Question: hey I need help with these two questions the first one isn't apart of the stack and queue question how ever the question that follows
hey I need help with these two questions the first one isn't apart of the stack and queue question how ever the question that follows after the class stack and class queue use them. there both in python;
Q1:

Q2:

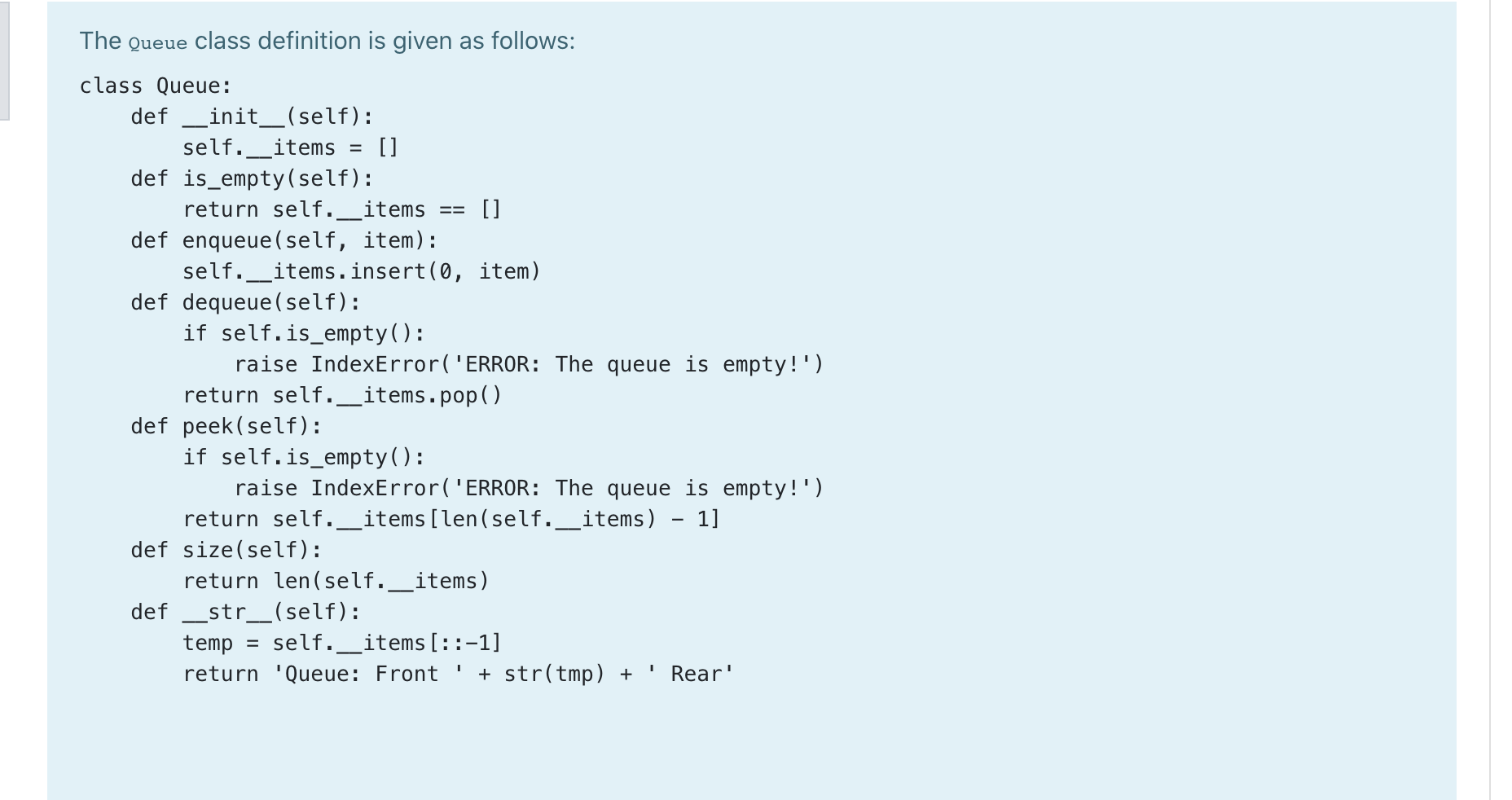
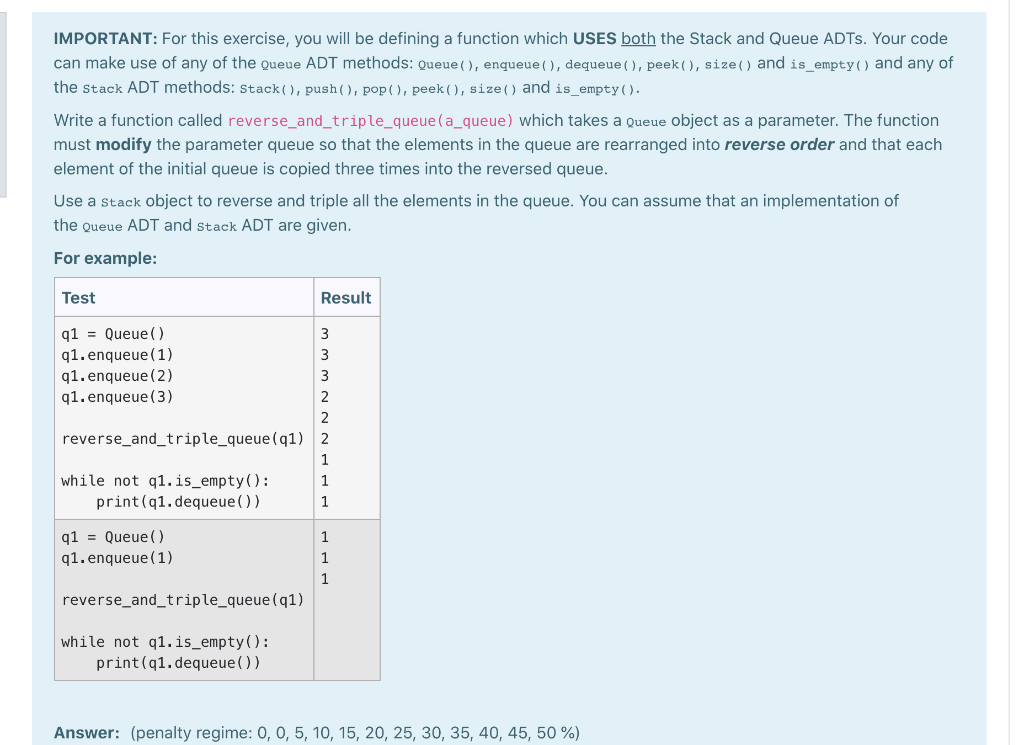
A simple hash function for numeric keys can be defined using the "folding" method: 1. Break the key (integer) into pairs of digits (e.g. if the key is 1234, then the pairs are: 12 34) 2. Add the values together (e.g. 12 + 34) = 46 3. Compute the sum modulo the table size (e.g. if the table size is 7, the hash is 46 % 7 = 4) Define a function called get_folding_hash(key, table_size) which takes a key integer to be hashed and the size of a hash table (i.e. the total number slots available) as parameters. The function uses the folding method to compute the hash value of the key and returns it. If the key is with an odd number of digits, for example, if the key is 12345 and the table size is 11, the result will be 7. (i.e. 12 + 34 + 5 = 51 and 51 % 11 = 7) Note: you can assume that the key is positive. For example: Test Result print(get_folding_hash(1234, 7)) 4 The Stack class definition is given as follows: class Stack: def __init__(self): self. items = [] def is_empty(self): return self._items [] def push(self, item): self._items.append(item) def pop (self): if self.is_empty(): raise IndexError('ERROR: The stack is empty!') return self._items.pop(). def peek (self): if self.is_empty(): raise IndexError('ERROR: The stack is empty!') return self._items [len(self._items) - 1] def size(self): return len(self. _items) def __str__(self): return 