Question: How to reduce my RMSE in my final code. My RMSE is 3 . 5 1 3 . Only step 2 - 9 is allowed
How to reduce my RMSE in my final code. My RMSE is Only step is allowed for editing.
Import the libraries.
from math import sqrt
from matplotlib import pyplot as plot
from random import seed
from random import randrange
from csv import reader
Step
Load the csv file.
def loadcsvfilename skip False:
dataset list
with openfilenamer as file:
csvreader readerfile
if skip:
nextcsvreader, None
for row in csvreader:
dataset.appendrow
return dataset
Step
Convert any string column to a float coulm.
def stringcolumntofloatdataset column:
for row in dataset:
# The strip function remove white space
# then convert the data into a decimal number float
# and overwrite the original data
#CONVERTING STRING TO FLOAT
rowcolumn floatrowcolumnstrip
###
Step
Calculate the mean value of a list of numbers.
def meanvalues:
meanresults
#MEAN RESULT CALCULATION
meanresults sumvalues floatlenvalues
###
return meanresults
Step
Calculate a regularisation value for the parameter.
def regularisationparameter lambdavalue:
#CALCULATION OF THE REHULARISED PARAMETER
regularisedparameter parameter lambdavalue
###
return parameter
Step
Calculate least squares between x and y
def leastSquaresdataset:
x list
y list
for row in dataset:
xappendrow
for row in dataset:
yappendrow
b
b
# using the formula to calculate the b and b
numerator
denominator
xmean meanx
ymean meany
#B SLOPE CALCULATION
numerator sumxi xmeanyi ymean for i in range lenx
denominator sumxi xmean for i in rangelenx
#B SLOPE CALCULATION
b ymean b xmean
###
return b b
Step
Calculate root mean squared error.
sumerror sumactuali predictedi for i in rangelenactual
meanerror sumerror floatlenactual
rmse sqrtmeanerror
def rootmeansquareerroractual predicted:
rmse
sumerror
###
sumerror sumactuali predictedi for i in rangelenactual
meanerror sumerror floatlenactual
rmse sqrtmeanerror
###
return rmse
Step
Make Predictions.
predictions list
b b leastSquarestrain
# This function takes the training data to calculate the linear regression model parameters b and b
# using the least squares method. Then it predicts the target values for the given test set.
# Each prediction is made using the formula yhat b b x where b is the intercept, b is the slope,
# and x is the independent variable. The predictions are stored in a list and returned.
for row in test:
x row
yhat b b x
predictions.appendyhat
def simplelinearregressiontrain test:
predictions list
b b leastSquarestrain
# This function takes the training data to calculate the linear regression model parameters b and b
# using the least squares method. Then it predicts the target values for the given test set.
# Each prediction is made using the formula yhat b b x where b is the intercept, b is the slope,
# and x is the independent variable. The predictions are stored in a list and returned.
for row in test:
x row
yhat b b x
predictions.appendyhat
return predictions
Step
Split the data into training and test sets.
def traintestsplitdataset split:
train list
trainsize split lendataset
datasetcopy listdataset
while lentrain trainsize:
index randrangelendatasetcopy # to
train.appenddatasetcopy.popindex
return train, datasetcopy
Step
Evaluate regression algorithm on training dataset.
def evaluatesimplelinearregressiondataset split:
testset list
train, test traintestsplitdataset split
for row in test:
rowcopy listrow
rowcopy None
testset.appendrowcopy
predicted simplelinearregressiontrain testset
actual row for row in test
rmse rootmeansquareerroractual predicted
return rmse
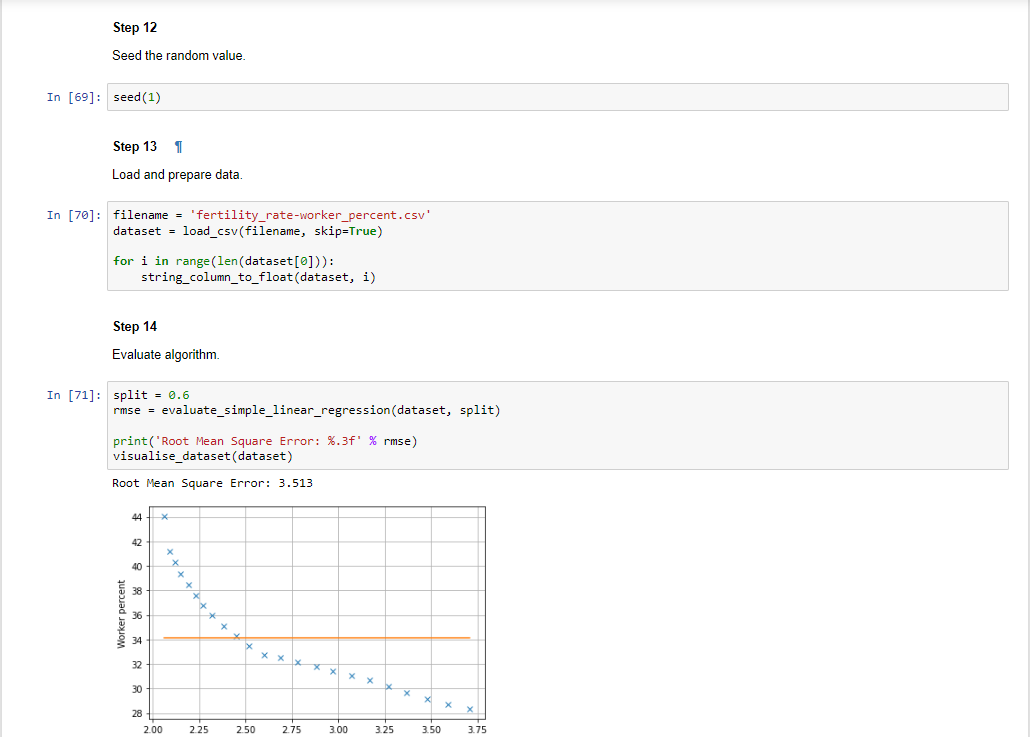
Step
Seed the random value.
In : seed
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


