Question: https://github.com/ut-amrl-private/planning-assignment-4 [IJ README ASS|gnment 4. BayeS|an Inference In this assignment, you will use Bayesian inference to track the position of a single piece on the
https://github.com/ut-amrl-private/planning-assignment-4




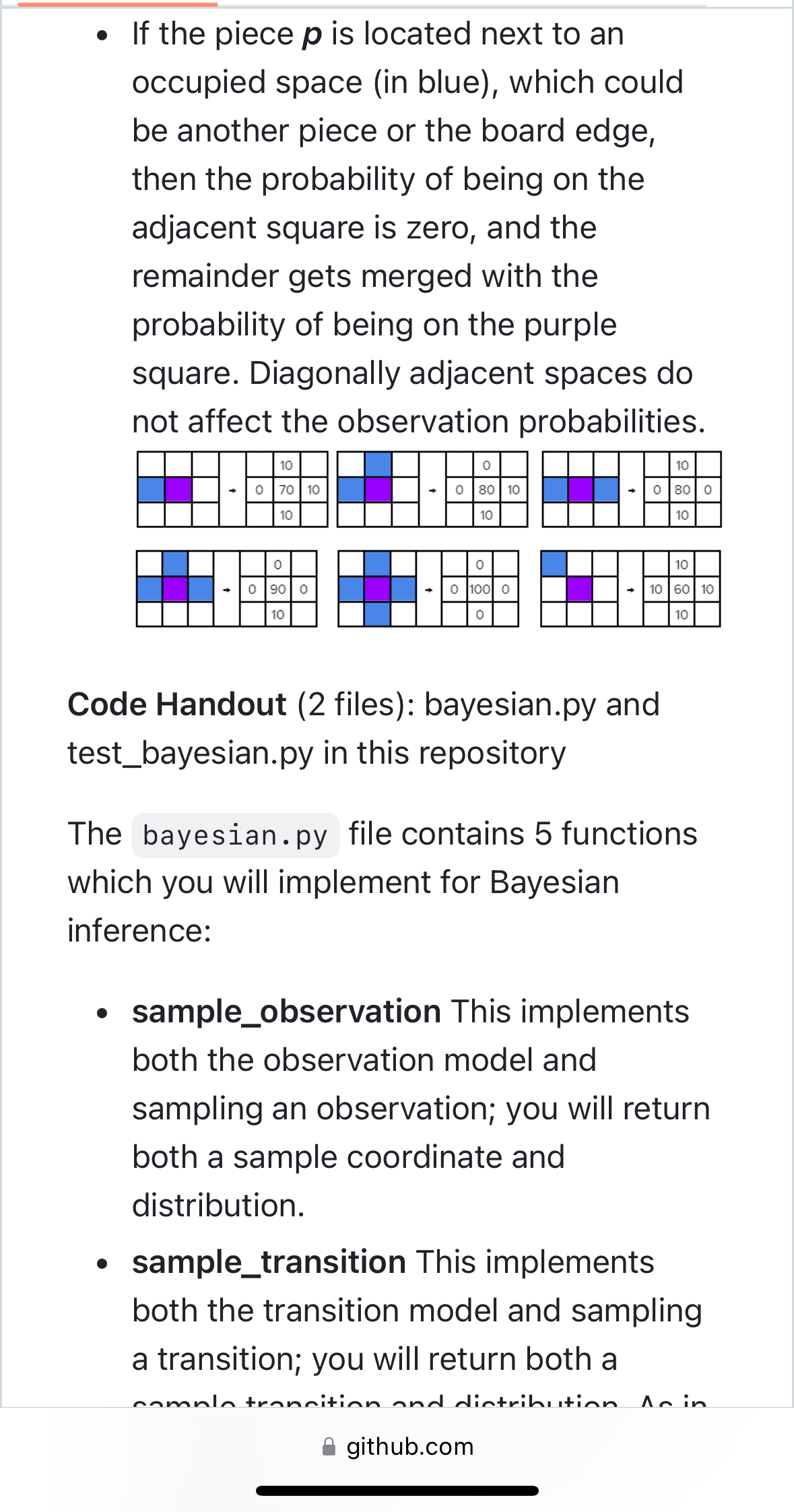
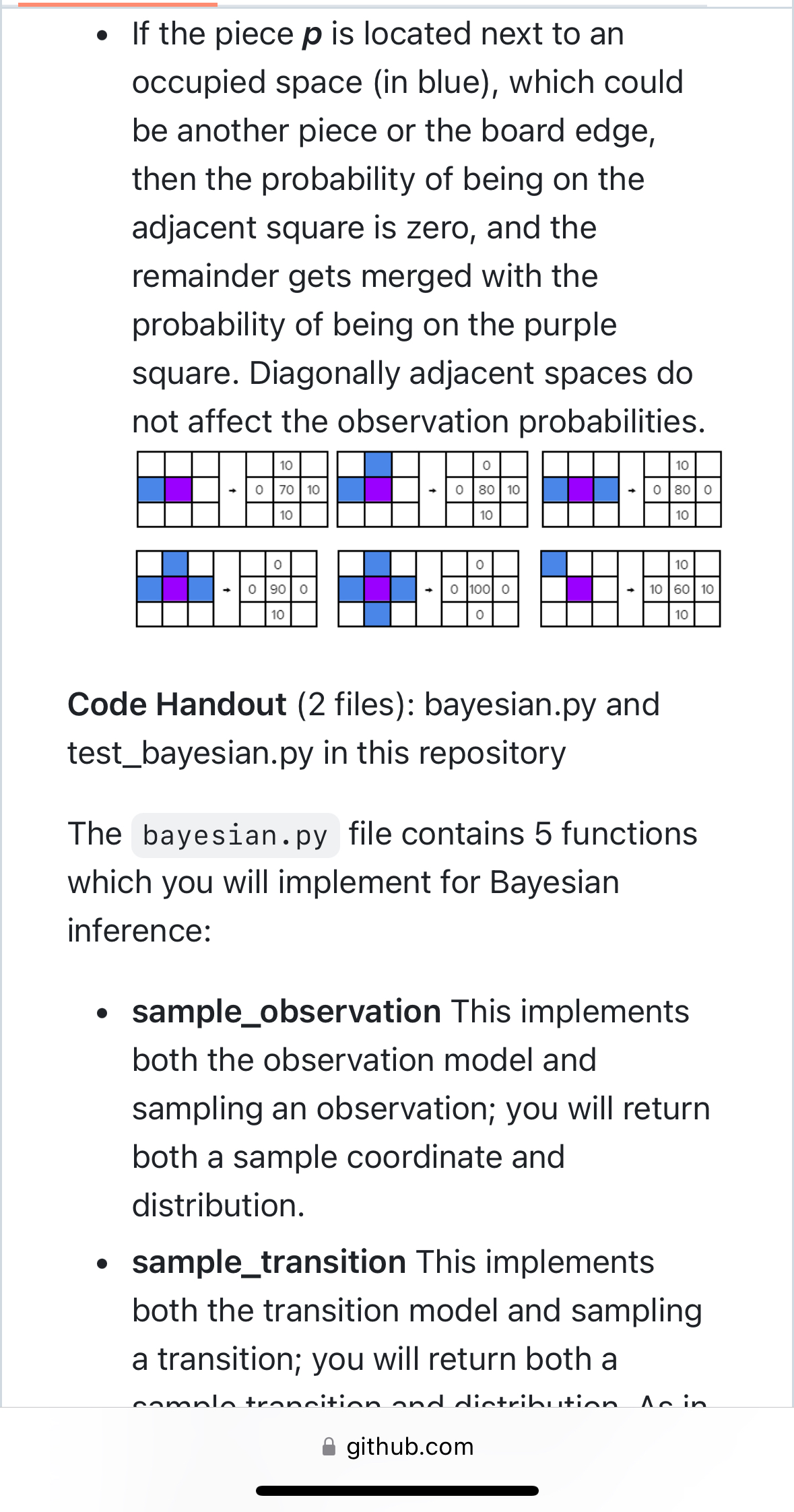
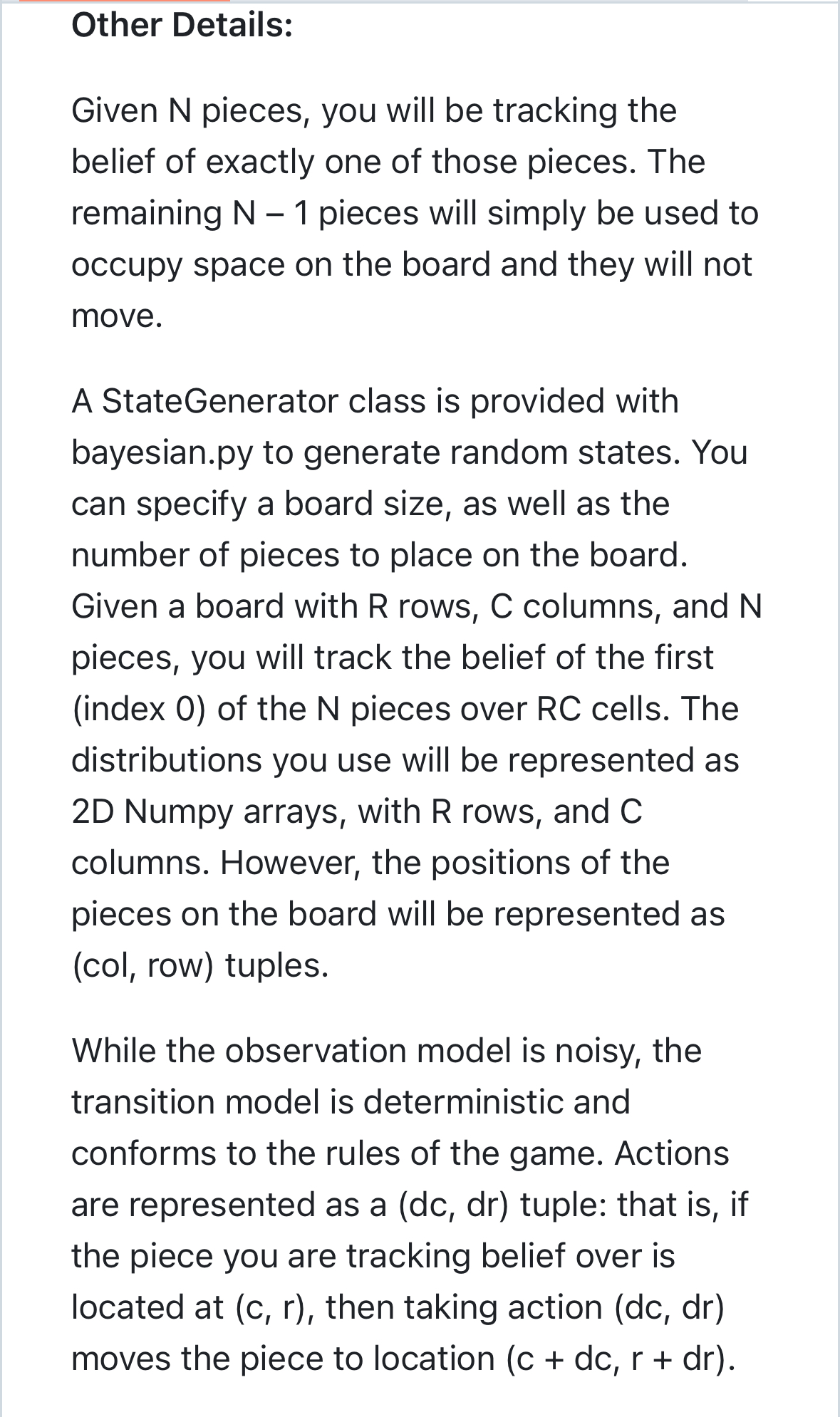
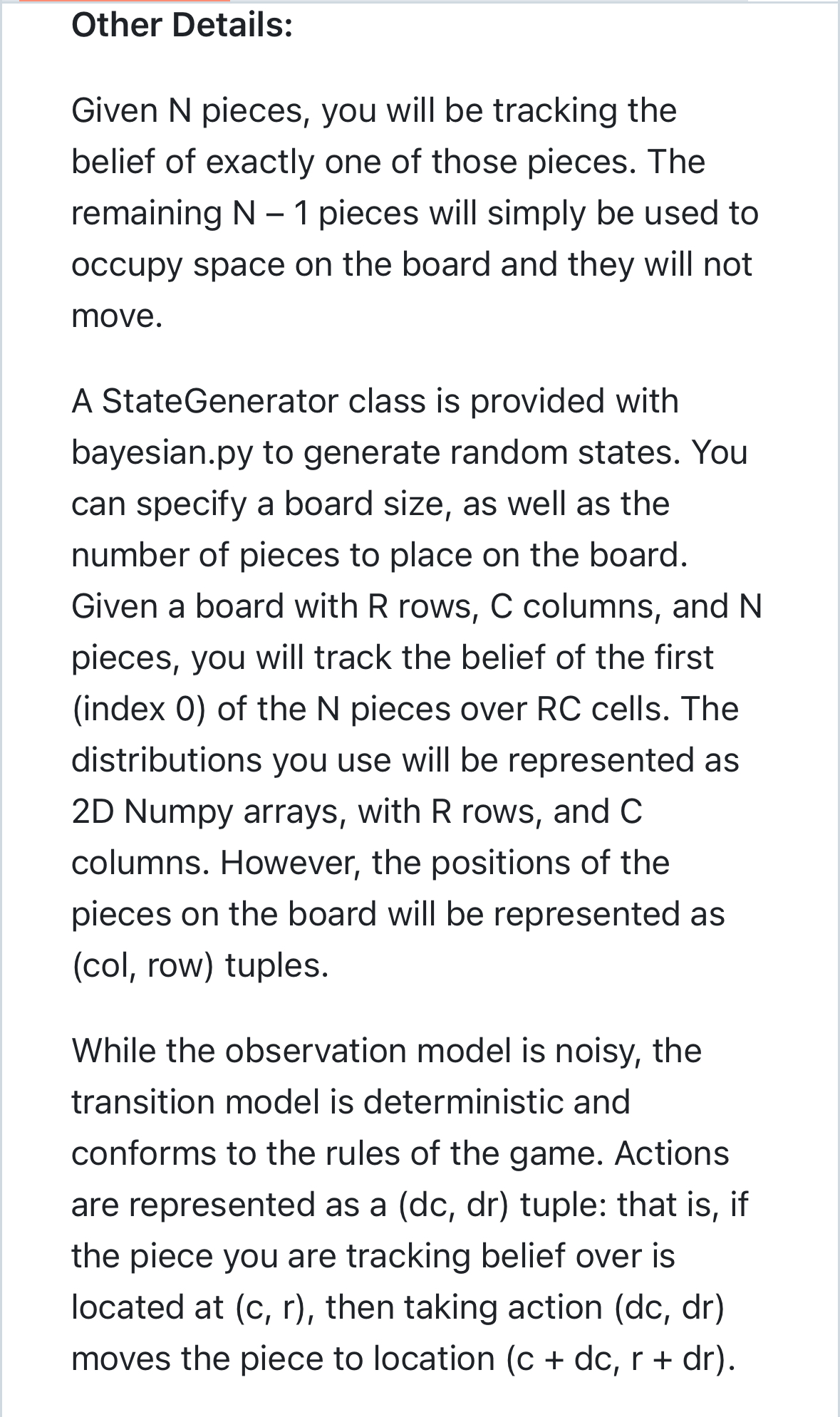 [IJ README ASS|gnment 4. BayeS|an Inference In this assignment, you will use Bayesian inference to track the position of a single piece on the gameboard of End of the Track, a two-player zero-sum board game, under an imperfect observation model. Please refer to Assignment 2 for the original rules of the game, which describe how the game pieces move, However, for this assignment, You only need care whether the action will move the piece out of bound of board, or move the piece to occupied position or not. In either such cases, returns None for the state, and a zero probability distribution. You don't need check it is knight move, queen move or king move for give action. Note: You don't need any code from assignment2 or assignment3 for this assignment. Description of the Observation Model: You will track the position of a single piece as it moves about the board. The positions of all the other pieces will remain fixed; you will know with certainty their positions at all times. However, you will be fed noisy s 00 [IJ README ASS|gnment 4. BayeS|an Inference In this assignment, you will use Bayesian inference to track the position of a single piece on the gameboard of End of the Track, a two-player zero-sum board game, under an imperfect observation model. Please refer to Assignment 2 for the original rules of the game, which describe how the game pieces move, However, for this assignment, You only need care whether the action will move the piece out of bound of board, or move the piece to occupied position or not. In either such cases, returns None for the state, and a zero probability distribution. You don't need check it is knight move, queen move or king move for give action. Note: You don't need any code from assignment2 or assignment3 for this assignment. Description of the Observation Model: You will track the position of a single piece as it moves about the board. The positions of all the other pieces will remain fixed; you will know with certainty their positions at all times. However, you will be fed noisy s 00 Description of the Observation Model: You will track the