Question: Here you can upload your proof for Macaulay or Modified Duration and Convexity formulas. The goal here is to take the first derivative of the
Here you can upload your proof for Macaulay or Modified Duration and Convexity formulas.
The goal here is to take the first derivative of the from the bond pricing formula (P = C/(1+y) + C/(1+y)^2 + ...) with respect to "y" to get to the formula on slide#9 on Topic 4 and then the second derivative to arrive at the convexity formula on slide#25 on the same set.
Slide #9
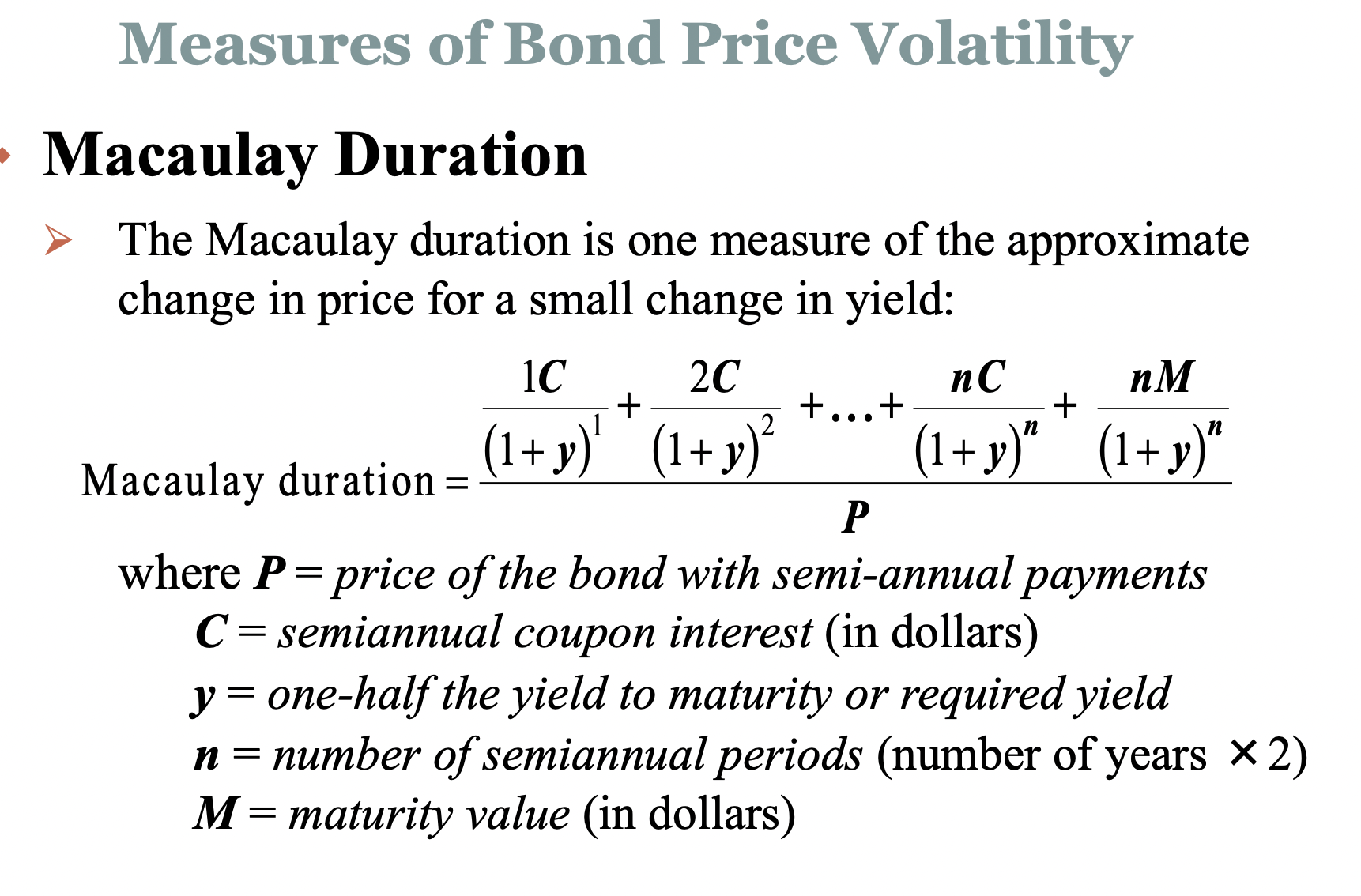
Slide #25
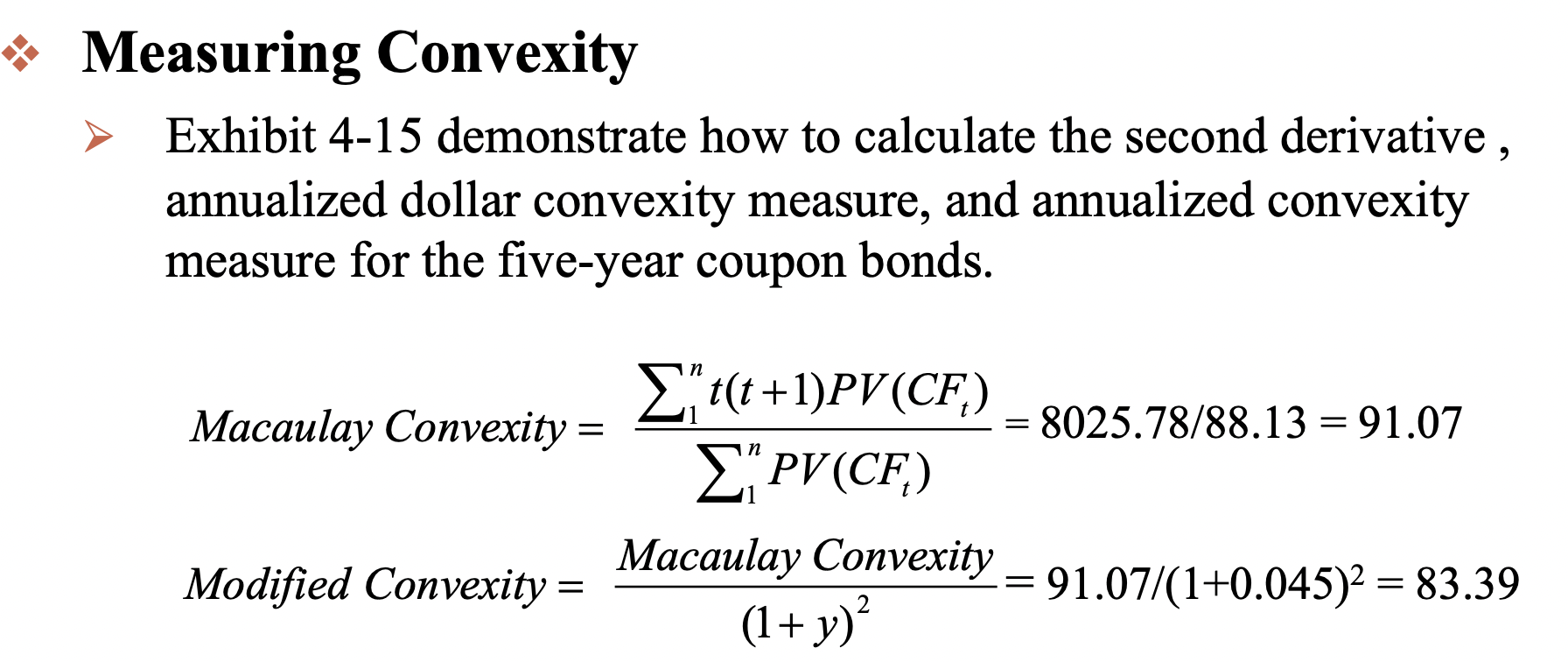
Measures of Bond Price Volatility Macaulay Duration The Macaulay duration is one measure of the approximate change in price for a small change in yield: Macaulayduration=P(1+y)11C+(1+y)22C++(1+y)nnC+(1+y)nnMwhereP=priceofthebondwithsemi-annualpaymentsC=semiannualcouponinterest(indollars)y=one-halftheyieldtomaturityorrequiredyieldn=numberofsemiannualperiods(numberofyears2)M=maturityvalue(indollars) Measuring Convexity Exhibit 4-15 demonstrate how to calculate the second derivative, annualized dollar convexity measure, and annualized convexity measure for the five-year coupon bonds. MacaulayConvexity=1nPV(CFt)1nt(t+1)PV(CFt)=8025.78/88.13=91.07ModifiedConvexity=(1+y)2MacaulayConvexity=91.07/(1+0.045)2=83.39
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


