Question: Homework (Ch 14) Back to Assignment Attempts Keep the Highest / 4 6. Deriving the short-run supply curve Consider the competitive market for halogen lamps.
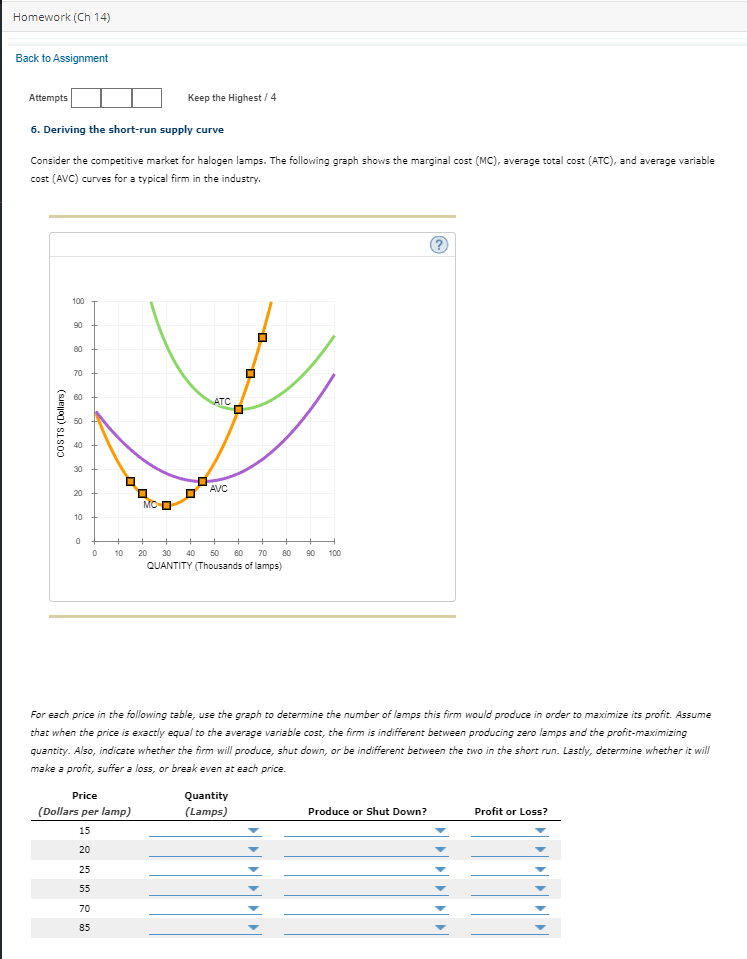
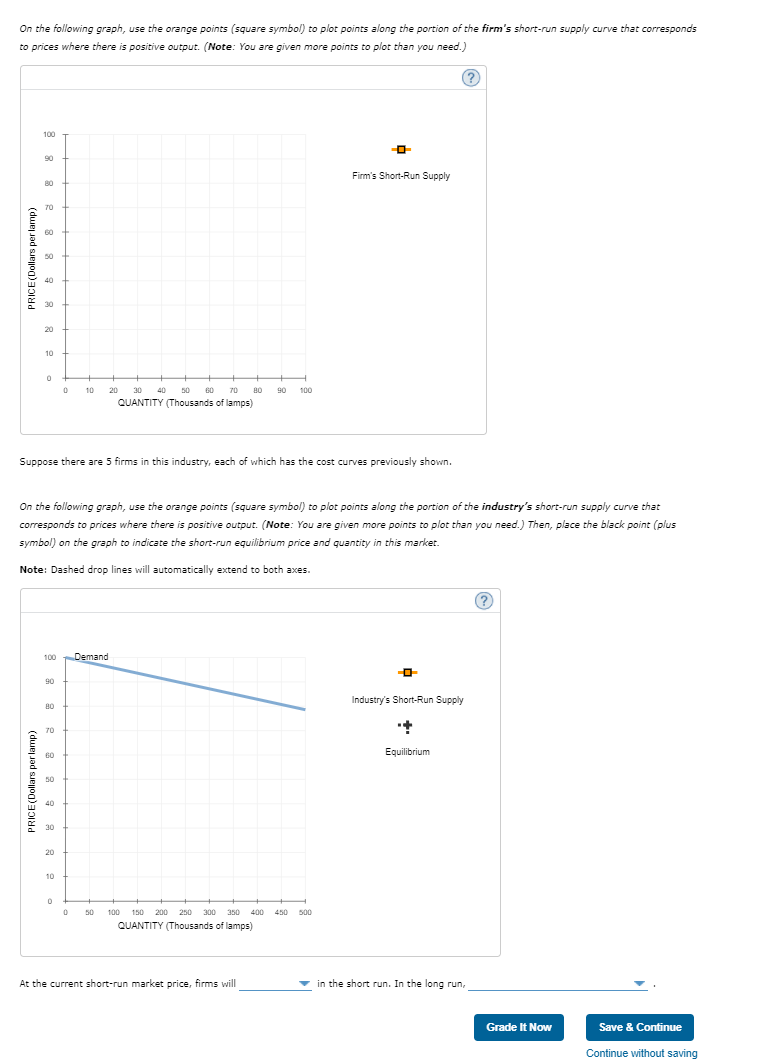
Homework (Ch 14) Back to Assignment Attempts Keep the Highest / 4 6. Deriving the short-run supply curve Consider the competitive market for halogen lamps. The following graph shows the marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves for a typical firm in the industry. (?) 100 g 8 ATC COSTS (Dollars) AVC 10 20 90 100 QUANTITY (Thousands of lamps) For each price in the following table, use the graph to determine the number of lamps this firm would produce in order to maximize its profit. Assume that when the price is exactly equal to the average variable cost, the firm is indifferent between producing zero lamps and the profit-maximizing quantity. Also, indicate whether the firm will produce, shut down, or be indifferent between the two in the short run. Lastly, determine whether it will make a profit, suffer a loss, or break even at each price. Price Quantity (Dollars per lamp) (Lamps) Produce or Shut Down? Profit or Loss? 15 20 25 55 70 85On the following graph, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot points along the portion of the firm's short-run supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is positive output. (Note: You are given more points to plot than you need.) (? 100 Firm's Short-Run Supply PRICE (Dollars per lamp) 20 30 40 50 60 70 90 QUANTITY (Thousands of lamps) Suppose there are 5 firms in this industry, each of which has the cost curves previously shown. On the following graph, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot points along the portion of the industry's short-run supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is positive output. (Note: You are given more points to plot than you need.) Then, place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the short-run equilibrium price and quantity in this market. Note: Dashed drop lines will automatically extend to both axes. 100 Demand -O 90 Industry's Short-Run Supply 70 Equilibrium PRICE (Dollars per lamp) 30 20 10 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Thousands of lamps) At the current short-run market price, firms will in the short run. In the long run, Grade It Now Save & Continue Continue without saving
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


