Question: Hi all, I need some help with these practice problems for MicroEconomics, and I haven't been quite able to understand it as well compared to












Hi all, I need some help with these practice problems for MicroEconomics, and I haven't been quite able to understand it as well compared to the others. Thank you in advance!

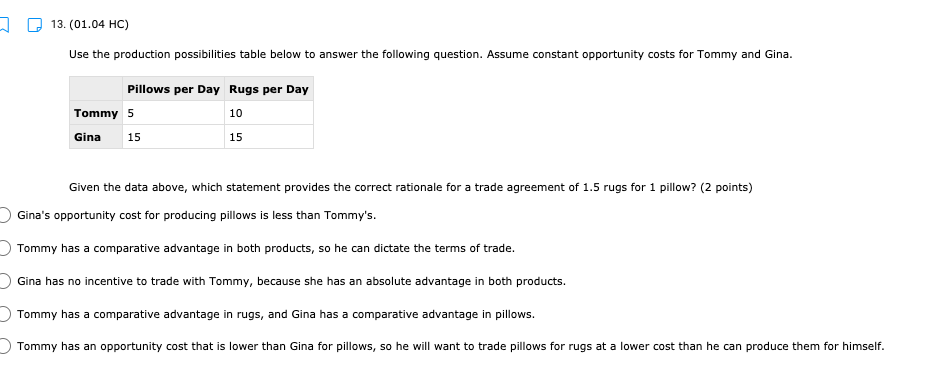
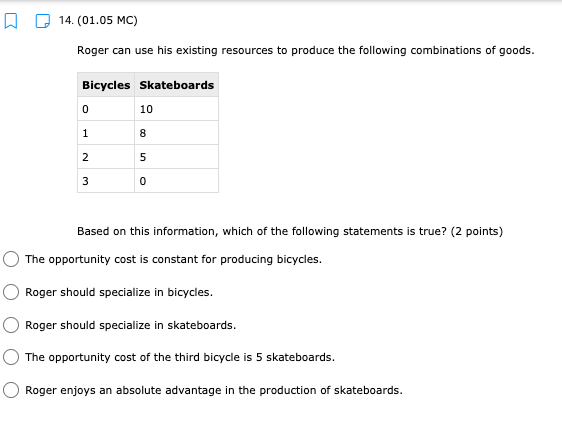




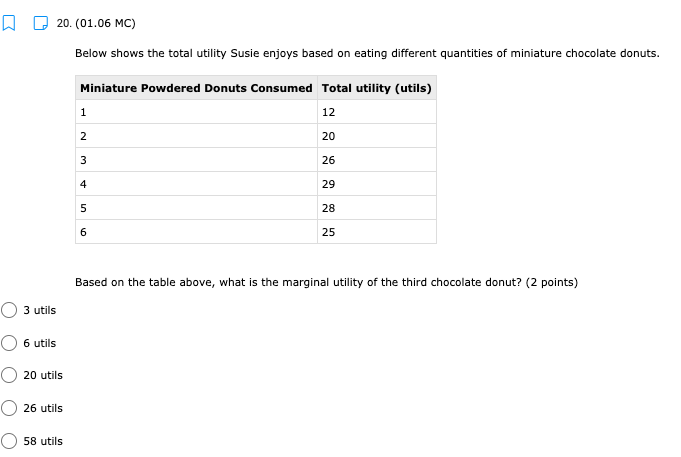


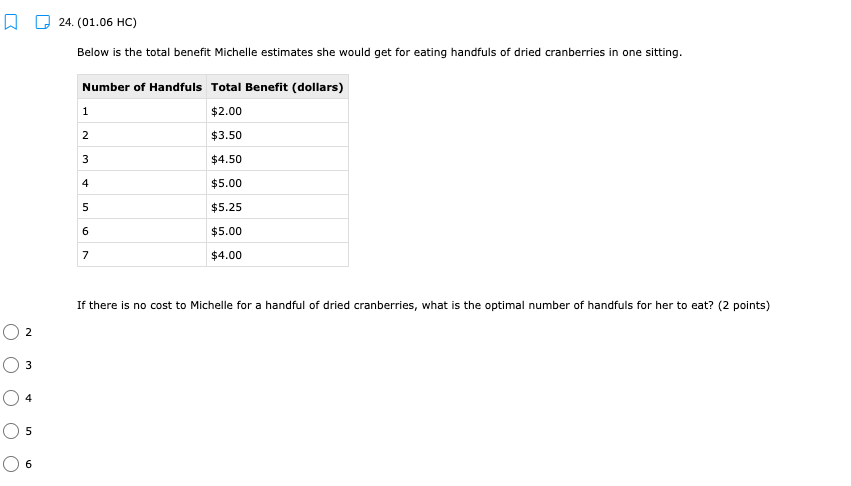


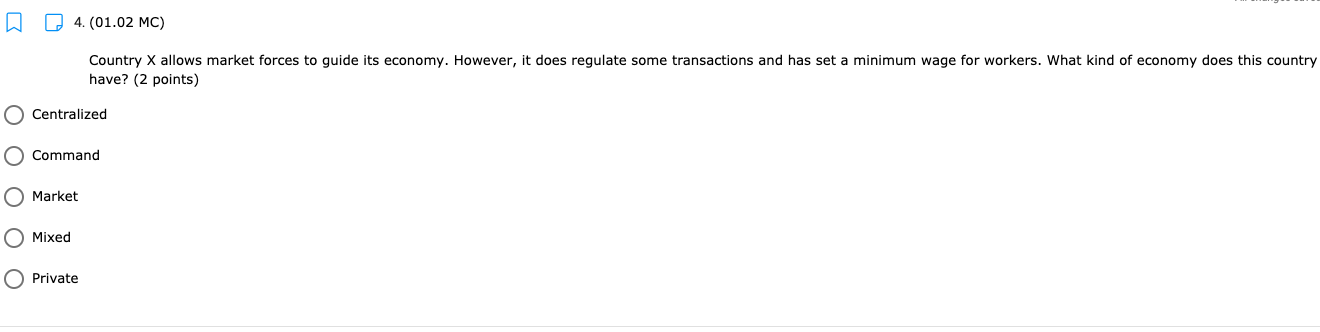

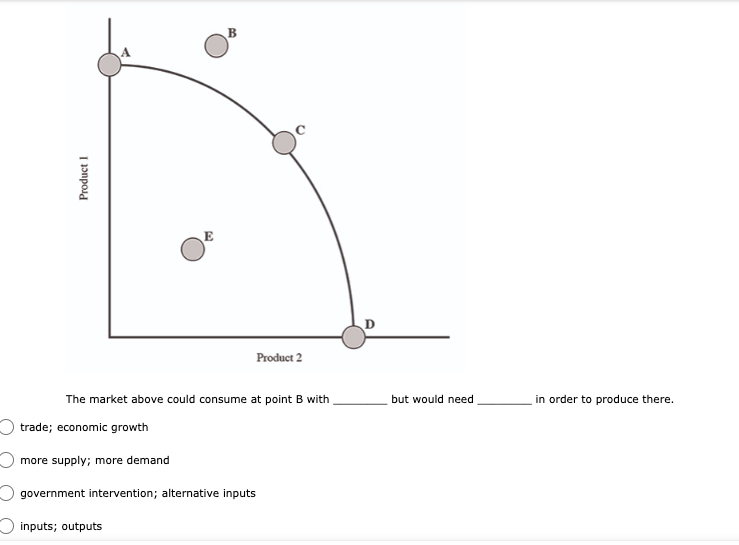


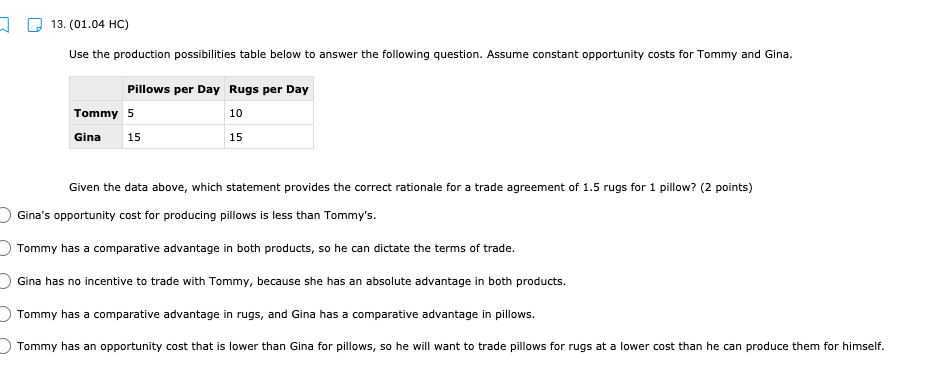
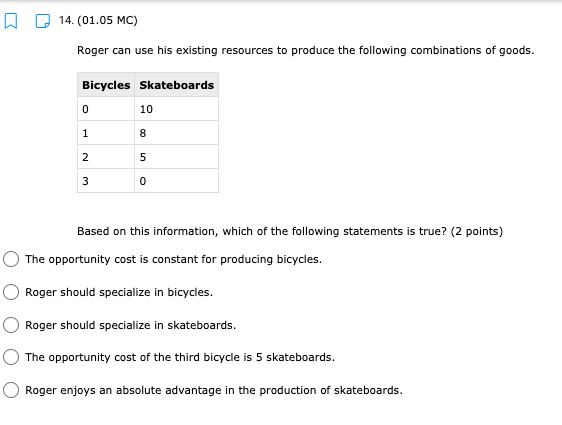
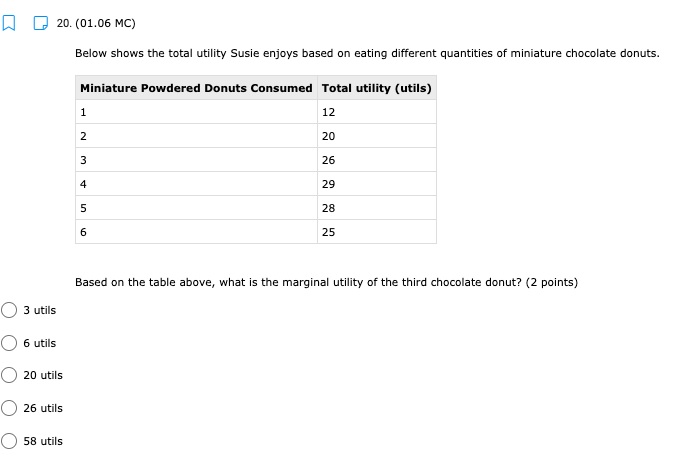
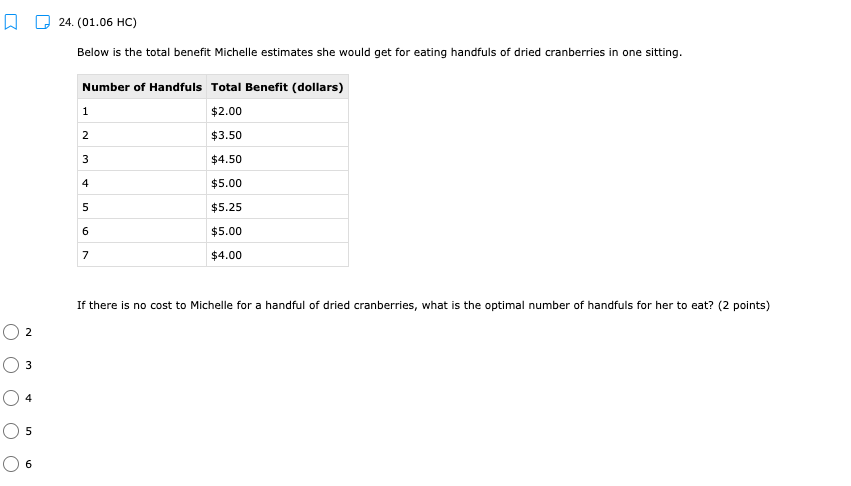
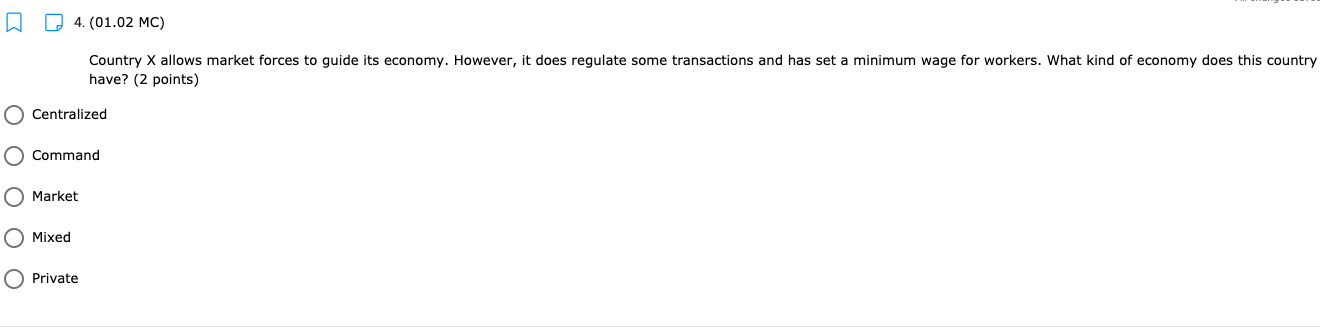
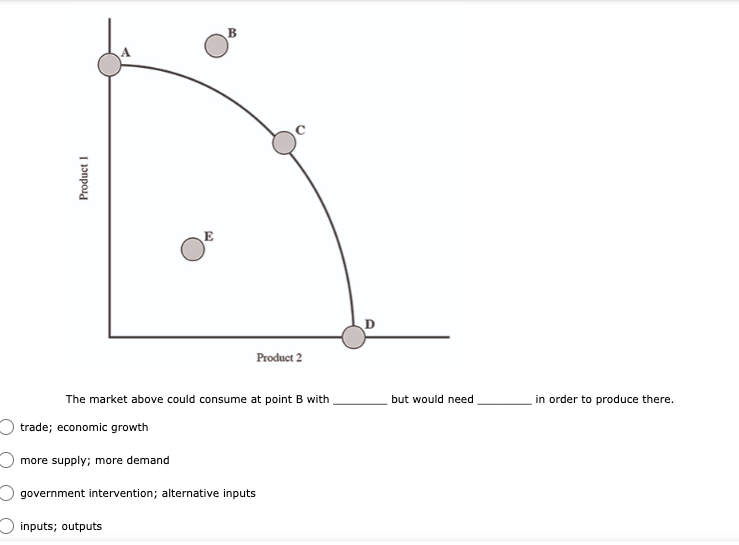
11. (01.04 HC) Using all of their resources, Company A can make either 100 computers or 50 cell phones while Company B can make either 200 computers or 150 cell phones. If both companies have the same quantity of resources, then has an absolute advantage in computers while has a comparative advantage in cell phones. (2 points) Neither; both Company A; Company B Company B; Company A O Company A; Company A Company B; Company B13. (01.04 HC) Use the production possibilities table below to answer the following question. Assume constant opportunity costs for Tommy and Gina. Pillows per Day Rugs per Day Tommy 5 10 Gina 15 15 Given the data above, which statement provides the correct rationale for a trade agreement of 1.5 rugs for 1 pillow? (2 points) Gina's