Question: how to solve this problem? Required information Use the following information for the Exercises 3-7 below. (Algo) (The following information applies to the questions displayed
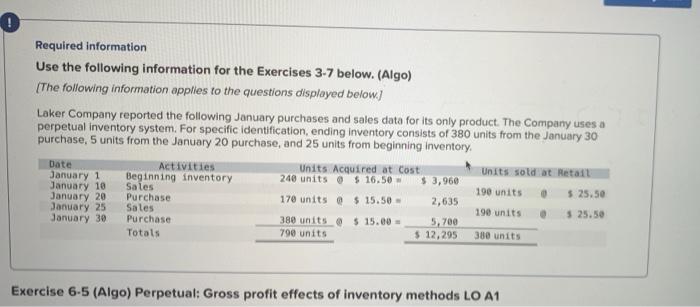
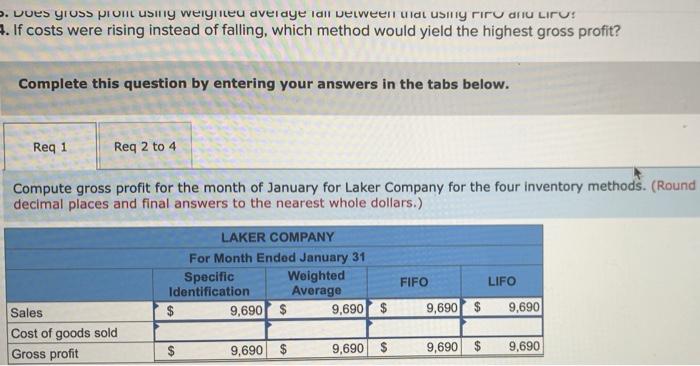
Required information Use the following information for the Exercises 3-7 below. (Algo) (The following information applies to the questions displayed below) Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 380 units from the January 30 purchase, 5 units from the January 20 purchase, and 25 units from beginning inventory Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units soldat Retail January 1 Beginning inventory 240 units $16.50 $ 3,960 January 10 Sales 190 units $ 25.50 January 20 Purchase 170 units @ $ 15.50 - 2,635 January 25 Sales 190 units $ 25.50 January 30 Purchase 380 units @ $ 15.00 - 5,700 Totals 790 units $ 12,295 380 units Exercise 6-5 (Algo) Perpetual: Gross profit effects of inventory methods LO A1 . Dues yiuss prom using weigneu avelaye Tall Delveen ulatusyriru anuliru! 1. If costs were rising instead of falling, which method would yield the highest gross profit? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req 1 Reg 2 to 4 Compute gross profit for the month of January for Laker Company for the four inventory methods. (Round decimal places and final answers to the nearest whole dollars.) LAKER COMPANY For Month Ended January 31 Specific Weighted Identification Average $ 9,690 $ 9,690 $ FIFO LIFO 9,690 $ 9,690 Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit $ 9,690 $ 9,690 $ 9,690 $ 9,690
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


