Question: I am looking for help declaring and designing a C++ function to add an intersection function to my myset.h and set.cpp files, that have been
I am looking for help declaring and designing a C++ function to add an "intersection" function to my "myset.h" and "set.cpp" files, that have been defined per instructions from question 3.5 in the textbook (https://www.chegg.com/homework-help/Data-Structures-and-Other-Objects-Using-C--4th-edition-chapter-3-problem-5PP-solution-9780132129480). All of the other functions work perfectly; I'm only in need of a function to handle the intersection of two sets that will work with my code. Here are my existing code and implementation + test files (copyable versions are listed below the pictures):
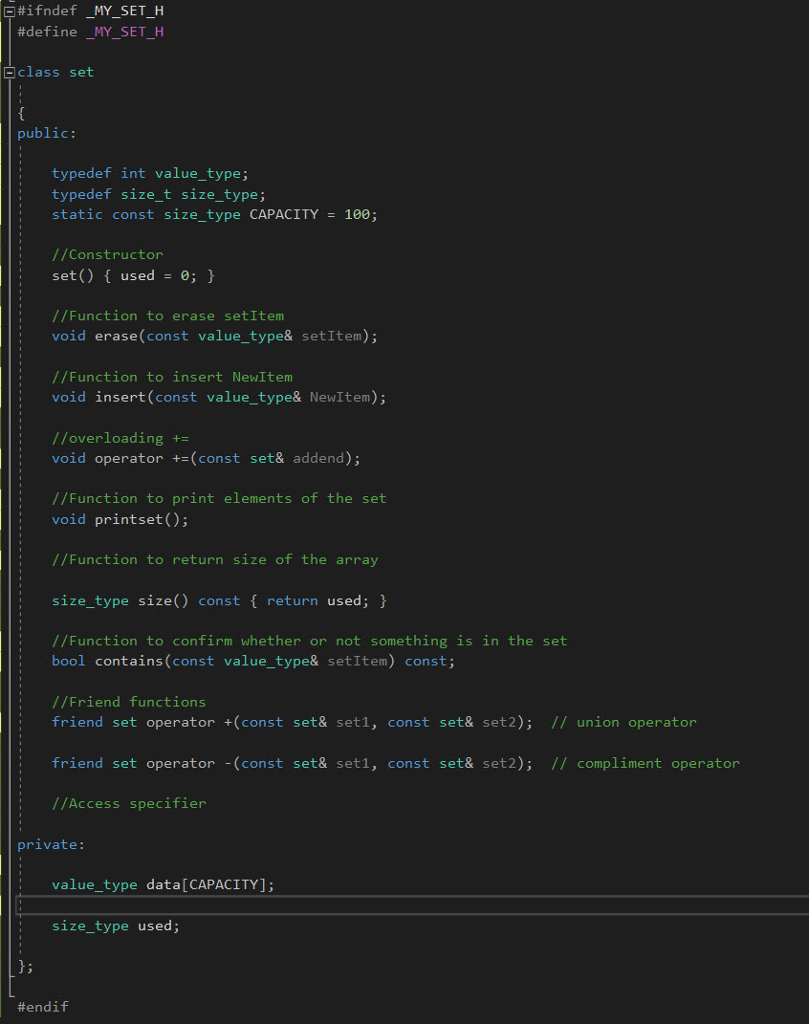
myset.h
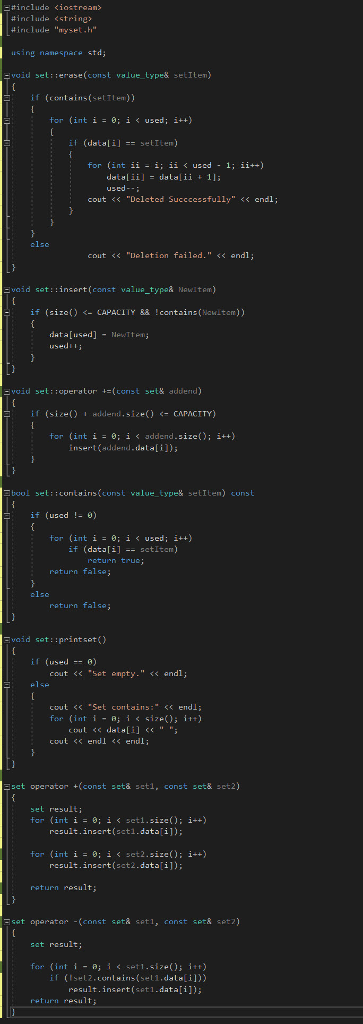
set.cpp
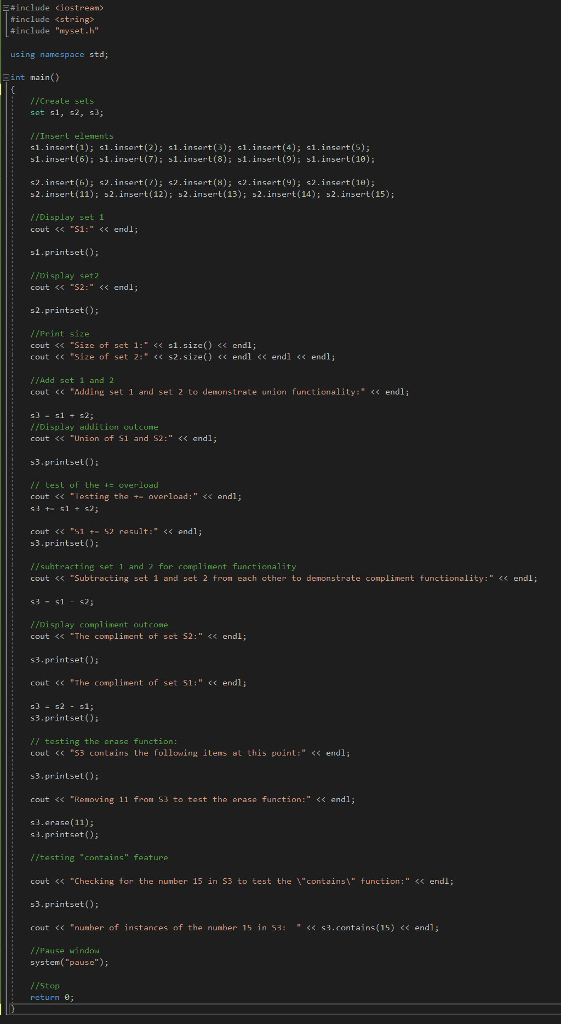
testset.cpp
COPYABLE CODE FOR MYSET.H:
#ifndef _MY_SET_H
#define _MY_SET_H
class set
{ public:
typedef int value_type; typedef size_t size_type; static const size_type CAPACITY = 100;
//Constructor set() { used = 0; }
//Function to erase setItem void erase(const value_type& setItem);
//Function to insert NewItem void insert(const value_type& NewItem);
//overloading += void operator +=(const set& addend);
//Function to print elements of the set void printset();
//Function to return size of the array
size_type size() const { return used; }
//Function to confirm whether or not something is in the set bool contains(const value_type& setItem) const;
//Friend functions friend set operator +(const set& set1, const set& set2); // union operator
friend set operator -(const set& set1, const set& set2); // compliment operator
//Access specifier
private:
value_type data[CAPACITY];
size_type used;
};
#endif
COPYABLE CODE FOR SET.CPP:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void set::erase(const value_type& setItem) { if (contains(setItem)) { for (int i = 0; i
void set::insert(const value_type& NewItem) { if (size()
void set::operator +=(const set& addend) { if (size() + addend.size()
bool set::contains(const value_type& setItem) const { if (used != 0) { for (int i = 0; i
