Question: Hi I need help with a, b and c. If possible can the questions be done using the following methods: a - observed modulus approach
Hi I need help with a, b and c. If possible can the questions be done using the following methods:
a - observed modulus approach
b - using the relationship between effectiveness factor and intrinsic rate
Would appreciate detailed solutions and explanations thanks!
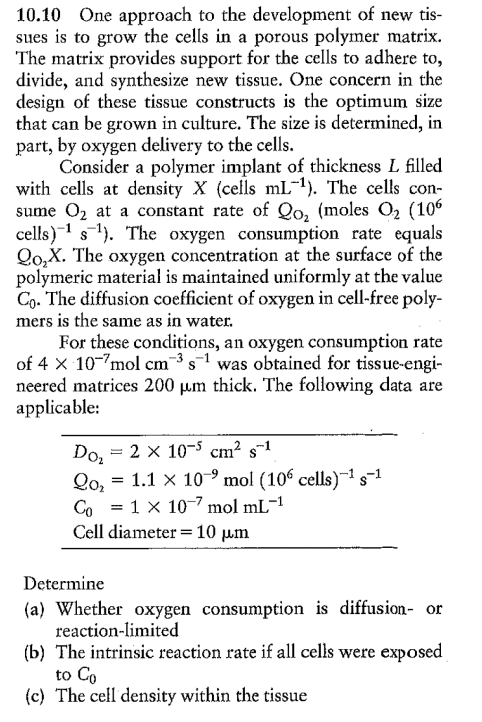
10.10 One approach to the development of new tissues is to grow the cells in a porous polymer matrix. The matrix provides support for the cells to adhere to, divide, and synthesize new tissue. One concern in the design of these tissue constructs is the optimum size that can be grown in culture. The size is determined, in part, by oxygen delivery to the cells. Consider a polymer implant of thickness L filled with cells at density X (cells mL1 ). The cells consume O2 at a constant rate of QO2 (moles O2(106 cells) 1s1 ). The oxygen consumption rate equals QO2X. The oxygen concentration at the surface of the polymeric material is maintained uniformly at the value C0. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen in cell-free polymers is the same as in water. For these conditions, an oxygen consumption rate of 4107molcm3s1 was obtained for tissue-engineered matrices 200m thick. The following data are applicable: DO2=2105cm2s1 QO2=1.1109mol(106cells)1s1 C0=1107molmL1 Cell diameter =10m Determine (a) Whether oxygen consumption is diffusion- or reaction-limited (b) The intrinsic reaction rate if all cells were exposed to C0 (c) The cell density within the tissue
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


