Question: How would I construct this quad tree? ***CODE GIVEN*** ImageBlob.java public class ImageBlob { ///////////////////////////////////////////////// /** DO NOT CHANGE/ALTER/REMOVE THESE FIELDS **/ /** DO NOT
How would I construct this quad tree?




***CODE GIVEN***
ImageBlob.java
public class ImageBlob { ///////////////////////////////////////////////// /** DO NOT CHANGE/ALTER/REMOVE THESE FIELDS **/ /** DO NOT ADD ANY OTHER FIELDS EITHER **/ /**/ ImageBlob NW, NE, SE, SW; /**/ /**/ Pixel value; /**/ /////////////////////////////////////////////////
/** YOU MAY ADD ANY METHODS YOU WANT BELOW THIS LINE **/ }
Project3.java
public class Project3 { public static void main(String[] args) { // load an image from a file Short[][] array = Utilities.loadFile("image1.pgm");
// construct the quadtree QuadTreeImage img1 = new QuadTreeImage(array);
// invoke toString() System.out.println(img1); // expected: // {0 0 4 255},{4 0 4 0},{0 4 2 255},{0 6 2 255},{2 4 2 0},{4 4 2 0},{4 6 2 255},{6 4 2 255},{2 6 1 0},{2 7 1 255},{3 7 1 255},{3 6 1 255},{6 6 1 255},{6 7 1 255},{7 7 1 0},{7 6 1 255}
// invoke the iterator for(ImageBlob iter : img1) System.out.print(iter+" "); // expected: // null 255 null null 0 255 255 null 0 0 255 null 255 0 255 255 255 255 255 0 255
// measure the storage benefit from using quadtrees System.out.println(img1.sizeRatio(10,4)); // expected: 0.853125
// load a second image from another file array = Utilities.loadFile("image2.pgm");
// construct a second quadtree QuadTreeImage img2 = new QuadTreeImage(array);
// compare the two images, i.e. which one is brighter System.out.println(img1.compareTo(img2)); // expected: -111
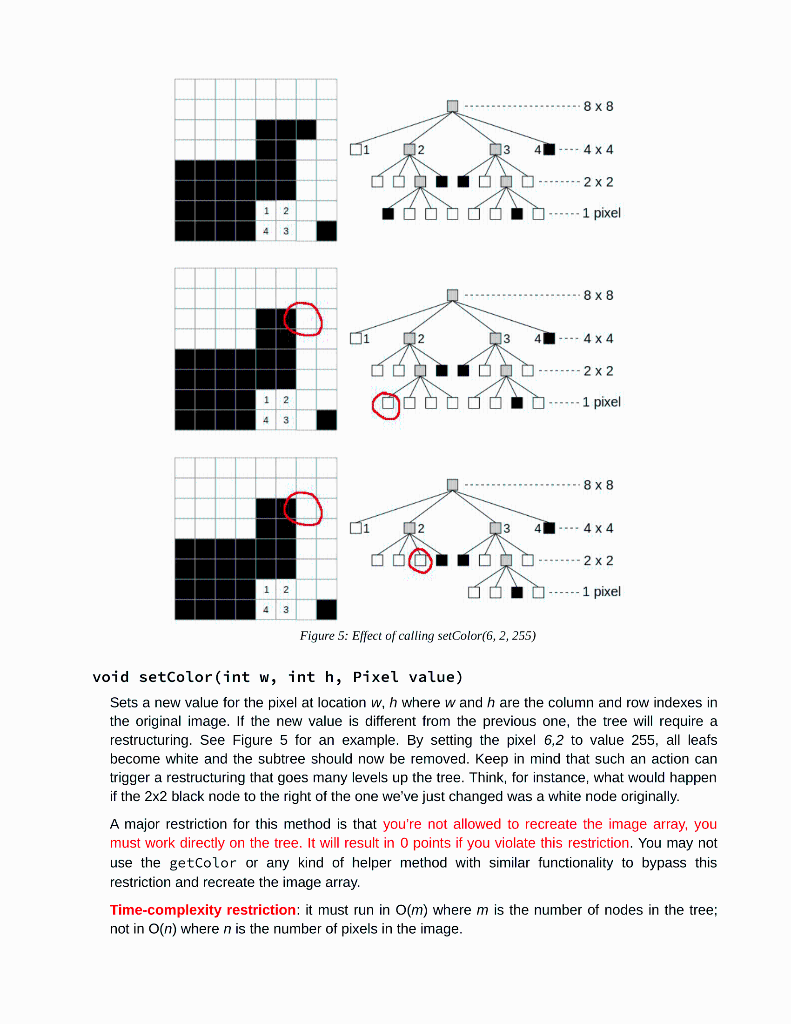
// change the color of a single pixel in image1 img1.setColor(6, 2, (short)255);
// save the modified image in a file Utilities.exportImage(img1,"image1_after_setColor.pgm"); // open the image to visually inspect the result
// invoke the toString to see how the tree looks like after the modification System.out.println(img1); // expected: // {0 0 4 255},{4 0 4 0},{0 4 2 255},{0 6 2 255},{2 6 2 255},{2 4 2 0},{4 4 2 0},{4 6 2 255},{6 4 2 255},{6 6 1 255},{6 7 1 255},{7 7 1 0},{7 6 1 255}
// inspect the values of all the nodes after the modification for(ImageBlob iter : img1) System.out.print(iter+" "); // expected: // null 255 null null 0 255 255 255 0 0 255 null 255 255 255 0 255
// construct an intersection mask image array = Utilities.loadFile("image4.pgm"); QuadTreeImage img4 = new QuadTreeImage(array); array = Utilities.loadFile("image5.pgm"); QuadTreeImage img5 = new QuadTreeImage(array); QuadTreeImage img6 = img4.intersectionMask(img5); Utilities.exportImage(img6,"image4_intersection_image5.pgm");
// construct a FIFO queue Queue queue = new Queue(); try { // it should throw an exception because queue is empty queue.dequeue(); System.out.println("Error: dequeue on an empty queue should throw an exception"); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("That's correct, the queue should throw an exception"); }
Integer r = null;
for (int i=0; i
if (queue.isEmpty()) System.out.println("That's correct, the queue is empty now"); else System.out.println("Error: the queue should be empty now");
if (r==999999) System.out.println("last dequeue is correct!"); else System.out.println("Error: last dequeue is incorrect!"); }
}
Rules and Assumptions You must: Have code that compiles with the command: javac *.java in your user directory without errors or warnings. You may Add additional methods and variables, however these must be private. Add additional nested, local, or anonymous classes, but any nested classes must be private. Use the provided Project3.java to get started and test your code but you should not include it in your submitted files. Keep in mind that this is not a tester, it is only provided to give you an idea of how your code should work. Import the following: File, Scanner, Printwriter, FileNotFoundException, Iterator You may NOT: Add additional public methods, variables, or classes. Exceptions: you may add public methods in ImageBlob and in private nested classes, and you may also override Object's public methods like equals, toString, etc. Use any built in Java Collections Framework classes in your program (e.g. no LinkedList, ArrayList, etc.). Add any additional import statements (or use the fully qualified name to get around adding import statements) Store anywhere in your program the Pixel[][] array that was passed to the QuadTree Image constructor. This array is used only for constructing the quadtree. Violation of this rule will result in a 0 on the entire assignment Make your program part of a package. Change any code in any "DO NOT EDIT" section. Add @suppressWarnings to avoid fixing warnings. There are a couple of places that are exempted from this rule and they're clearly stated in the description. Add any additional libraries/packages which require downloading from the internet. Assumptions We will assume that images have a square size and the width of an image is a power of 2 (i.e. 