Question: I have already completed Problem 1 but I need Problem 2 to be completed: import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; class Edge implements Comparable { private Integer
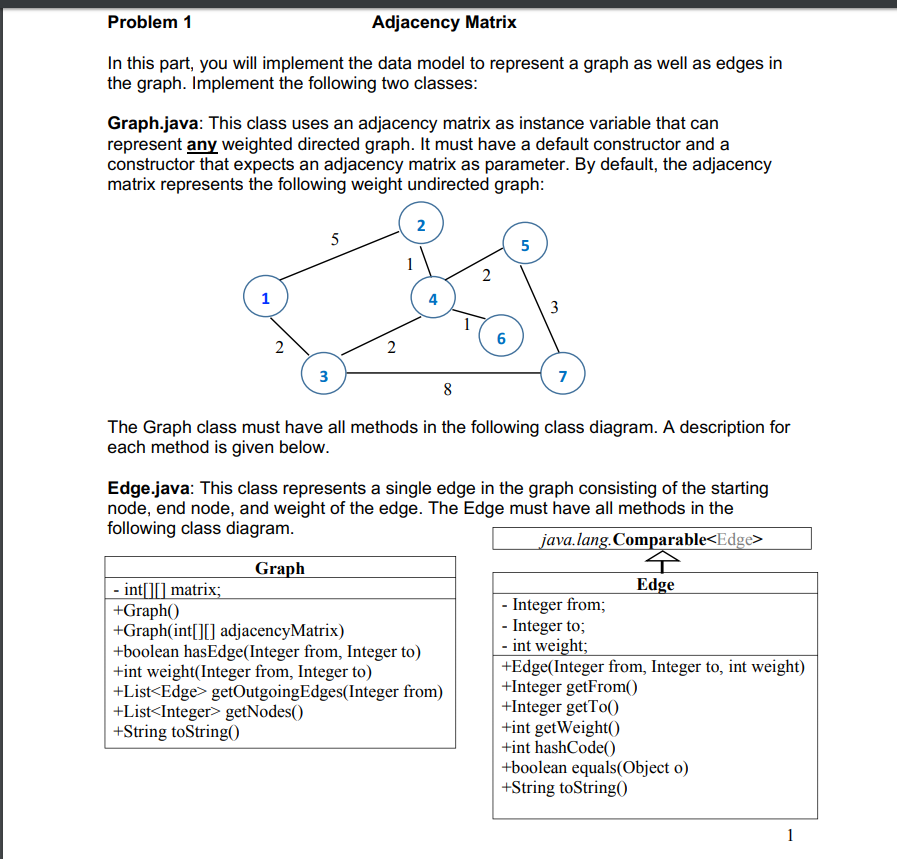

I have already completed Problem 1 but I need Problem 2 to be completed:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Edge implements Comparable
private Integer from;
private Integer to;
private int weight;
public Edge(Integer from, Integer to, int weight)
{
this.from=from;
this.to=to;
this.weight=weight;
}
public Integer getFrom()
{
return from;
}
public Integer getTo()
{
return to;
}
public int getWeight()
{
return weight;
}
public int hashCode()
{
return this.hashCode();
}
public boolean equals(Object o)
{
if(o instanceof Edge)
{
if(((Edge)o).getWeight()==weight)
return true;
else
return false;
}
return false;
}
public String toString()
{
return "From: "+from+"\tTo: "+to+"\tWeight: "+weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge edge) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(this.weight return -1; else if(this.weight==edge.weight) return 0; else return 1; } } class Graph{ private int[][] matrix; public Graph() { matrix=null; } public Graph(int[][] matrix) { this.matrix=matrix; } public boolean hasEdge(Integer from, Integer to) { return matrix[from][to]!=0; } public int weight(Integer from, Integer to) { return matrix[from][to]; } public List { List for(int i=0; i { if(matrix[from][i]!=0) { Edge edge=new Edge(from, i, matrix[from][i]); list.add(edge); } } return list; } public List { List for(int i=0; i list.add(i); return list; } public String toString() { String result=""; for(int i=0; i { for(int j=0; j { result=result+matrix[i][j]+"\t"; } result+=" "; } return result; } }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