position of a single piece as it moves about the board. The positions of all the other pieces will remain fixed; you will know with certainty their positions at all times. However, you will be fed noisy observations of the single piece p as it moves about the board. The noisy observation model p(s | x) of the piece p, where x is the state, and s is the observation, can be pictorially described as follows (numerical values are in percentage units), given that p is located at the purple square, and that blue squares represent occupied spaces. e [f the piece p has free space around it, then the observation model looks like this: Description of the Observation Model: You will track the position of a single piece as it moves about the board. The positions of all the other pieces will remain fixed; you will know with certainty their positions at all times. However, you will be fed noisy observations of the single piece p as it moves about the board. The noisy observation model p(s | x) of the piece p, where x is the state, and s is the observation, can be pictorially described as follows (numerical values are in percentage units), given that p is located at the purple square, and that blue squares represent occupied spaces. e [f the piece p has free space around it, then the observation model looks like this: . If the piece p is located next to an occupied space (in blue), which could be another piece or the board edge, then the probability of being on the adjacent square is zero, and the remainder gets merged with the probability of being on the purple square. Diagonally adjacent spaces do not affect the observation probabilities. 10 10 0 70 10 O 80 10 80 0 10 10 10 O O 10 0 90 O 100 10 60 10 10 10 Code Handout (2 files): bayesian.py and test_bayesian.py in this repository The bayesian. py file contains 5 functions which you will implement for Bayesian inference: . sample_observation This implements both the observation model and sampling an observation; you will return both a sample coordinate and distribution. . sample_transition This implements both the transition model and sampling a transition; you will return both a camala transition and distribution An in github.com. If the piece p is located next to an occupied space (in blue), which could be another piece or the board edge, then the probability of being on the adjacent square is zero, and the remainder gets merged with the probability of being on the purple square. Diagonally adjacent spaces do not affect the observation probabilities. 