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, etc). This will simplify the creation of the quadtree as you won't have to deal with rectangular regions. It will also make memory usage more efficient since you don't need to store the coordinates of the image regions into the tree nodes. . Tasks You must implement the following classes and methods final class Utilities It contains two utility methods that we need in order to read/write images from/to files. static Short[][] loadFile(String pgmFile) It reads a PGB image from a file and stores the data in an array of type Short. Modifying the return type of this method to Integer or Float should not affect the rest of your program since everything else in this project is using generics. static void exportImage (QuadTree Image image, String filename) It writes a QuadTree Image into a PGM file. The signature is not complete, you need to add the generic type. There is no time-complexity restriction for this method. This means that you are allowed to call the getColor method if you want. This is the only place in your entire code that you can use the getColor. class QuadTree Image This class is the most important component of this project. It uses a quadtree structure to represent a grayscale image and provides various methods for processing the tree (a.k.a. image). The generic type Pixel can be any subtype of java.lang.Number. The class must implement the Comparable and the Iterable interfaces. The above signature is obviously not complete. QuadTree Image (Pixel[][] array) The constructor builds the quadtree from an array that holds the original data read from the PGM file. You may not store the array (or the pointer to the array) anywhere in your program after the creation of the tree. Pixel getColor(int w, int h) Returns the value of the pixel at location w, h where w and h are the column and row indexes in the original image respectively. If the coordinates w and h are invalid, it throws an IndexOutOfBoundsException. You may not make any use of this method anywhere outside the method exportImage. It will result in 0 points for any method that violates this restriction. The same is true if you try to bypass the restriction by building your own helper method that has the same or a similar functionality, 8x8 01 2 03 4x4 DID 2 x 2 1 2 1 pixel 8x8 D1 12 03 4. 4X4 ODOIDO 2x2 O.1 pixel 8x8 01 02 03 4 - 4x4 D.......2 x 2 - 1 pixel Figure 5: Effect of calling setColor(6, 2, 255) void setColor(int w, int h, Pixel value) Sets a new value for the pixel at location w, h where w and h are the column and row indexes in the original image. If the new value is different from the previous one, the tree will require a restructuring. See Figure 5 for an example. By setting the pixel 6,2 to value 255, all leafs become white and the subtree should now be removed. Keep in mind that such an action can trigger a restructuring that goes many levels up the tree. Think, for instance, what would happen if the 2x2 black node to the right of the one we've just changed was a white node originally. A major restriction for this method is that you're not allowed to recreate the image array, you must work directly on the tree. It will result in 0 points if you violate this restriction. You may not use the getColor or any kind of helper method with similar functionality to bypass this restriction and recreate the image array. Time-complexity restriction: it must run in O(m) where m is the number of nodes in the tree; not in O(n) where n is the number of pixels in the image. float sizeRatio(int bytesPerPixel, int bytesPerPointer) Returns the ratio of the size (in bytes) of the image stored as a quadtree to the size (in bytes) of the same image stored as an array. In Figure 2, for example, the original image requires 64 pixels and the quadtree requires 21 nodes. Assume that each node contains the minimum information which is one pixel value plus the four pointers to its children. String toString() Overrides the default behavior. It returns a representation of the quadtree that lists the nodes of the quadtree in a breadth-first-traversal order and clockwise within each