2, 4, ..., 1000 segments. In Figure 2, plot as a function of n using a logarithmic scale for the horizontal axis. in Figure 3, plot the approximate percent relative error as a function of n using logarithmic scales for both axes (use a cross symbol instead of a continuous line).
Write a function named Simp38 that returns the single application of the 3/8 rule. The inputs should be the value of the step size, h, and the values of the function at the 4 points (f0,f1,f2 and f3)
Write a function named SimpInt that computes the integral for any value of n 2 (Simpsons 3/8 rule for the last 3 segments if n is odd, Simpsons 1/3 rule for the remaining segments). The inputs of the function should be the vectors x and y (of length n + 1). The function SimpInt should call the functions Simp38 and compositeSimp13.
Using your SimpInt function, compute using n = 2, 3, ..., 1000 segments. In Figure 2, plot as a function of n using a logarithmic scale for the horizontal axis. in Figure 3, plot the approximate percent relative error as a function of n using logarithmic scales for both axes (use a continuous line).
The acoustic radiation efficiency, is a non-dimensional quantity that measures the efficiency of a structure to radiate sound. For a circular piston, the radiation efficiency, , is given by the formula: /2 =0 where f(0) = 1- J1 (ka sin L kasin@.] sin if where k is the acoustic wavenumber, a is the radius of the piston and Ji is the Bessel function of the 1st kind. For this projet, assumes that ka -1. Ji(x) can be computed in MATLAB by typing besselj(1, z). In this computer project, you will implement numerical integration algorithms to compute the radiation efficiency. The acoustic radiation efficiency, is a non-dimensional quantity that measures the efficiency of a structure to radiate sound. For a circular piston, the radiation efficiency, , is given by the formula: /2 =0 where f(0) = 1- J1 (ka sin L kasin@.] sin if where k is the acoustic wavenumber, a is the radius of the piston and Ji is the Bessel function of the 1st kind. For this projet, assumes that ka -1. Ji(x) can be computed in MATLAB by typing besselj(1, z). In this computer project, you will implement numerical integration algorithms to compute the radiation efficiency
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


