Question: Hint: 1. Chemical Processing - Input/Output Processing - Blending The Massoil Refinery processes two different kinds of crude oil, Venezuelan and Saudi to produce two

Hint:
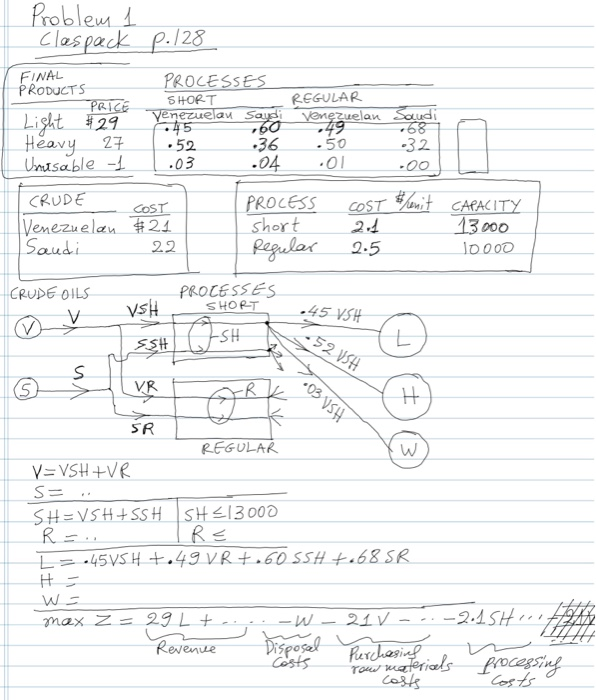

1. Chemical Processing - Input/Output Processing - Blending The Massoil Refinery processes two different kinds of crude oil, Venezuelan and Saudi to produce two general classes of products, Light and Heavy. Either crude oil can be processed by either of two modes of processing, Short or Regular. The processing cost and the amounts of Heavy and Light produced depend upon the mode of processing used and the type of crude oil used. Costs vary, both across crude oils and across processing modes. The relevant characteristics are summarized in the table below. For example, the short process converts each unit of Venezuelan crude to .45 units of Light product, .52 units of Heavy product and.03 units of waste REGULAR PROCESS Venezuelan Saudi Venezuelan Saudi SHORT PROCESS Light product fraction Heavy product fraction Unusable product fraction 45 .52 03 60 .36 04 49 .50 01 68 Saudi crude costs $22 per unit while Venezuelan crude costs $21 per unit. The short process costs $2.10 per unit processed while the regular process costs $2.50 per unit. During any week, Massoil can process at most 10,000 units of crude at the regular mode and 13,000 units of crude at the short mode The respective market values of light and heavy products are $29 and $27 per unit, while the unusable product is disposed of at the cost of $1 per unit. Formulate a LP problem that optimally determines the amounts of crudes to buy and the processes to run What are the optimal purchasing and operating decisions? 1. Chemical Processing - Input/Output Processing - Blending The Massoil Refinery processes two different kinds of crude oil, Venezuelan and Saudi to produce two general classes of products, Light and Heavy. Either crude oil can be processed by either of two modes of processing, Short or Regular. The processing cost and the amounts of Heavy and Light produced depend upon the mode of processing used and the type of crude oil used. Costs vary, both across crude oils and across processing modes. The relevant characteristics are summarized in the table below. For example, the short process converts each unit of Venezuelan crude to .45 units of Light product, .52 units of Heavy product and.03 units of waste REGULAR PROCESS Venezuelan Saudi Venezuelan Saudi SHORT PROCESS Light product fraction Heavy product fraction Unusable product fraction 45 .52 03 60 .36 04 49 .50 01 68 Saudi crude costs $22 per unit while Venezuelan crude costs $21 per unit. The short process costs $2.10 per unit processed while the regular process costs $2.50 per unit. During any week, Massoil can process at most 10,000 units of crude at the regular mode and 13,000 units of crude at the short mode The respective market values of light and heavy products are $29 and $27 per unit, while the unusable product is disposed of at the cost of $1 per unit. Formulate a LP problem that optimally determines the amounts of crudes to buy and the processes to run What are the optimal purchasing and operating decisions
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