level). Only leafs should be included in the string. For each leaf, you report: the top row coordinate, followed by the left column coordinate, followed by the size of the image region it represents, followed by the pixel value. The following is an example of the string returned for Figure 2 (assuming it's a proper PGB where black is represented with a 0 and white is represented with a 255): {0 0 4 255},{4 0 4 0},{0 4 2 255},{0 6 2 255}, {2 4 2 0},{4 4 2 0},{4 6 2 255}, {6 4 2 255}, {2 6 1 0}, {2 7 1 255},{3 7 1 255}, {3 6 1 255},{6 6 1 255},{6 7 1 255},{7 7 1 0},{7 6 1 255} int compareTo(QuadTree Image other) Class QuadTree Image implements the comparable interface and, therefore, it must provide this method. If the two trees are not the same, it returns the difference in the brightness of the two images. We measure the brightness as the sum of all the Pixel values in an image. A brighter image is considered larger. Please note that the sum should take into account all pixels in the image not just the ones in the leafs of the tree. Time-complexity restriction: it must run in O(m) where m is the number of nodes in the tree; not in O(n) where n is the number of pixels in the image. Practically, this means that you can't use getColor or any other approach to recreate the full image array. QuadTree Image intersectionMask (QuadTree Image other) Returns a new image that represents the intersection of the current image with another one as a binary mask. This means that the returned image will only have values of 0 and 255. All pixels that match in the two images will generate a white (255) pixel in the output mask, while the non- matching ones will generate a black (0) pixel. Instead of doing this computation pixel by pixel, we can compute this mask efficiently by leveraging the quadtree's ability to represent multiple pixels with a single node. You are not allowed to use getColor or any other similar functionality. But you are allowed to use the annotation @suppressWarnings Time-complexity restriction: it must calculate the mask in O(m) where m is the number of nodes in the tree; not in O(n) where n is the number of pixels in the image. Iterator> iterator() It creates a QuadTree ImageIterator that is iterating over the quadtree nodes (.e. ImageBlob) by a breadth-first-traversal order (and clockwise within each level). Every node should be included in the iteration, regardless if it's an inner or a leaf. The following output is an example of a for-each loop that prints the returned iterator of the QuadTree Image in Figure 2 (assuming it's a proper PGB where black is represented with a 0 and white is represented with a 255). The 21 tokens correspond to the 21 nodes of the tree. null 255 null null o 255 255 null 0 0 255 null 255 0 255 255 255 255 255 0 255 class ImageBlob This class represents a single node in the quadtree structure. You may not alter or add any fields. Pixel value The value of the pixel if the node is a leaf or null if it's an inner node. ImageBlob NW, NE, SE, SW The four pointers to the children nodes (in clockwise order). class Queue An array implementation of a circular queue. It's required for certain tree traversals. In this class you are allowed to use the annotation @SuppressWarnings boolean isEmpty() Returns true if the queue is empty, false otherwise void enqueue (T value) Adds an item to the back of the queue. T dequeue Removes the front item from the queue. Throws a RuntimeException if empty. T peek() Inspects the front item in the queue without removing it. Throws a RuntimeException if empty. class QuadTree ImageIterator It creates an iterator of the quadtree that traverses the nodes in a breadth-first-search approach. Also, this is the iterator that an enhanced for-loop on QuadTree Image will invoke automatically. boolean hasNext() Returns true if there are more nodes to be traversed, false otherwise ImageBlob next() Returns the next node in the quadtree according to a breadth-first-traversal. Rules and Assumptions You must: Have code that compiles with the command: javac *.java in your user directory without errors or warnings. You may Add additional methods and variables, however these must be private. Add additional nested, local, or anonymous classes, but any nested classes must be private. Use the provided Project3.java to get started and test your code but you should not include it in your submitted files. Keep in mind that this is not a tester, it is only provided to give you an idea of how your code should work. Import the following: File, Scanner, Printwriter, FileNotFoundException, Iterator You may NOT: Add