Question: How would you make a decision to select a building site for a new waste-treatment plant in the Philippines? Where would you start with this
How would you make a decision to select a building site for a new waste-treatment plant in the Philippines? Where would you start with this complex decision, and what steps would you take? Explain which decision model in the chapter best describes your approach.
** Words 150-250, Please do not copy and paste other answers***
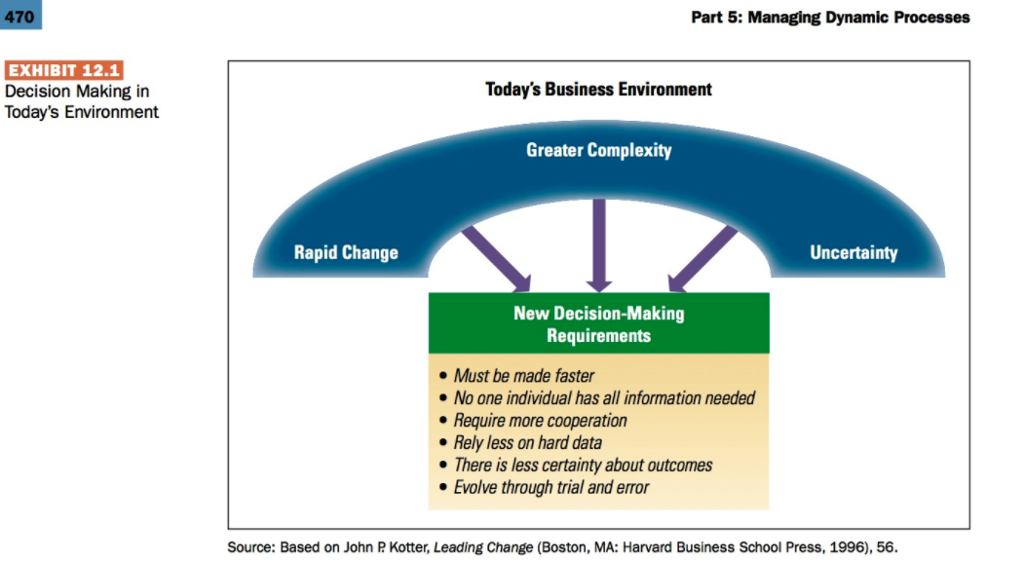
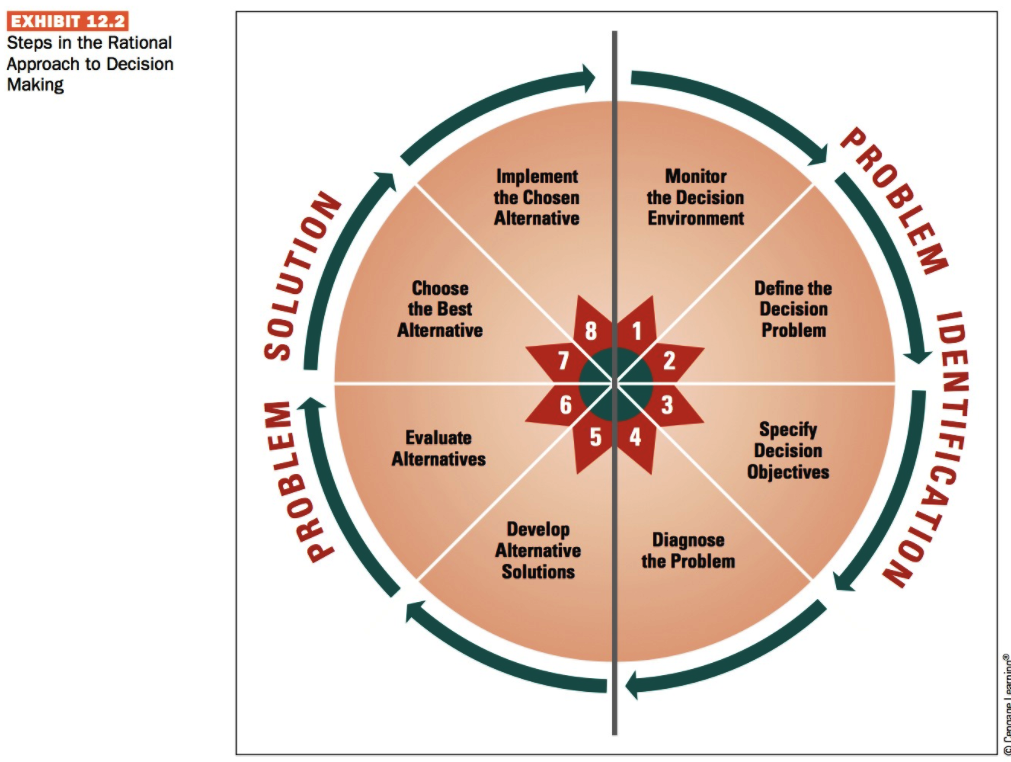
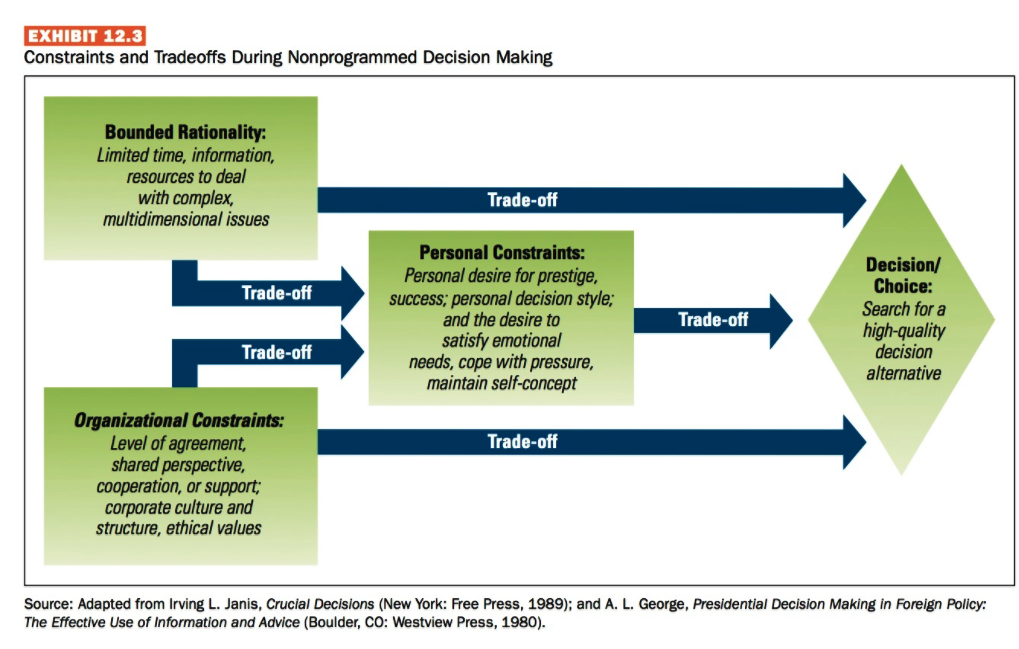
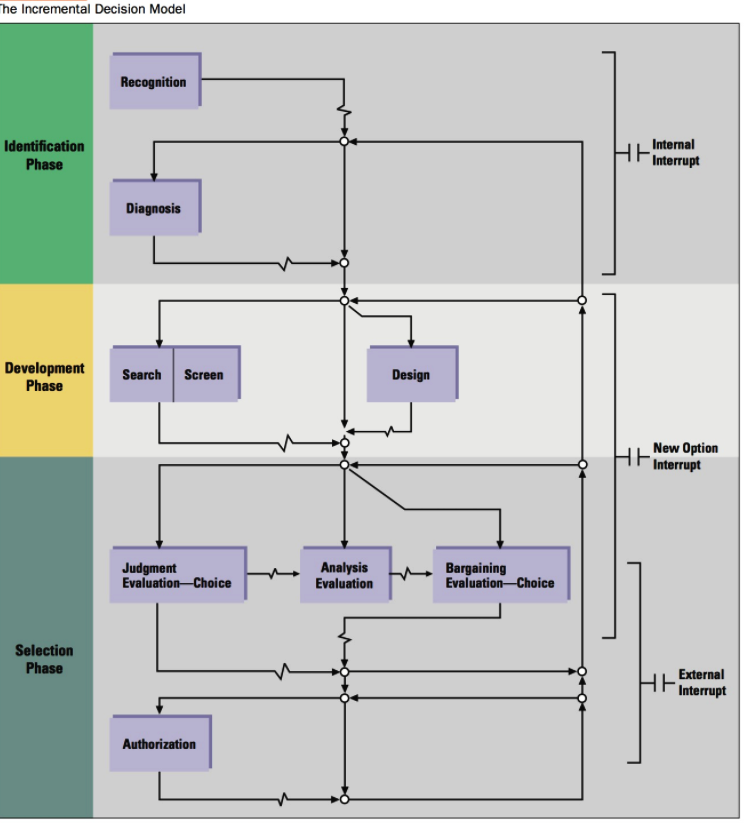
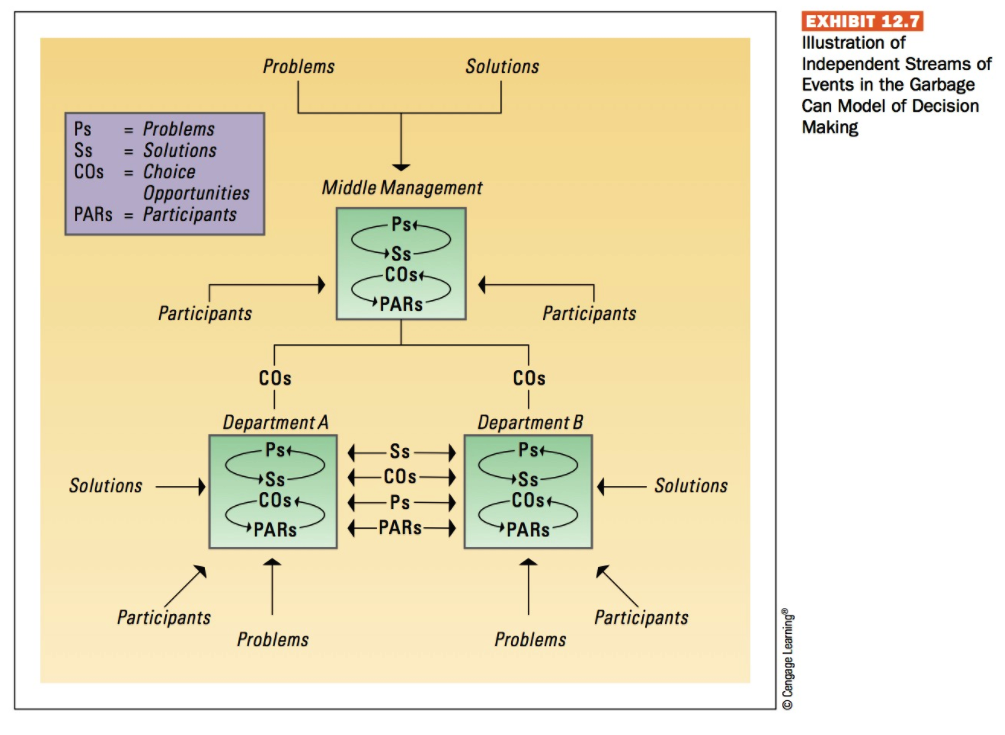
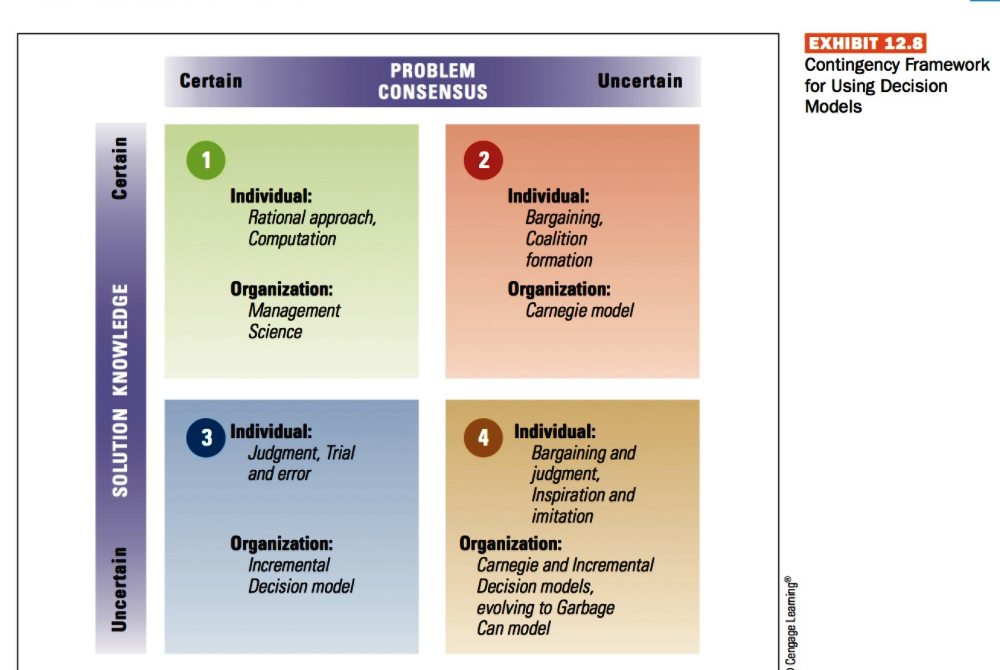
470 Part 5: Managing Dynamic Processes EXHIBIT 12.1 Decision Making in Today's Environment Today's Business Environment Greater Complexity Rapid Change Uncertainty New Decision-Making Requirements . Must be