opportunity cost for producing pillows is less than Tommy's. Tommy has a comparative advantage in both products, so he can dictate the terms of trade. Gina has no incentive to trade with Tommy, because she has an absolute advantage in both products. Tommy has a comparative advantage in rugs, and Gina has a comparative advantage in pillows. Tommy has an opportunity cost that is lower than Gina for pillows, so he will want to trade pillows for rugs at a lower cost than he can produce them for himself.14. (01.05 MC) Roger can use his existing resources to produce the following combinations of goods. Bicycles Skateboards 0 10 1 8 2 5 3 0 Based on this information, which of the following statements is true? (2 points) The opportunity cost is constant for producing bicycles. Roger should specialize in bicycles. Roger should specialize in skateboards. The opportunity cost of the third bicycle is 5 skateboards. ()Roger enjoys an absolute advantage in the production of skateboards.15. (01.05 LC) The benefits to businesses are known as and the benefits to consumers are known as (2 points) O revenues; utility O profits, revenues O incentives; revenues O subsidies; taxes utility; profits 16. (01.05 LC) The optimal choice will (2 points) C equalize total benefits and total costs O maximize benefits regardless of costs O minimize total costs regardless of total benefits O maximize revenues O maximize the difference between total benefits and total costs17. (01.05 LC) Deciding whether to purchase an additional unit of a good involves (2 points) O non-rational decision-making O marginal cost-benefit