10 10 0 70 10 O 80 10 80 0 10 10 10 O O 10 0 90 O 100 10 60 10 10 10 Code Handout (2 files): bayesian.py and test_bayesian.py in this repository The bayesian. py file contains 5 functions which you will implement for Bayesian inference: . sample_observation This implements both the observation model and sampling an observation; you will return both a sample coordinate and distribution. . sample_transition This implements both the transition model and sampling a transition; you will return both a camala transition and distribution An in github.come sample_transition This implements both the transition model and sampling a transition; you will return both a sample transition and distribution. As in the game, the transition model is deterministic. o initialize_belief This implements initializing the prior, or initial belief. You will implement both uniform and dirac versions of the prior; you will return a distribution. e belief_update This corresponds to updating the belief given an observation; you will return the updated belief (a distribution). e belief_predict This corresponds to updating the belief given an action; you will return the updated belief (a distribution). The test_bayesian.py file contains a few test cases; you should implement tests to ensure your code works as expected . e sample_transition This implements both the transition model and sampling a transition; you will return both a sample transition and distribution. As in the game, the transition model is deterministic. o initialize_belief This implements initializing the prior, or initial belief. You will implement both uniform and dirac versions of the prior; you will return a distribution. e belief_update This corresponds to updating the belief given an observation; you will return the updated belief (a distribution). e belief_predict This corresponds to updating the belief given an action; you will return the updated belief (a distribution). The test_bayesian.py file contains a few test cases; you should implement tests to ensure your code works as expected . Other Details: Given N pieces, you will be tracking the belief of exactly one of those pieces. The remaining N 1 pieces will simply be used to occupy space on the board and they will not move. A StateGenerator class is provided with bayesian.py to generate random states. You can specify a board size, as well as the number of pieces to place on the board. Given a board with R rows, C columns, and N pieces, you will track the belief of the first (index 0) of the N pieces over RC cells. The