Question: HW # 3: PROBLEM SET Labor Migration Model There are two countries, the US and Mexico.The United States, which has more capital per worker and
HW # 3: PROBLEM SET
Labor Migration Model
There are two countries, the US and Mexico.The United States, which has more capital per worker and a higher level of technology, has higher labor productivity and hence higher wages. Assume purely competitive labor and goods markets, only one product, full employment, and that labor is therefore paid its marginal product.Further assume that the United States allows no labor immigration.Migrations are typically driven by wage differentials, with labor moving from the location of low wages toward the location of high wages.In essence, labor votes with its feet.The labor supplies for the two countries are as follows:
Mexican Labor Supply: LMex = 50
US Labor Supply: LUS = 100
Mexican Marginal Product of Labor: wMex = MPLMex = 40 .60LMex
US Marginal Product of Labor:wUS = MPLUS = 90 .50LUS
Use these equations to construct a basic Todaro Migration Model as shown in the textbook in Figure 4-13 on page 69. Add the two labor supplies to get a world labor supply.This forms the horizontal axis.On the two vertical axes, let the left axis be the US marginal product of labor and wages, and let the right axis be the Mexican marginal product of labor and wages. Now plot out the two marginal product of labor curves. These also serve as the demand curves for labor.
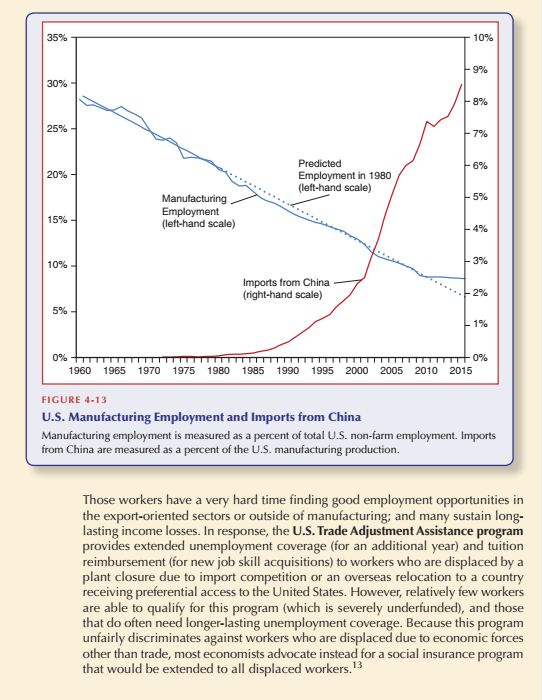
35% 10% - 9% 30% 8% 25% - 79% Predicted - 6% 20% Employment in 1980 (left-hand scale) Manufacturing - 5% Employment 15% (left-hand scale) - 498 10% - 358 Imports from China (right-hand scale) .4.- 270 5% 19% TITT TITT 0% 1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 FIGURE 4-13 U.S. Manufacturing Employment and Imports from China Manufacturing employment is measured as a percent of total U.S. non-farm employment. Imports from China are measured as a percent of the U.S. manufacturing production. Those workers have a very hard time finding good employment opportunities in the export-oriented sectors or outside of manufacturing; and many sustain long- lasting income losses. In response, the U.S. Trade Adjustment Assistance program provides extended unemployment coverage (for an additional year) and tuition reimbursement (for new job skill acquisitions) to workers who are displaced by a plant closure due to import competition or an overseas relocation to a country receiving preferential access to the United States. However, relatively few workers are able to qualify for this program (which is severely underfunded), and those that do often need longer-lasting unemployment coverage. Because this program unfairly discriminates against workers who are displaced due to economic forces other than trade, most economists advocate instead for a social insurance program that would be extended to all displaced workers. 13
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