additional public methods, variables, or classes. Exceptions: you may add public methods in ImageBlob and in private nested classes, and you may also override Object's public methods like equals, toString, etc. Use any built in Java Collections Framework classes in your program (e.g. no LinkedList, ArrayList, etc.). Add any additional import statements (or use the fully qualified name to get around adding import statements) Store anywhere in your program the Pixel[][] array that was passed to the QuadTree Image constructor. This array is used only for constructing the quadtree. Violation of this rule will result in a 0 on the entire assignment Make your program part of a package. Change any code in any "DO NOT EDIT" section. Add @suppressWarnings to avoid fixing warnings. There are a couple of places that are exempted from this rule and they're clearly stated in the description. Add any additional libraries/packages which require downloading from the internet. Assumptions We will assume that images have a square size and the width of an image is a power of 2 (i.e. 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, etc). This will simplify the creation of the quadtree as you won't have to deal with rectangular regions. It will also make memory usage more efficient since you don't need to store the coordinates of the image regions into the tree nodes. . Tasks You must implement the following classes and methods final class Utilities It contains two utility methods that we need in order to read/write images from/to files. static Short[][] loadFile(String pgmFile) It reads a PGB image from a file and stores the data in an array of type Short. Modifying the return type of this method to Integer or Float should not affect the rest of your program since everything else in this project is using generics. static void exportImage (QuadTree Image image, String filename) It writes a QuadTree Image into a PGM file. The signature is not complete, you need to add the generic type. There is no time-complexity restriction for this method. This means that you are allowed to call the getColor method if you want. This is the only place in your entire code that you can use the getColor. class QuadTree Image This class is the most important component of this project. It uses a quadtree structure to represent a grayscale image and provides various methods for processing the tree (a.k.a. image). The generic type Pixel can be any subtype of java.lang.Number. The class must implement the Comparable and the Iterable interfaces. The above signature is obviously not complete. QuadTree Image (Pixel[][] array) The constructor builds the quadtree from an array that holds the original data read from the PGM file. You may not store the array (or the pointer to the array) anywhere in your program after the creation of the tree. Pixel getColor(int w, int h) Returns the value of the pixel at location w, h where w and h are the column and row indexes in the original image respectively. If the coordinates w and h are invalid, it throws an IndexOutOfBoundsException. You may not make any use of this method anywhere outside the method exportImage. It will result in 0 points for any method that violates this restriction. The same is true if you try to bypass the restriction by building your own helper method that has the same or a similar functionality, 8x8 01 2 03 4x4 DID 2 x 2 1 2 1 pixel 8x8 D1 12 03 4. 4X4 ODOIDO 2x2 O.1 pixel 8x8 01 02 03 4 - 4x4 D.......2 x 2 - 1 pixel Figure 5: Effect of calling setColor(6, 2, 255) void setColor(int w, int h, Pixel value) Sets a new value for the pixel at location w, h where w and h are the column and row indexes in the original image. If the new value is different from the previous one, the tree will require a restructuring. See Figure 5 for an example. By setting the pixel 6,2 to value 255, all leafs become white and the subtree should now be removed. Keep in mind that such an action can trigger a restructuring that goes many levels up the tree. Think, for instance, what would happen if the 2x2 black node to the right of the one we've just changed was a white node originally. A major restriction for this method is that you're not allowed to recreate the image array, you must work directly on the tree. It will result in 0 points if you violate this restriction. You may not use the getColor or any kind of helper method with similar functionality to bypass this restriction and recreate the image array. Time-complexity restriction: it must run in O(m) where m is the number of nodes in the tree; not in O(n) where n is the number of