made faster No one individual has all information needed Require more cooperation Rely less on hard data There is less certainty about outcomes Evolve through trial and error Source: Based on John P. Kotter, Leading Change (Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press, 1996), 56. EXHIBIT 12.2 Steps in the Rational Approach to Decision Making Implement the Chosen Alternative Monitor the Decision Environment SOLUTION PROBLEM Choose the Best Alternative Define the Decision Problem 8 1 7 2 6 3 5 4 Evaluate Alternatives Specify Decision Objectives PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION Develop Alternative Solutions Diagnose the Problem EXHIBIT 12.3 Constraints and Tradeoffs During Nonprogrammed Decision Making Bounded Rationality: Limited time, information, resources to deal with complex, multidimensional issues Trade-off Trade-off Personal Constraints: Personal desire for prestige, success, personal decision style; and the desire to satisfy emotional needs, cope with pressure, maintain self-concept Trade-off Decision/ Choice: Search for a high-quality decision alternative Trade-off Trade-off Organizational Constraints: Level of agreement, shared perspective, cooperation, or support: corporate culture and structure, ethical values Source: Adapted from Irving L. Janis, Crucial Decisions (New York: Free Press, 1989); and A. L. George, Presidential Decision Making in Foreign Policy: The Effective Use of Information and Advice (Boulder, CO: Westview Press, 1980). The Incremental Decision Model Recognition Identification Phase HE Internal Interrupt Diagnosis Development Phase Search Screen Design Interrupt Judgment Evaluation-Choice Analysis Evaluation Bargaining EvaluationChoice Selection Phase HF Interrupt External Authorization Problems Solutions EXHIBIT 12.7 Illustration of Independent Streams of Events in the Garbage Can Model of Decision Making Ps = Problems Ss = Solutions COS = Choice Opportunities PARS = Participants Middle Management Pst Ss -COS PARS Participants Participants COS COS Department -Ps+ Solutions SS- COs Ps PARS Ss COs PARS Department B -Ps Ss -COS PARS Solutions Participants Participants Problems Problems Cengage Learning Certain PROBLEM CONSENSUS Uncertain EXHIBIT 12.8 Contingency Framework for Using Decision Models Certain 2 Individual: Rational approach, Computation Individual: Bargaining Coalition formation Organization: Carnegie model Organization: Management Science SOLUTION KNOWLEDGE 3 Individual: Judgment, Trial and error Individual: Bargaining and judgment Inspiration and imitation Organization: Carnegie and Incremental Decision models, evolving to Garbage Can model Uncertain Organization: Incremental Decision model Cengage LeamingStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


