Question: how to solve this question, thanks 2. {15 marks} Let (1P) be the following integer program: max (llUm 5.3. 1 10 -10 G 1 $1:
how to solve this question, thanks
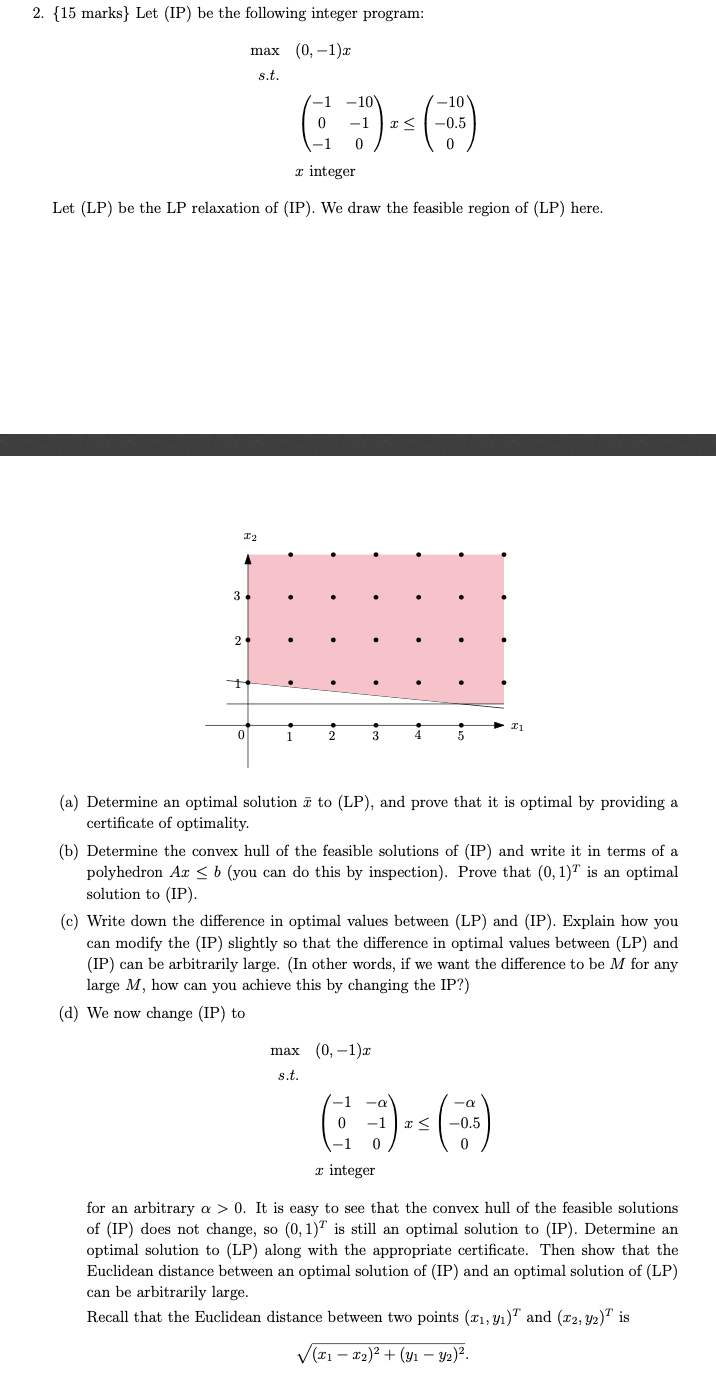
2. {15 marks} Let (1P) be the following integer program: max (llUm 5.3. 1 10 -10 G 1 $1: D.5 (-1 .l (.l minteger Let (LP) be the LP relaxation of (IP). We draw the feasible region of (LP) here. (a) Determine an optimal solution 3? to {LP}, and prove that it is optimal by providing a certicate of optimality. {b} Determine the convex hull of the feasible solutions of (IP) and mite it in terms of a polyhedron Am 3 b (you can do this by inspection). Prove that [U,1)T is an optimal solution to (1P). (6} Write down the difference in optimal values between (LP) and (IP). Explain how you can modify the (1P) slightly so that the difference in optimal values between (LP) and (IP) can be arbitrarily large. (In other mrds, if we want the difference to be M for any large M, how can you achieve this by changing the IF?) (:1) We now change (IP) to max (ILlb 3.3. 1 o: o: 0 1 IS -05 1 Cl 0 minteger for an arbitrary or > D. It is easy to see that the convex hull of the feasible solutions of (IF) does not change, so (D,1}T is still an optimal solution to ([P). Determine an optimal solution to (LP) along with the appropriate certicate. Then show that the Euclidean distance between an optimal solution of (IP) and an optimal solution of (LP) can be arbitrarily large. Recall that the Euclidean distance between two points (whyl)? and (1:2, gaff is [$1 - 32F +(y1 3'2]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