void set::printset() { if (used == 0) cout
set operator +(const set& set1, const set& set2) { set result; for (int i = 0; i
for (int i = 0; i
return result; }
set operator -(const set& set1, const set& set2) { set result;
for (int i = 0; i
COPYABLE CODE FOR TESTSET.CPP:
#include
using namespace std;
int main() { //Create sets set s1, s2, s3;
//Insert elements s1.insert(1); s1.insert(2); s1.insert(3); s1.insert(4); s1.insert(5); s1.insert(6); s1.insert(7); s1.insert(8); s1.insert(9); s1.insert(10);
s2.insert(6); s2.insert(7); s2.insert(8); s2.insert(9); s2.insert(10); s2.insert(11); s2.insert(12); s2.insert(13); s2.insert(14); s2.insert(15);
//Display set 1 cout
s1.printset();
//Display set2 cout
s2.printset();
//Print size cout
//Add set 1 and 2 cout
s3 = s1 + s2; //Display addition outcome cout
s3.printset();
// test of the += overload cout
cout
//subtracting set 1 and 2 for compliment functionality cout
s3 = s1 - s2;
//Display compliment outcome cout
s3.printset();
cout
s3 = s2 - s1; s3.printset();
// testing the erase function: cout
s3.printset();
cout
s3.erase(11); s3.printset();
//testing "contains" feature
cout
s3.printset();
cout
//Pause window system("pause");
//Stop return 0; }
#ifndef MY SETH #define MY SETH - class set public: typedef int value_type; static const size_type CAPACITY 100; //Constructor typedef size t size type set) used ; //Function to erase setItem : void erase(const value_type& setItem); //Function to insert NewItem void insert(const value_type& NewItem); /overloading + void operator +=(const set& addend); //Function to print elements of the set void printset (); //Function to return size of the array size type size() const return used: /Function to confirm whether or not something is in the set : bool contains (const value_type& setItem) const; //Friend functions friend set operator +(const set& set1, const set& set2) I/ union operator friend set operator -(const set& set1, const set& set2); I/ compliment operator //Access specifier private: value_type data[CAPACITY] size type used; 3; #endif
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