analysis O total cost-benefit analysis O no opportunity costs O finding the least utility per dollar for consumers19. (01.06 LC) The foundational principle of consumer choice theory is that people make choices in order to (2 points) maximize their total utility minimize costs consume the highest quantity for the least price compete with other consumers experience diminishing marginal benefitsm D 2.031111 MC] Which of the following statements about the factors of production is accurate? (2 points] 0 They are all scarce because of unlimited wants and needs. 0 They are not subject to the law of diminishing marginal benet. 0 They are categorized Into consumer, capital, labor, and entrepreneurship. 0 Most are scarce, except for non-rival factors. 0 They are acquired in the product market. 20. (01.06 MC) Below shows the total utility Susie enjoys based on eating different quantities of miniature chocolate donuts. Miniature Powdered Donuts Consumed Total utility (utils) 1 12 2 20 3 26 4 29 28 6 25 Based on the table above, what is the marginal utility of the third chocolate donut? (2 points) 3 utils 6 utils O 20 utils 26 utils O 58 utilsW 22. (01.06 HC) Below is the marginal utilities Rachel receives from books and coffee. Units of Books Marginal Utility of Books Units of Coffee Marginal Utility of Coffee 1 16 1 6 14 2 5 3 12 3 4 4 10 4 3 5 8 5 2 6 6 6 1 Rachel has $10 of income and spends it all on books and coffee. If the price of a book is $2 and the price of a coffee is $1, Rachel will maximize utility by purchasing which of the following combinations of books and coffee? (2 points) 5 