'Stack: + str(self._items) 1 The Queue class definition is given as follows: class Queue: def init__(self): self._items = [] def is_empty(self): return self._items [] def enqueue (self, item) : self. __items.insert(0, item) def dequeue (self): if self.is_empty(): raise IndexError('ERROR: The queue is empty!') return self._items.pop() def peek(self): if self.is_empty(): raise IndexError('ERROR: The queue is empty!') return self._items [len(self._items) 1] def size(self): return len(self._items) def _str_(self): temp = self._items [::-1] return 'Queue: Front + str(tmp) + Rear' IMPORTANT: For this exercise, you will be defining a function which USES both the Stack and Queue ADTs. Your code can make use of any of the Queue ADT methods: Queue (), enqueue (), dequeue (), peek(), size() and is_empty() and any of the stack ADT methods: Stack(), push(), pop(), peek(), size() and is_empty(). Write a function called reverse_and_triple_queue (a_queue) which takes a Queue object as a parameter. The function must modify the parameter queue so that the elements in the queue are rearranged into reverse order and that each element of the initial queue is copied three times into the reversed queue. Use a stack object to reverse and triple all the elements in the queue. You can assume that an implementation of the Queue ADT and stack ADT are given. For example: Test Result 91 = Queue () 3 91. enqueue (1) 3 91. enqueue (2) 3 91. enqueue (3) 2 2 reverse_and_triple_queue (q1) 2 1 while not q1. is_empty(): 1 print(91. dequeue()) 1 91 = Queue () q1. enqueue (1) 1 1 1 reverse_and_triple_queue (91) while not 91.is_empty(): print(q1. dequeue()) Answer: (penalty regime: 0, 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 %)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


