Question: Here's question 1 for reference: 2. (30 points) A prototype of a dialyzer is built using 2 m? of the membrane in Problem 1 to
Here's question 1 for reference:
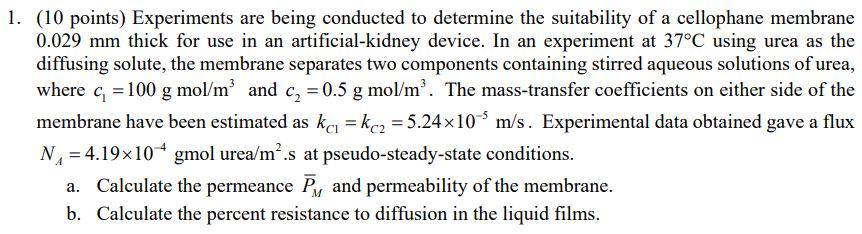
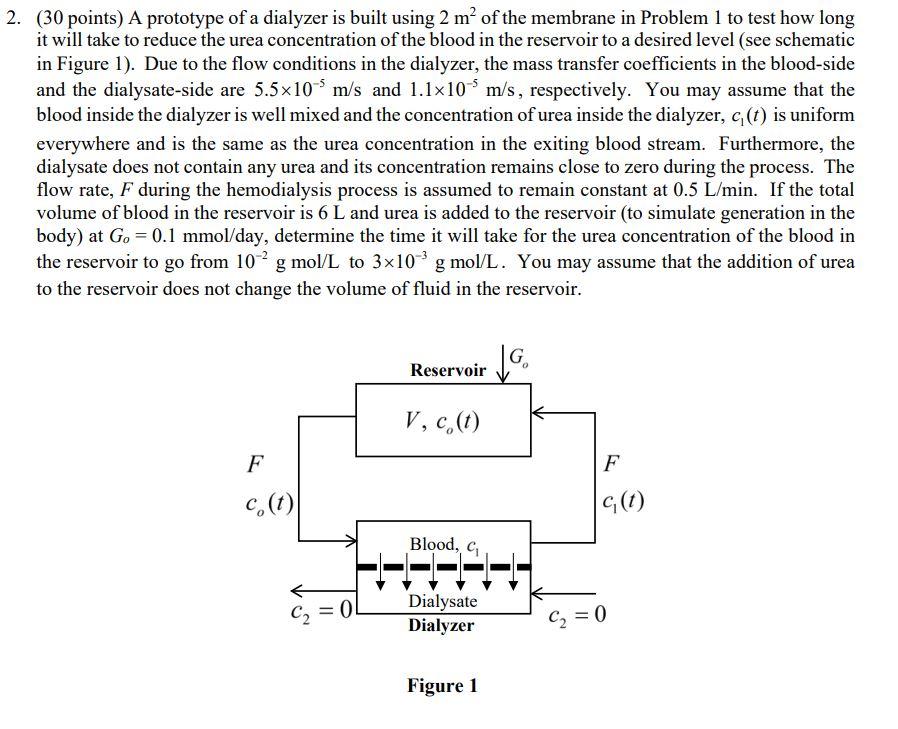
2. (30 points) A prototype of a dialyzer is built using 2 m? of the membrane in Problem 1 to test how long it will take to reduce the urea concentration of the blood in the reservoir to a desired level (see schematic in Figure 1). Due to the flow conditions in the dialyzer, the mass transfer coefficients in the blood-side and the dialysate-side are 5.5x10-4 m/s and 1.1x10 m/s, respectively. You may assume that the blood inside the dialyzer is well mixed and the concentration of urea inside the dialyzer, g(t) is uniform everywhere and is the same as the urea concentration in the exiting blood stream. Furthermore, the dialysate does not contain any urea and its concentration remains close to zero during the process. The flow rate, F during the hemodialysis process is assumed to remain constant at 0.5 L/min. If the total volume of blood in the reservoir is 6 L and urea is added to the reservoir (to simulate generation in the body) at G. = 0.1 mmol/day, determine the time it will take for the urea concentration of the blood in the reservoir to go from 10-2 g mol/L to 3x10 g mol/L. You may assume that the addition of urea to the reservoir does not change the volume of fluid in the reservoir. Reservoir JG V, c,(t) F F c.(t) c(t) Blood, C2 = 0 Dialysate Dialyzer C2 = 0 Figure 1 1. (10 points) Experiments are being conducted to determine the suitability of a cellophane membrane 0.029 mm thick for use in an artificial-kidney device. In an experiment at 37C using urea as the diffusing solute, the membrane separates two components containing stirred aqueous solutions of urea, where c = 100 g mol/m and c, = 0.5 g mol/m. The mass-transfer coefficients on either side of the membrane have been estimated as ka = kcz = 5.24x10 m/s. Experimental data obtained gave a flux N = 4.19x10* gmol urea/ms at pseudo-steady-state conditions. a. Calculate the permeance By and permeability of the membrane. b. Calculate the percent resistance to diffusion in the liquid films
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


