Question: How do I find the answer to problem set 3.5 f? I don't understand what equations I need to find the critical t for a=0.05
How do I find the answer to problem set 3.5 f? I don't understand what equations I need to find the critical t for a=0.05 (two tails) Could you show work?
Is the rest of problem set correct?
II

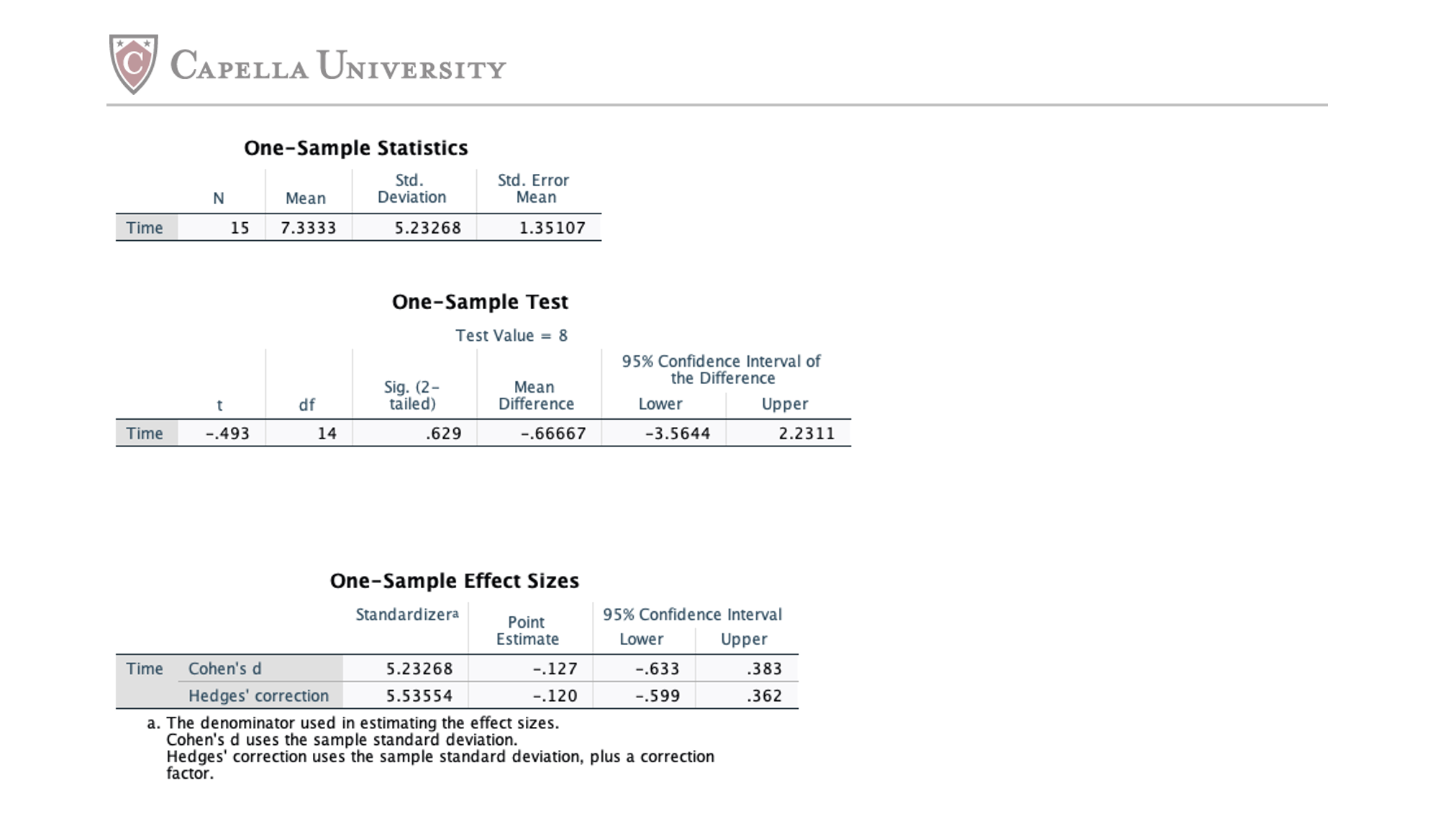
Problem Set 3.5: One-Sample t test in SPSS Criterion: Calculate a one-sample t test in SPSS. Data: Riverbend City online news advertises that it is read longer than the national news. The mean for national news is 8 hours per week. The following sample of the Riverbend City online news readers is: 5, 7, 6, 2, 4, 8, 5, 4, 18, 21, 8, 7, 4, 5, 6. Instructions: Complete the following: a. Enter the data from Problem Set 3.5 into SPSS and name the variable as Time. b. In the Toolbar, click Analyze, select Compare Means, and then select One-Sample t Test. c. Select Time, then click Arrow to send it over to the right side of the table. In the box labeled Test Value, enter 8. d. Click OK and copy and paste the output into the Word document. e. State the nondirectional hypothesis. The null hypothesis is H.: M = 8 The alternative hypothesis is Hill # 8 f. State the critical t for a = .05 (two tails). | g. Answer the following: Is the length of viewing for Riverbend City online news significantly different than the population mean? Explain. No, the length of viewing for riverbend city online news is not significant because t= -4.93 which is less than the critical value (2.145).CAPELLA UNIVERSITY One-Sample Statistics Std. Std. Error N Mean Deviation Mean Time 15 7.3333 5.23268 1.35107 One-Sample Test Test Value = 8 95% Confidence Interval of Sig. (2- Mean the Difference t df tailed) Difference Lower Upper Time -.493 14 .629 -.66667 -3.5644 2.2311 One-Sample Effect Sizes Standardizera Point 95% Confidence Interval Estimate Lower Upper Time Cohen's d 5.23268 -.127 -.633 383 Hedges' correction 5.53554 -.120 -.599 .362 a. The denominator used in estimating the effect sizes. Cohen's d uses the sample standard deviation. Hedges' correction uses the sample standard deviation, plus a correction factor
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


