Question: Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The idea of Huffman coding is quite
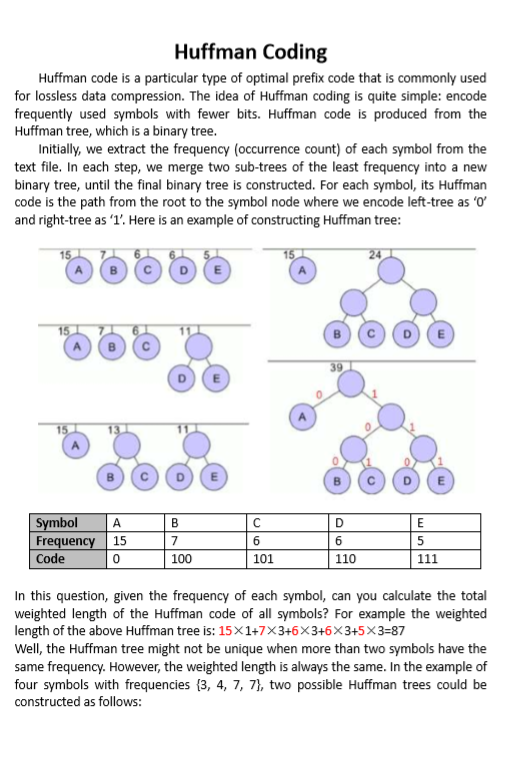
Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The idea of Huffman coding is quite simple: encode frequently used symbols with fewer bits. Huffman code is produced from the Huffman tree, which is a binary tree.Initially, we extract the frequency occurrence count of each symbol from the text file. In each step, we merge two subtrees of the least frequency into a new binary tree, until the final binary tree is constructed. For each symbol, its Huffman code is the path from the root to the symbol node where we encode lefttree as and righttree as Here is an example of constructing Huffman tree:In this question, given the frequency of each symbol, can you calculate the total weighted length of the Huffman code of all symbols? For example the weighted length of the above Huffman tree is: times times times times times Well, the Huffman tree might not be unique when more than two symbols have the same frequency. However, the weighted length is always the same. In the example of four symbols with frequencies two possible Huffman trees could be constructed as follows:InputThe input contains multiple test cases. Each test case begins with one integer n n indicating the number of symbols. The following line gives positive integers representing the frequency of each symbol where OutputFor each test case, print the total weighted length of the Huffman codes in a separate line.Sample inputSample output
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