distributions you use will be represented as 2D Numpy arrays, with R rows, and C columns. However, the positions of the pieces on the board will be represented as (col, row) tuples. While the observation model is noisy, the transition model is deterministic and conforms to the rules of the game. Actions are represented as a (dc, dr) tuple: that is, if the piece you are tracking belief over is located at (c, r), then taking action (dc, dr) moves the piece to location ( + dc, r + dr). Other Details: Given N pieces, you will be tracking the belief of exactly one of those pieces. The remaining N 1 pieces will simply be used to occupy space on the board and they will not move. A StateGenerator class is provided with bayesian.py to generate random states. You can specify a board size, as well as the number of pieces to place on the board. Given a board with R rows, C columns, and N pieces, you will track the belief of the first (index 0) of the N pieces over RC cells. The distributions you use will be represented as 2D Numpy arrays, with R rows, and C columns. However, the positions of the pieces on the board will be represented as (col, row) tuples. While the observation model is noisy, the transition model is deterministic and conforms to the rules of the game. Actions are represented as a (dc, dr) tuple: that is, if the piece you are tracking belief over is located at (c, r), then taking action (dc, dr) moves the piece to location ( + dc, r + dr)
[IJ README ASS|gnment 4. BayeS|an Inference In this assignment, you will use Bayesian inference to track the position of a single piece on the gameboard of End of the Track, a two-player zero-sum board game, under an imperfect observation model. Please refer to Assignment 2 for the original rules of the game, which describe how the game pieces move, However, for this assignment, You only need care whether the action will move the piece out of bound of board, or move the piece to occupied position or not. In either such cases, returns None for the state, and a zero probability distribution. You don't need check it is knight move, queen move or king move for give action. Note: You don't need any code from assignment2 or assignment3 for this assignment. Description of the Observation Model: You will track the position of a single piece as it moves about the board. The positions of all the other pieces will remain fixed; you will know with certainty their positions at all times. However, you will be fed noisy s 00 [IJ README ASS|gnment 4. BayeS|an Inference In this