books and 0 coffees 4 books and 4 coffees 4 books and 2 coffees 3 books and 4 coffees 2 books and 6 coffees23. (01.06 LC) According to rational consumer choice, what will happen to the optimal quantity of consumption for a good if the price decreases? (2 points) O It will decrease along with total utility. O It will decrease. O It will increase. O It will be unaffected. O Insufficient data to determine24. (01.06 HC) Below is the total benefit Michelle estimates she would get for eating handfuls of dried cranberries in one sitting. Number of Handfuls Total Benefit (dollars) 1 $2.00 2 $3.50 3 $4.50 4 $5.00 5 $5.25 6 $5.00 7 $4.00 If there is no cost to Michelle for a handful of dried cranberries, what is the optimal number of handfuls for her to eat? (2 points) O 2 3 O 4 0 5 O 625. (01.06 MC) A consumer purchases a vehicle that gets very few miles per gallon and realizes that a significant portion of his income is going to gasoline. Which of the following statements accurately represents marginal analysis? (2 points) The consumer should ignore the cost of purchasing the vehicle because the money has already been spent. The consumer should consider getting adequate benefit for the purchase price of the vehicle. O The consumer should evaluate whether it was wise to buy the vehicle. O The consumer should lower his weekly driving miles until the marginal cost is less than the marginal benefit. The consumer should give car rides to his neighbors until the marginal benefit of owning the car is greater than the marginal cost.m D 3.