Question: Hi, I'm having some difficulty understanding what the null and alternative hypotheses are and how to construct an ANOVA table. Question #1: (10 marks) Lecture
Hi, I'm having some difficulty understanding what the null and alternative hypotheses are and how to construct an ANOVA table.
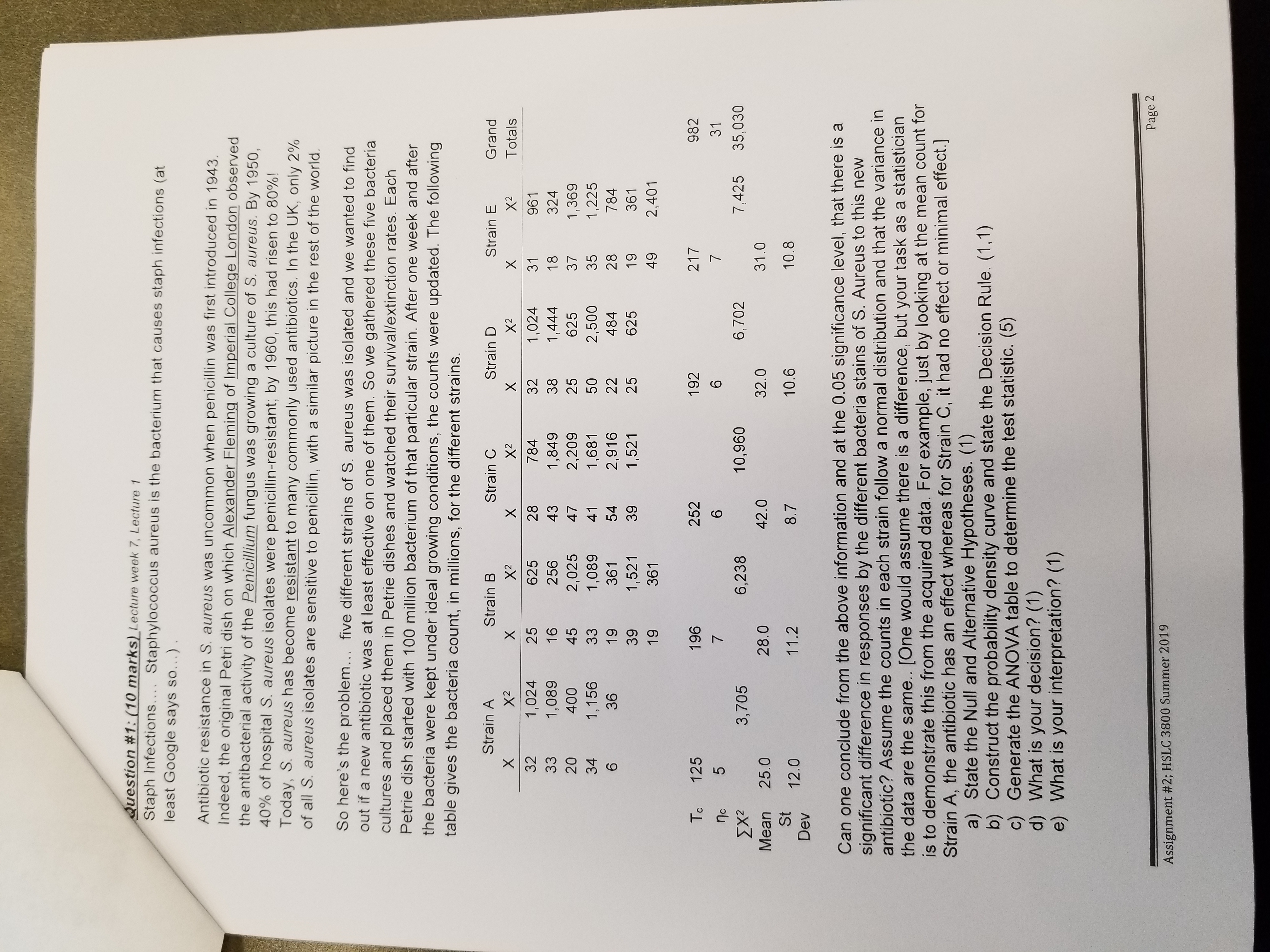
Question #1: (10 marks) Lecture week 7, Lecture 1 Staph Infections.... Staphylococcus aureus is the bacterium that causes staph infections (at least Google says so...) Antibiotic resistance in S. aureus was uncommon when penicillin was first introduced in 1943. Indeed, the original Petri dish on which Alexander Fleming of Imperial College London observed the antibacterial activity of the Penicillium fungus was growing a culture of S. aureus. By 1950, 40% of hospital S. aureus isolates were penicillin-resistant; by 1960, this had risen to 80%! Today, S. aureus has become resistant to many commonly used antibiotics. In the UK, only 2% of all S. aureus isolates are sensitive to penicillin, with a similar picture in the rest of the world. So here's the problem... five different strains of S. aureus was isolated and we wanted to find out if a new antibiotic was at least effective on one of them. So we gathered these five bacteria cultures and placed them in Petrie dishes and watched their survival/extinction rates. Each Petrie dish started with 100 million bacterium of that particular strain. After one week and after the bacteria were kept under ideal growing conditions, the counts were updated. The following table gives the bacteria count, in millions, for the different strains Strain A Strain B Strain C Strain D Strain E Grand X X X X Totals 1,024 625 784 1,024 X m 961 1,089 256 1,849 1,444 324 20 400 2,025 2,209 625 1,369 34 CO 1, 156 1,089 1,681 50 2,500 1,225 36 361 54 2,916 22 484 784 1,52 39 1,521 625 361 361 2,401 125 196 252 192 217 982 SX 3,705 6,238 10,960 6,702 7,425 35,030 Mean 25.0 28. 42.0 32.0 31.0 Dev 12.0 11.2 10.6 10.8 Can one conclude from the above information and at the 0.05 significance level, that there is a significant difference in responses by the different bacteria stains of S. Aureus to this new antibiotic? Assume the counts in each strain follow a normal distribution and that the variance in the data are the same.. [One would assume there is a difference, but your task as a statistician is to demonstrate this from the acquired data. For example, just by looking at the mean count for Strain A, the antibiotic has an effect whereas for Strain C, it had no effect or minimal effect.] a) State the Null and Alternative Hypotheses. (1) b) Construct the probability density curve and state the Decision Rule. (1, 1) c) Generate the ANOVA table to determine the test statistic. (5) d) What is your decision? (1) e) What is your interpretation? (1) Page 2 Assignment #2; HSLC 3800 Summer 2019
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