assignment, you will use Bayesian inference to track the position of a single piece on the gameboard of End of the Track, a two-player zero-sum board game, under an imperfect observation model. Please refer to Assignment 2 for the original rules of the game, which describe how the game pieces move, However, for this assignment, You only need care whether the action will move the piece out of bound of board, or move the piece to occupied position or not. In either such cases, returns None for the state, and a zero probability distribution. You don't need check it is knight move, queen move or king move for give action. Note: You don't need any code from assignment2 or assignment3 for this assignment. Description of the Observation Model: You will track the position of a single piece as it moves about the board. The positions of all the other pieces will remain fixed; you will know with certainty their positions at all times. However, you will be fed noisy s 00 Description of the Observation Model: You will track the position of a single piece as it moves about the board. The positions of all the other pieces will remain fixed; you will know with certainty their positions at all times. However, you will be fed noisy observations of the single piece p as it moves about the board. The noisy observation model p(s | x) of the piece p, where x is the state, and s is the observation, can be pictorially described as follows (numerical values are in percentage units), given that p is located at the purple square, and that blue squares represent occupied spaces. e [f the piece p has free space around it, then the observation model looks like this: Description of the Observation Model: You will track the position of a single piece as it moves about the board. The positions of all the other pieces will remain fixed; you will know with certainty their positions at all times. However, you will be fed noisy observations of the single piece p as it moves about the board. The noisy observation model p(s | x) of the piece p, where x is the state, and s is the observation, can be pictorially described as follows (numerical values are in percentage units), given that p is located at the purple square, and that blue squares represent occupied spaces. e [f the piece p has free space around it, then the observation model looks like this: . If the piece p is located next to an occupied space (in blue), which could be another piece or the board edge, then the probability of being on the adjacent square is zero, and the remainder gets merged with the probability of being on the purple square. Diagonally adjacent spaces do not affect the observation probabilities. 