(o1.02 MC) The government of country X owns the means of production, determines incomes and Investment, and decides what goods should be produced and how they should be traded. What economic system does Country X have? (2 points) 0 Comm 3 nd 0 Capitalist O Entrepreneurial 0 Free Enterprise 0 Mixed 4. (01.02 MC) Country X allows market forces to guide its economy. However, it does regulate some transactions and has set a minimum wage for workers. What kind of economy does this country have? (2 points) O Centralized O Command O Market O Mixed Private5. (01.03 LC) The primary function of a PPC is to show (2 points) O allocation efficiency O productive efficiency and opportunity cost O marginal utility O circular flow O the general suitability of all resources for any good or serviceC Product 1 D Product 2 The market above could consume at point B with but would need in order to produce there. trade; economic growth more supply; more demand government intervention; alternative inputs inputs; outputs9. (01.03 MC) How would economic growth be reflected on a production possibility curve? (2 points) O Movement along the curve Not reflected on the PPC O Shift outward of entire curve O Shift inward of entire curve O Stretching along a range of the curvem I] 1.(o1.o1Lc;: Which of the following must be true for a good for which there is demand and a limited supply? [2 points} 0 The good has no utility. O The good's producer enjoys a comparative advantage. 0 Most consumers will nd the good their optimal choice. 0 The good is scarce. O The production of the good will have a constant opportunity:r cost
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


