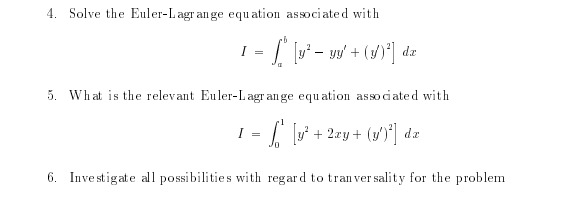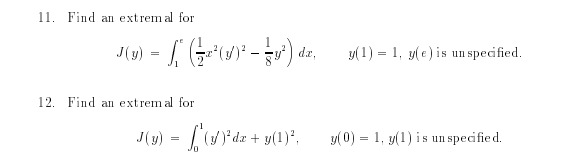Question: Higher dimensional problems; 1. Solve the problem minimize I = ly - () with left end point fixed and y(2, ) is along the curve
Higher dimensional problems;
1. Solve the problem minimize I = ly - () with left end point fixed and y(2, ) is along the curve 2. Find the extremals for where end values of y are free. 3. Solve the Euler-Lagrange equation for I = ( WI+(y) de where y( a) = A, , y(b) = B. b. Investigate the special case when a = -b, A = B and show that depending upon the relative size of b, B there may be none, one or two can didate curves that satisfy the requisite endpoints conditions.4. Solve the Euler-Lagrange equation associated with " ly' - my + ly)' de 5. What is the relevant Euler-Lagrange equation associated with 1 = [y' + zay+ (y') da 6. Investigate all possibilities with regard to tranversality for the problemmin f le'l (frets: T. Determine the stationary functions associated with the integral I = 1 [hf]? Ethyl! Ey" dz where o and [[3 are constants. in each of the following situations: a The end conditions yEUII = U and ylZlIl = l are preassigned. b. Only the end conditions y[U] = U is preassigned. c. Only the end conditions 34:1] = l is preasagned. d. No end conditions are preasagned. 3. Determine the natural boundary conditions associated with the determination of ex tremals in each of the cases considered in Problem 1 of Chapter 3. 9. Find the curves for which the functional I = i LITE-dz with yl:U:| = U can have extrema, if a The point (1:1. [n] can 1vary along the line y = z 5. b. The point [31. m] can 1.rary along the circle [3 9]: + y2 = 9. ID. If F depends upon 1:3. show that the transversality condition must be replaced by F+i'y') 5F y\" :=:! J." 51!: \f1. A particle moves on the surface d(2, y, = ) = 0 from the point (21, 1, 2 ) to the point (21, ya, 2) in the time 7. Show that if it moves in such a way that the integral of its kinetic energy over that time is a minimum, its coordinates must also satisfy the equations 2. Specialize problem I in the case when the particle moves on the unit sphere, from (0, 0, 1) to (0, 0, - 1), in time T. 3. Determine the equation of the shortest arc in the first quadrant, which passes through Pic the points (0, 0) and (1, 0) and encloses a prescribed area A with the r-axis, where AS -. 4. Finish the example on page 51. What if I = 5. Solve the following variation al problem by finding extremals satisfying the condition s y1 (0) = 1, 91 = 0, 12(0) = 0, yz = 1