10 10 0 70 10 O 80 10 80 0 10 10 10 O O 10 0 90 O 100 10 60 10 10 10 Code Handout (2 files): bayesian.py and test_bayesian.py in this repository The bayesian. py file contains 5 functions which you will implement for Bayesian inference: . sample_observation This implements both the observation model and sampling an observation; you will return both a sample coordinate and distribution. . sample_transition This implements both the transition model and sampling a transition; you will return both a camala transition and distribution An in github.com. If the piece p is located next to an occupied space (in blue), which could be another piece or the board edge, then the probability of being on the adjacent square is zero, and the remainder gets merged with the probability of being on the purple square. Diagonally adjacent spaces do not affect the observation probabilities. 10 10 0 70 10 O 80 10 80 0 10 10 10 O O 10 0 90 O 100 10 60 10 10 10 Code Handout (2 files): bayesian.py and test_bayesian.py in this repository The bayesian. py file contains 5 functions which you will implement for Bayesian inference: . sample_observation This implements both the observation model and sampling an observation; you will return both a sample coordinate and distribution. . sample_transition This implements both the transition model and sampling a transition; you will return both a camala transition and distribution An in github.come sample_transition This implements both the transition model and sampling a transition; you will return both a sample transition and distribution. As in the game, the transition model is deterministic. o initialize_belief This implements initializing the prior, or initial belief. You will implement both uniform and dirac versions of the prior; you will return a distribution. e belief_update This corresponds to updating the belief given an observation; you will return the updated belief (a distribution). e belief_predict This corresponds to updating the belief given an action; you will return the updated belief (a distribution). The test_bayesian.py file contains a few test cases; you should implement tests to ensure your code works as expected . e sample_transition This implements both the transition model and sampling a transition; you will return both a sample transition and distribution. As in the game, the transition model is deterministic. o initialize_belief This