Question: Hi, This is a task on pricing in Black-Scholes. Can someone help me with the following: 1. The interest rate, given at 2%, is semi-annually
Hi,
This is a task on pricing in Black-Scholes. Can someone help me with the following:
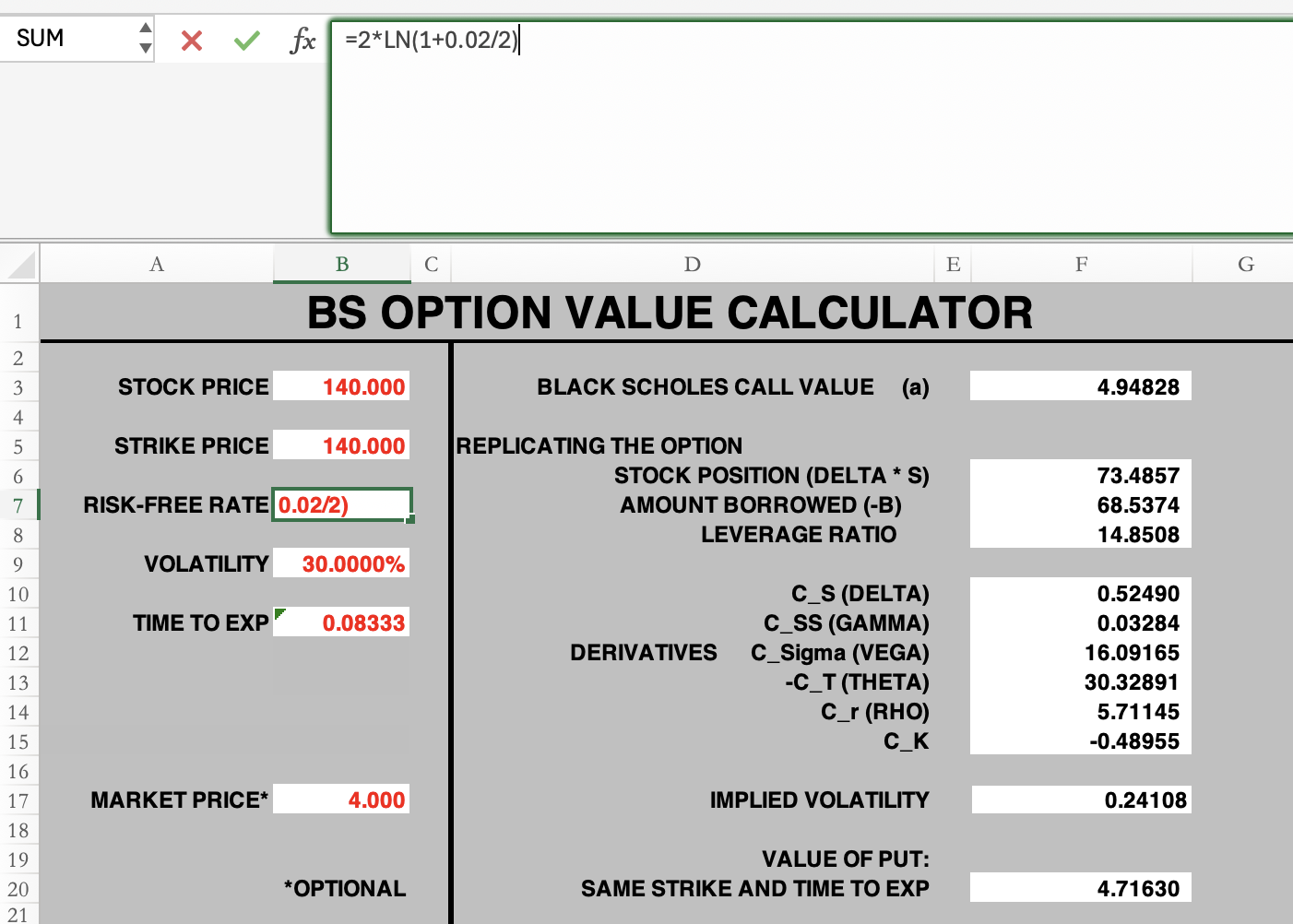
1. The interest rate, given at 2%, is semi-annually continuously compounded. It is stated earlier in the task that it must be semi-annual. However, I do not understand why my teacher derives it as: 2 * LN ( 1 + r / 2). Can you please explain this?
2. Can someone explain me the difference between T, t, and T-t, and which cases we use it to compound the interest rate? I assume that T = 1/12 and t = 1, with T-t being the difference. Why don't we compound using this? I have seen some cases, where we do, and now we dont?

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


