Question: how do you do the 2nd page Data and Results: Part B Enthalpy of Formation of MgO Thermochemistry Experiment 6 Hess's Law Calculation: Refer to



how do you do the 2nd page
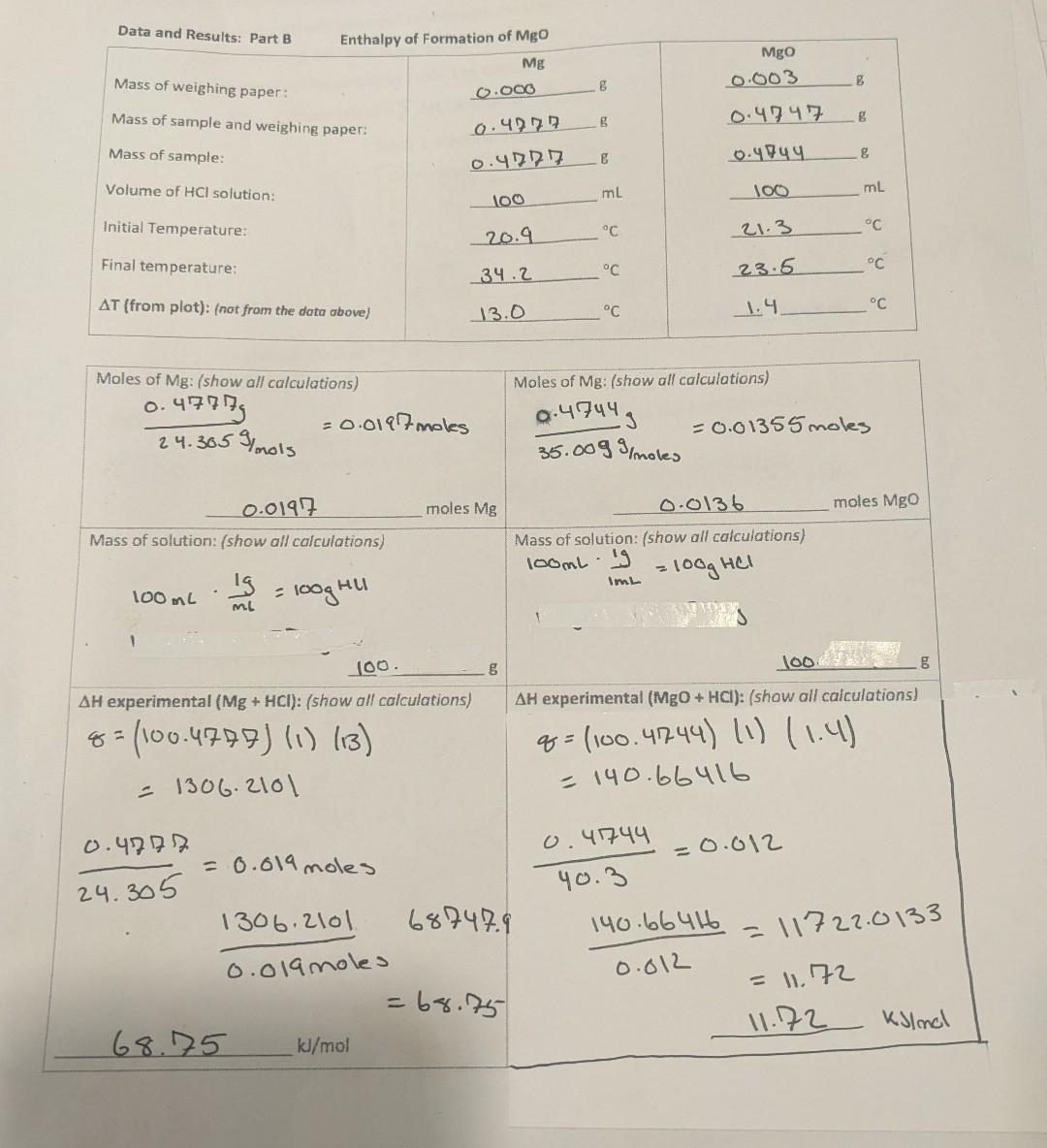
Data and Results: Part B Enthalpy of Formation of MgO Thermochemistry Experiment 6 Hess's Law Calculation: Refer to reactions in introduction. AH Mg(s)+HCl(aq) SH2 MgO(s)+HCl(aq) H3=285.9kJ/mol H2(g)+1/2O2(g)H2O(l) (heat of formation of water) Combine H:,H2&H, using Hess's law to find H(MgO):Mg(s)+1/2O2(g)MgO(s) SHOW YOUR WORK HERE: Comparison of Experimental Results with Theoretical Values You will also compare your experimental results with theoretical values. To do this: a. Write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction. b. Use the heats of formation in Table 1 to calculate the actual value of H. Hreaction(theoretical)=Hf(products)Hf(reactants) Table 1. Heats of Formation*1 the particular acid or base used. The nature of the spectator ions, sodium and chloride in this case, is not important. Hess 's Law-Part B In part B of this experiment, we will be finding the enthalpy of formation for MgO(s) using an indirect method. According to Hess's Law, if two or more reactions can be added to give a net reaction, H for the net reaction is simply the sum of the Hs for the reactions which are added. Consider the following three reactions: (1) Mg(s)+2H+(aq)Mg2+(aq)+H2(g)H1 (2) Mg+2(aq)+H2O(I)MgO(s)+2H+(aq)H2 (3) H2(g)+1/2O2(g)H2O(l) H3 (4) Mg(s)+1/2O2 (g) MgO(s)H4=H1+H2+H3 Notice that when the three reactions are added, they form the formation reaction for MgO. Analogously, when we add the enthalpies for the three reactions, they give the enthalpy change associated with the formation reaction
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


