Question: how to do this? comment what it is that you need more info on if you do, thanks pls just answer this 1 question, answer
 how to do this?
how to do this?
comment what it is that you need more info on if you do, thanks
pls just answer this 1 question, answer 1 question, method and answer also
anything else needed comment, this is all, thank u
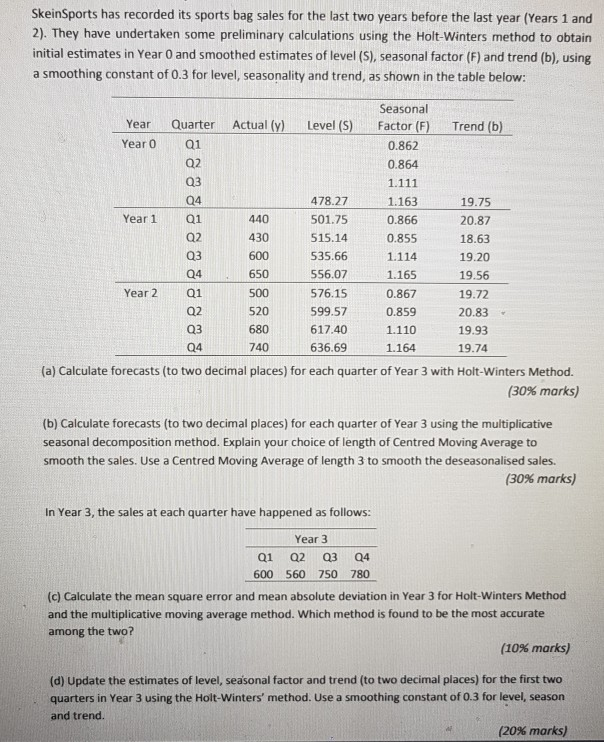
(b) Calculate forecasts (to two decimal places) for each quarter of Year 3 using the multiplicative seasonal decomposition method. Explain your choice of length of Centred Moving Average to smooth the sales. Use a Centred Moving Average of length 3 to smooth the deseasonalised sales. (30% marks) In Year 3, the sales at each quarter have happened as follows: Year 3 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 600 560 750 780 (c) Calculate the mean square error and mean absolute deviation in Year 3 for Holt-Winters Method and the multiplicative moving average method. Which method is found to be the most accurate among the two? (10% marks) (d) Update the estimates of level, seasonal factor and trend (to two decimal places) for the first two quarters in Year 3 using the Holt-Winters' method. Use a smoothing constant of 0.3 for level, season and trend. (20% marks) (e) Forecasting accuracy in this example is improved when the smoothing constant for trend is changed from 0.3 to 0.1. Explain why this might be. (No calculations required). (10% marks) SkeinSports has recorded its sports bag sales for the last two years before the last year (Years 1 and 2). They have undertaken some preliminary calculations using the Holt-Winters method to obtain initial estimates in Year and smoothed estimates of level(s), seasonal factor (F) and trend (b), using a smoothing constant of 0.3 for level, seasonality and trend, as shown in the table below: Seasonal Year Quarter Actual (y) Level (S) Factor (F) Trend (b) Year 0 Q1 0.862 Q2 0.864 Q3 1.111 Q4 478.27 1.163 19.75 Year 1 Q1 440 501.75 0.866 20.87 Q2 430 515.14 0.855 18.63 Q3 600 535.66 1.114 19.20 Q4 650 556.07 1.165 19.56 Year 2 Q1 500 576.15 0.867 19.72 Q2 520 599.57 0.859 20.83 Q3 680 617.40 1.110 19.93 Q4 740 636.69 1.164 19.74 (a) Calculate forecasts (to two decimal places) for each quarter of Year 3 with Holt-Winters Method. (30% marks) (b) Calculate forecasts (to two decimal places) for each quarter of Year 3 using the multiplicative seasonal decomposition method. Explain your choice of length of Centred Moving Average to smooth the sales. Use a Centred Moving Average of length 3 to smooth the deseasonalised sales. (30% marks) In Year 3, the sales at each quarter have happened as follows: Year 3 Q1 600 Q2 Q3 560 750 Q4 780 (c) Calculate the mean square error and mean absolute deviation in Year 3 for Holt-Winters Method and the multiplicative moving average method. Which method is found to be the most accurate among the two? (10% marks) (d) Update the estimates of level, seasonal factor and trend (to two decimal places) for the first two quarters in Year 3 using the Holt-Winters' method. Use a smoothing constant of 0.3 for level, season and trend. (20% marks) (b) Calculate forecasts (to two decimal places) for each quarter of Year 3 using the multiplicative seasonal decomposition method. Explain your choice of length of Centred Moving Average to smooth the sales. Use a Centred Moving Average of length 3 to smooth the deseasonalised sales. (30% marks) In Year 3, the sales at each quarter have happened as follows: Year 3 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 600 560 750 780 (c) Calculate the mean square error and mean absolute deviation in Year 3 for Holt-Winters Method and the multiplicative moving average method. Which method is found to be the most accurate among the two? (10% marks) (d) Update the estimates of level, seasonal factor and trend (to two decimal places) for the first two quarters in Year 3 using the Holt-Winters' method. Use a smoothing constant of 0.3 for level, season and trend. (20% marks) (e) Forecasting accuracy in this example is improved when the smoothing constant for trend is changed from 0.3 to 0.1. Explain why this might be. (No calculations required). (10% marks) SkeinSports has recorded its sports bag sales for the last two years before the last year (Years 1 and 2). They have undertaken some preliminary calculations using the Holt-Winters method to obtain initial estimates in Year and smoothed estimates of level(s), seasonal factor (F) and trend (b), using a smoothing constant of 0.3 for level, seasonality and trend, as shown in the table below: Seasonal Year Quarter Actual (y) Level (S) Factor (F) Trend (b) Year 0 Q1 0.862 Q2 0.864 Q3 1.111 Q4 478.27 1.163 19.75 Year 1 Q1 440 501.75 0.866 20.87 Q2 430 515.14 0.855 18.63 Q3 600 535.66 1.114 19.20 Q4 650 556.07 1.165 19.56 Year 2 Q1 500 576.15 0.867 19.72 Q2 520 599.57 0.859 20.83 Q3 680 617.40 1.110 19.93 Q4 740 636.69 1.164 19.74 (a) Calculate forecasts (to two decimal places) for each quarter of Year 3 with Holt-Winters Method. (30% marks) (b) Calculate forecasts (to two decimal places) for each quarter of Year 3 using the multiplicative seasonal decomposition method. Explain your choice of length of Centred Moving Average to smooth the sales. Use a Centred Moving Average of length 3 to smooth the deseasonalised sales. (30% marks) In Year 3, the sales at each quarter have happened as follows: Year 3 Q1 600 Q2 Q3 560 750 Q4 780 (c) Calculate the mean square error and mean absolute deviation in Year 3 for Holt-Winters Method and the multiplicative moving average method. Which method is found to be the most accurate among the two? (10% marks) (d) Update the estimates of level, seasonal factor and trend (to two decimal places) for the first two quarters in Year 3 using the Holt-Winters' method. Use a smoothing constant of 0.3 for level, season and trend. (20% marks)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