implements initializing the prior, or initial belief. You will implement both uniform and dirac versions of the prior; you will return a distribution. e belief_update This corresponds to updating the belief given an observation; you will return the updated belief (a distribution). e belief_predict This corresponds to updating the belief given an action; you will return the updated belief (a distribution). The test_bayesian.py file contains a few test cases; you should implement tests to ensure your code works as expected . Other Details: Given N pieces, you will be tracking the belief of exactly one of those pieces. The remaining N 1 pieces will simply be used to occupy space on the board and they will not move. A StateGenerator class is provided with bayesian.py to generate random states. You can specify a board size, as well as the number of pieces to place on the board. Given a board with R rows, C columns, and N pieces, you will track the belief of the first (index 0) of the N pieces over RC cells. The distributions you use will be represented as 2D Numpy arrays, with R rows, and C columns. However, the positions of the pieces on the board will be represented as (col, row) tuples. While the observation model is noisy, the transition model is deterministic and conforms to the rules of the game. Actions are represented as a (dc, dr) tuple: that is, if the piece you are tracking belief over is located at (c, r), then taking action (dc, dr) moves the piece to location ( + dc, r + dr). Other Details: Given N pieces, you will be tracking the belief of exactly one of those pieces. The remaining N 1 pieces will simply be used to occupy space on the board and they will not move. A StateGenerator class is provided with bayesian.py to generate random states. You can specify a board size, as well as the number of pieces to place on the board. Given a board with R rows, C columns, and N pieces, you will track the belief of the first (index 0) of the N pieces over RC cells. The distributions you use will be represented as 2D Numpy arrays, with R rows, and C columns. However, the positions of the pieces on the board will be represented as (col, row) tuples. While the observation model is noisy, the transition model is deterministic and conforms to the rules of the game. Actions are represented as a (dc, dr) tuple: that is, if the piece you are tracking belief over is located at (c, r), then taking action (dc, dr) moves the piece to location ( + dc, r + dr)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


