Question: Hi, I need help coding this in MATLAB. I just need help with the Za, Zb, and Zc parts in the second pages project requirements.
Hi, I need help coding this in MATLAB. I just need help with the Za, Zb, and Zc parts in the second pages project requirements. The figure addressed to recreate in Zb is the last page but all the results for the a4 parameters have to be shown, so a4 goes from .005,.006,.007,....,.0016. Thank you and I will thumbs up helpful answers!

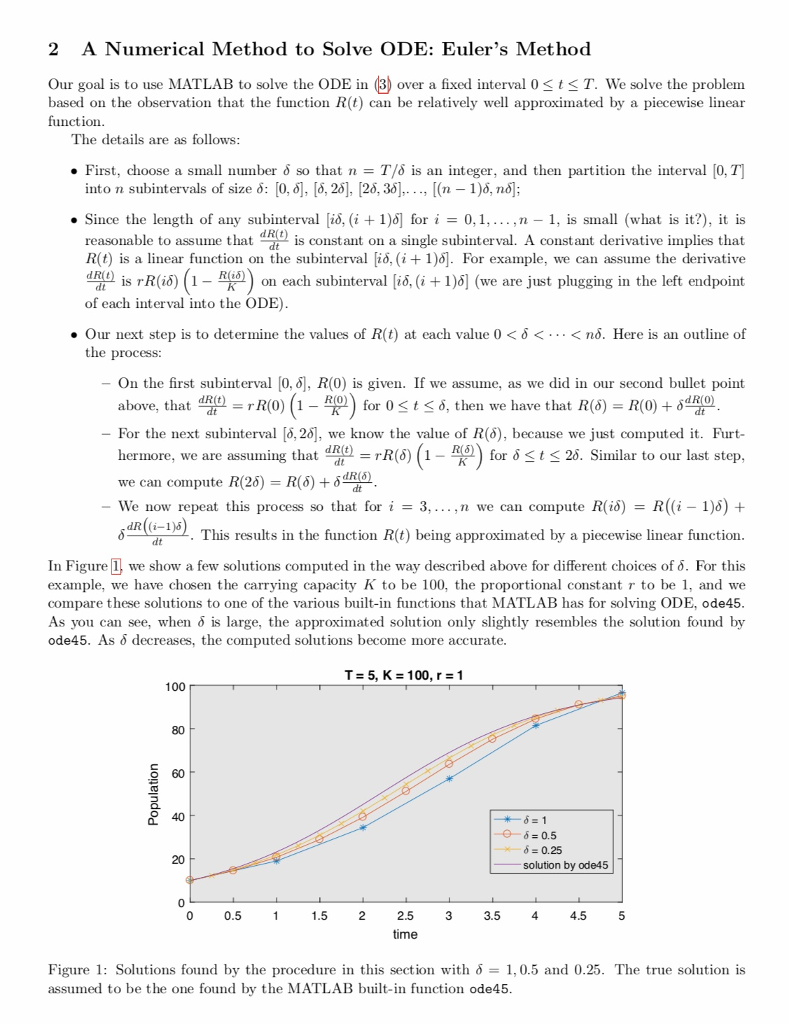





1 Introduction and Models An ordinary differential equation (ODE) is an equation in which a function and its derivatives appear as variables. Because of this, the solution of an ODE is a function rather than just a number. ODE and systems of ODE are prevalent in the sciences and engineering. In this project we explore a particular class of ODE related to population growth and/or decay. In order to illustrate different population models, suppose that we are ecologists interested in a particular population of rabbit on an isolated island. The function R(t) will be used to represent the rabbit population, and gives the number of rabbits at time t. We will assume that the initial (t 0) population of the rabbits is 10 (R(0) = 10). The goal is to determine the rest of the function R(t) so that we know the number of rabbits at any particular time t The first model that we will explore is the exponential population growth model. In this model the growth rate, proportional to the population R(t). This results in the following ODE dR(t) dt where the positive constant r is related to the fecundity of rabbits, that is, the potential for the rabbits to produce offspring. It can be verified (take the derivative of (2)) that the solution to ) is R(t) = R(0)ert 10ert. As t increases, we can see that according to our solution in (2) the rabbit population will increase exponentially with no upper bound. This model fails to take into account a finite supply of resources such as food, water, living space, etc. Therefore this model is not realistic for larger values of t. This necessitates the introduction of the logistic population growth model: where K is the largest possible population of rabbits that the island can hold, also known as the carrying capacity. If the population R(t) is much smaller than the carrying capacity K, then the right hand side of (3) is approximately rR(t) since 1 population R(t) is close to the carrying capacity K, then the right hand side of 3) is approximately 0 and the population grows slowly. From advanced math courses, one can show that the solution is R(t) 1, and the population grows exponentially as in (2). If the KR(0)et K R(0) (ert -1) K10(ert - 1) 10Kert This can also be verified if you have the patience (or Wolfram Alpha). In numerous applications, however, the closed form of the solution is unknown, and so we need a systematic way of solving (or at least approximating the solution to) ODE. 1 Introduction and Models An ordinary differential equation (ODE) is an equation in which a function and its derivatives appear as variables. Because of this, the solution of an ODE is a function rather than just a number. ODE and systems of ODE are prevalent in the sciences and engineering. In this project we explore a particular class of ODE related to population growth and/or decay. In order to illustrate different population models, suppose that we are ecologists interested in a particular population of rabbit on an isolated island. The function R(t) will be used to represent the rabbit population, and gives the number of rabbits at time t. We will assume that the initial (t 0) population of the rabbits is 10 (R(0) = 10). The goal is to determine the rest of the function R(t) so that we know the number of rabbits at any particular time t The first model that we will explore is the exponential population growth model. In this model the growth rate, proportional to the population R(t). This results in the following ODE dR(t) dt where the positive constant r is related to the fecundity of rabbits, that is, the potential for the rabbits to produce offspring. It can be verified (take the derivative of (2)) that the solution to ) is R(t) = R(0)ert 10ert. As t increases, we can see that according to our solution in (2) the rabbit population will increase exponentially with no upper bound. This model fails to take into account a finite supply of resources such as food, water, living space, etc. Therefore this model is not realistic for larger values of t. This necessitates the introduction of the logistic population growth model: where K is the largest possible population of rabbits that the island can hold, also known as the carrying capacity. If the population R(t) is much smaller than the carrying capacity K, then the right hand side of (3) is approximately rR(t) since 1 population R(t) is close to the carrying capacity K, then the right hand side of 3) is approximately 0 and the population grows slowly. From advanced math courses, one can show that the solution is R(t) 1, and the population grows exponentially as in (2). If the KR(0)et K R(0) (ert -1) K10(ert - 1) 10Kert This can also be verified if you have the patience (or Wolfram Alpha). In numerous applications, however, the closed form of the solution is unknown, and so we need a systematic way of solving (or at least approximating the solution to) ODE
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