pixels in the image. float sizeRatio(int bytesPerPixel, int bytesPerPointer) Returns the ratio of the size (in bytes) of the image stored as a quadtree to the size (in bytes) of the same image stored as an array. In Figure 2, for example, the original image requires 64 pixels and the quadtree requires 21 nodes. Assume that each node contains the minimum information which is one pixel value plus the four pointers to its children. String toString() Overrides the default behavior. It returns a representation of the quadtree that lists the nodes of the quadtree in a breadth-first-traversal order and clockwise within each level). Only leafs should be included in the string. For each leaf, you report: the top row coordinate, followed by the left column coordinate, followed by the size of the image region it represents, followed by the pixel value. The following is an example of the string returned for Figure 2 (assuming it's a proper PGB where black is represented with a 0 and white is represented with a 255): {0 0 4 255},{4 0 4 0},{0 4 2 255},{0 6 2 255}, {2 4 2 0},{4 4 2 0},{4 6 2 255}, {6 4 2 255}, {2 6 1 0}, {2 7 1 255},{3 7 1 255}, {3 6 1 255},{6 6 1 255},{6 7 1 255},{7 7 1 0},{7 6 1 255} int compareTo(QuadTree Image other) Class QuadTree Image implements the comparable interface and, therefore, it must provide this method. If the two trees are not the same, it returns the difference in the brightness of the two images. We measure the brightness as the sum of all the Pixel values in an image. A brighter image is considered larger. Please note that the sum should take into account all pixels in the image not just the ones in the leafs of the tree. Time-complexity restriction: it must run in O(m) where m is the number of nodes in the tree; not in O(n) where n is the number of pixels in the image. Practically, this means that you can't use getColor or any other approach to recreate the full image array. QuadTree Image intersectionMask (QuadTree Image other) Returns a new image that represents the intersection of the current image with another one as a binary mask. This means that the returned image will only have values of 0 and 255. All pixels that match in the two images will generate a white (255) pixel in the output mask, while the non- matching ones will generate a black (0) pixel. Instead of doing this computation pixel by pixel, we can compute this mask efficiently by leveraging the quadtree's ability to represent multiple pixels with a single node. You are not allowed to use getColor or any other similar functionality. But you are allowed to use the annotation @suppressWarnings Time-complexity restriction: it must calculate the mask in O(m) where m is the number of nodes in the tree; not in O(n) where n is the number of pixels in the image. Iterator> iterator() It creates a QuadTree ImageIterator that is iterating over the quadtree nodes (.e. ImageBlob) by a breadth-first-traversal order (and clockwise within each level). Every node should be included in the iteration, regardless if it's an inner or a leaf. The following output is an example of a for-each loop that prints the returned iterator of the QuadTree Image in Figure 2 (assuming it's a proper PGB where black is represented with a 0 and white is represented with a 255). The 21 tokens correspond to the 21 nodes of the tree. null 255 null null o 255 255 null 0 0 255 null 255 0 255 255 255 255 255 0 255 class ImageBlob This class represents a single node in the quadtree structure. You may not alter or add any fields. Pixel value The value of the pixel if the node is a leaf or null if it's an inner node. ImageBlob NW, NE, SE, SW The four pointers to the children nodes (in clockwise order). class Queue An array implementation of a circular queue. It's required for certain tree traversals. In this class you are allowed to use the annotation @SuppressWarnings boolean isEmpty() Returns true if the queue is empty, false otherwise void enqueue (T value) Adds an item to the back of the queue. T dequeue Removes the front item from the queue. Throws a RuntimeException if empty. T peek() Inspects the front item in the queue without removing it. Throws a RuntimeException if empty. class QuadTree ImageIterator It creates an iterator of the quadtree that traverses the nodes in a breadth-first-search approach. Also, this is the iterator that an enhanced for-loop on QuadTree Image will invoke automatically. boolean hasNext() Returns true if there are more nodes to be traversed, false otherwise ImageBlob next() Returns the next node in the quadtree according to a breadth-first-traversal








