Question: I got the EEFrameConfig function. How to get the R_sb and p_sb? And the TODO part of SpatialpostionQ main.m function [q_s] = SpatialpositionQ(t) % This
I got the EEFrameConfig function. How to get the R_sb and p_sb? And the TODO part of SpatialpostionQ
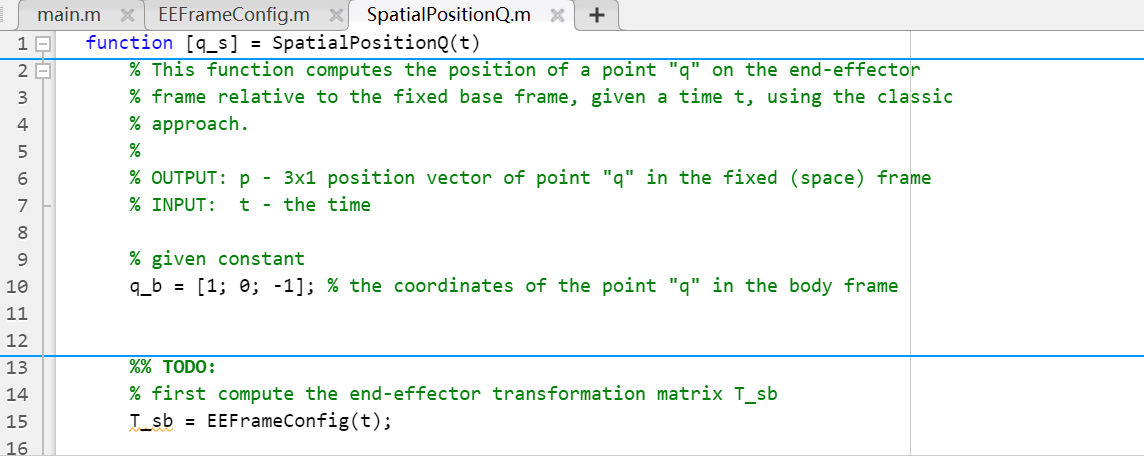
![And the TODO part of SpatialpostionQ main.m function [q_s] = SpatialpositionQ(t) %](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f0b1ca05958_18566f0b1c995b0b.jpg)


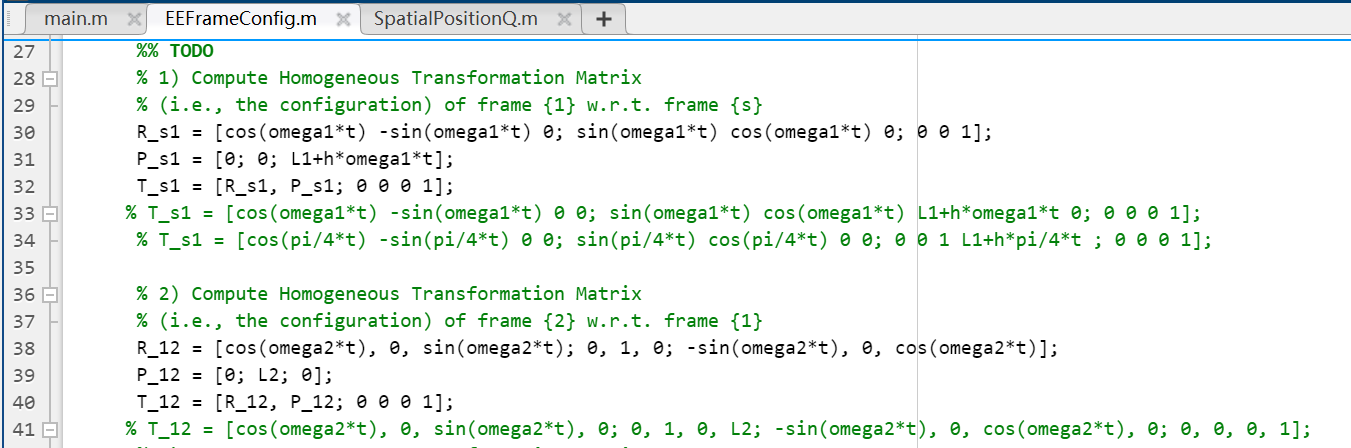
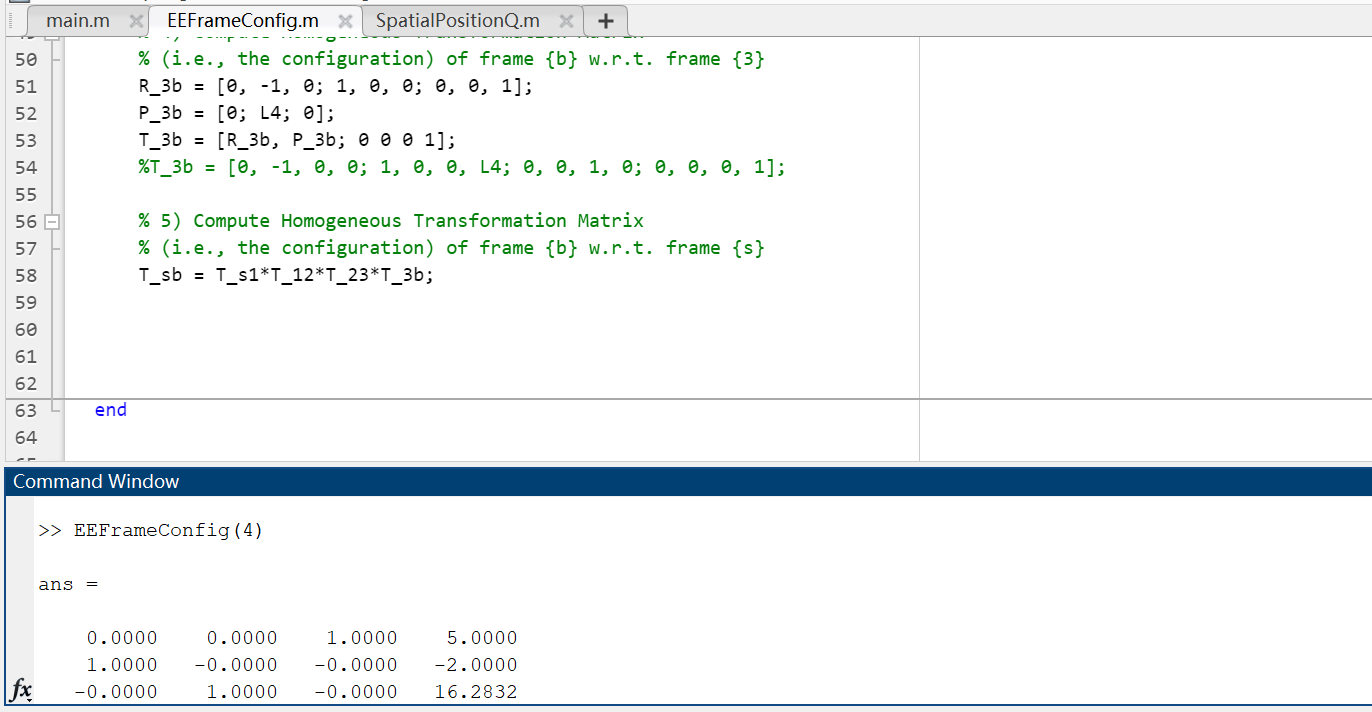
main.m function [q_s] = SpatialpositionQ(t) % This function computes the position of a point "q" on the end-effector % frame relative to the fixed base frame, given a time t, using the classic % approach. % % OUTPUT: p - 31 position vector of point "q" in the fixed (space) frame % INPUT: t - the time \% given constant q_b =[1;0;1];% the coordinates of the point "q" in the body frame \%\% TOD0: % first compute the end-effector transformation matrix T_sb T_sb = EEFrameConfig(t); >> SpatialPositionQ Not enough input arguments. Error in SpatialPositionQ (line 15) \[ \text { T_sb }_{\text {_ }} \text { = EEFrameConfig (t); } \] \% This function computes the configuration ( T ) of the end-effector frame \% relative to the fixed base frame, given a time t. % \% OUTPUT: T - 4x4 homogeneous transformation matrix of T_sb \% INPUT: t - the time \% Given constants % angular velocities can be used to determine the angles rotated after % time ' t ' omega1 = pi/4; omega2 = pi/8; omega3 =pi/4; % initial offsets L1=10; L2=5; L3=5; L4=3; % pitch can be used to determine the linear translation of the first % moving link given the angle rotated h=2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


