Question: Hi, Please, I really need help with this experiment. Thank you very much! SIMULATION : https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/gas-properties/latest/gas-properties_en.html Instruction: Complete table 2 and answer the following discussion
Hi, Please, I really need help with this experiment. Thank you very much!
SIMULATION : https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/gas-properties/latest/gas-properties_en.html
Instruction: Complete table 2 and answer the following discussion below.

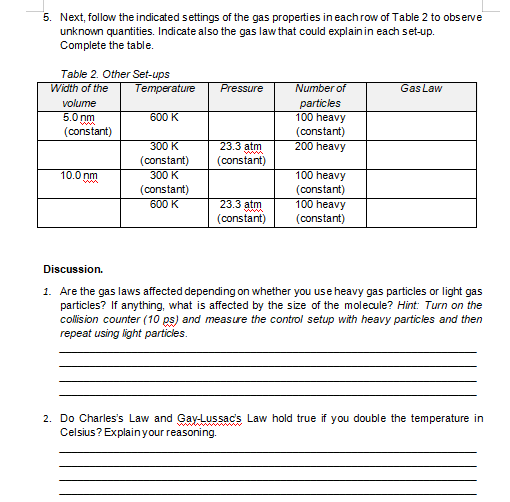
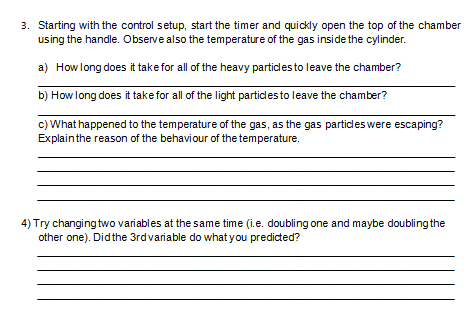
GAS LAWSI Introduction Gas laws relate the physical quantities of gas - temperature, pressure, volume and number of moles. The four fundamental gas laws are Boyle's law, Charles' Law, Gay-Lussac's Law and Avogadro's Law. Boyle's law is the relationship between pressure and volume when temperature and number of moles are held constant. Charles' law is the relationship between volume and temperature when pressure and number of moles are held constant. Gay-Lussac's law is the relationship between pressure and temperature when volume and number of moles are held constant. While Avogadro's law is the relationship between volume and number of moles when temperature and pressure are held constant. Objectives: To verify gas laws. To predict gas properties using gas laws. Procedure: 1. Launch the Gas Properties Simulator at: https://phet. colorado.edu/sims/html/gas- properties/latest/gas-properties en.html 2. Click Ideal tab to see interface in the photo. 3. Get acquainted with the interface. 4. Once you are acquainted with the interface, set-up the control settings. Move the left handle of the cylinder to set the width of the volume of the cylinder to 5.0 nm. Set the temperature to 300K, number of gas heavy particles to100, and the average pressure to 23.3 atm. Refer Table 1. Width of the volume Temperature Pressure Number of particles 5.0 nm 300 K 23.3 atm 100 Heavy Table 1. Control Setting.5. Next, follow the indicated settings of the gas properties in each row of Table 2 to observe unknown quantities. Indicate also the gas law that could explain in each set-up. Complete the table. Table 2. Other Set-ups Width of the Temperature Pressure Number of Gas Law volume particles 5.0 nm 600 K 100 heavy (constant) ( constant) 300 K 23.3 atm 200 heavy ( constant) ( constant) 10.0 nm 300 K 100 heavy ( constant) ( constant) 600 K 23.3 atm 100 heavy ( constant) ( constant) Discussion. 1. Are the gas laws affected depending on whether you use heavy gas particles or light gas particles? If anything, what is affected by the size of the molecule? Hint: Turn on the collision counter (10 ps) and measure the control setup with heavy particles and then repeat using light particles. 2. Do Charles's Law and Gay-Lussacs Law hold true if you double the temperature in Celsius ? Explain your reasoning.3. Starting with the control setup, start the timer and quickly open the top of the chamber using the handle. Observe also the temperature of the gas inside the cylinder. a) How long does it take for all of the heavy particles to leave the chamber? b) How long does it take for all of the light particles to leave the chamber? c) What happened to the temperature of the gas, as the gas particles were escaping? Explain the reason of the behaviour of the temperature. 4) Try changing two variables at the same time (i.e. doubling one and maybe doubling the other one). Did the 3rdvariable do what you predicted
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


