Question: I have the .h file for this: GeoGeo1.h #include #include using namespace std; typedef double ArrivalTime; // arrival time typedef int FileSize; // file size
I have the .h file for this:
GeoGeo1.h
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef double ArrivalTime; // arrival time
typedef int FileSize; // file size
class DNode { // doubly linked list node
public:
ArrivalTime aTime; // node element value
FileSize fSize; // file size
DNode* prev; // previous node in list
DNode* next; // next node in list
friend class DLinkedList; // allow DLinkedList access
};
class DLinkedList { // doubly linked list
public:
DLinkedList(); // constructor
~DLinkedList(); // destructor
bool empty() const; // is list empty?
const ArrivalTime& front() const; // get front element
//const Elem& back() const; // get back element
//const WaitingTime& front() const;
void addFront(const ArrivalTime& arrival, const FileSize& size); // add to front of list
void addBack(const ArrivalTime& arrival, const FileSize& size); // add to back of list
void removeFront(); // remove from front
void removeBack(); // remove from back
//void displayViaAge();
//void displayViaName();
public: // local type definitions
DNode* header; // list sentinels
DNode* trailer;
protected: // local utilities
void add(DNode* v, const ArrivalTime& arrival, const FileSize& size); // insert new node before v
void remove(DNode* v); // remove node v
};
DLinkedList::DLinkedList() { // constructor
header = new DNode; // create sentinels
trailer = new DNode;
header->next = trailer; // have them point to each other
trailer->prev = header;
}
DLinkedList::~DLinkedList() { // destructor
while (!empty()) removeFront(); // remove all but sentinels
delete header; // remove the sentinels
delete trailer;
}
// insert new node before v
void DLinkedList::add(DNode* v, const ArrivalTime& arrival, const FileSize& size) {
DNode* u = new DNode; // create a new node
u->aTime = arrival;
u->fSize = size;
u->next = v; // link u in between v
u->prev = v->prev; // ...and v->prev
v->prev->next = u;
v->prev = u;
//v->prev->next = v->prev = u;
}
void DLinkedList::addFront(const ArrivalTime& arrival, const FileSize& size) // add to front of list
{
add(header->next, arrival, size);
}
void DLinkedList::addBack(const ArrivalTime& arrival, const FileSize& size) // add to back of list
{
add(trailer, arrival, size);
}
void DLinkedList::remove(DNode* v) { // remove node v
DNode* u = v->prev; // predecessor
DNode* w = v->next; // successor
u->next = w; // unlink v from list
w->prev = u;
delete v;
}
void DLinkedList::removeFront() // remove from font
{
remove(header->next);
}
void DLinkedList::removeBack() // remove from back
{
remove(trailer->prev);
}
bool DLinkedList::empty() const // is list empty?
{
return (header->next == trailer);
}
const ArrivalTime& DLinkedList::front() const // get front element
{
return header->next->aTime;
}
/*const Elem& DLinkedList::back() const // get back element
{
return trailer->prev->elem;
}*/
/*void DLinkedList::displayViaAge() { //Displays person via age
DNode*temp = header;
while (temp != trailer)
{
//if(howold = age)
cout elem
temp = temp->next;
}
cout elem
}*/
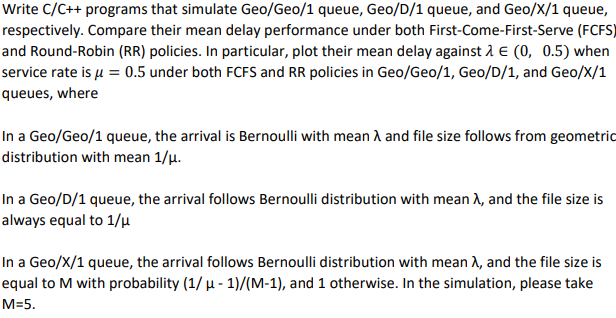
Write C/C++ programs that simulate Geo/Geo/1 queue, Geo/D/1 queue, and Geo/x/1 queue, respectively. Compare their mean delay performance under both First-Come-First-Serve (FCFS) and Round-Robin (RR) policies. In particular, plot their mean delay against 2 E (0, 0.5) when service rate is -0.5 under both FCFS and RR policies in Geo/Geo/1, Geo/D/1, and Geo/X/1 queues, where In a Geo/Geo/1 queue, the arrival is Bernoulli with mean A and file size follows from geometric distribution with mean 1/u. In a Geo/D/1 queue, the arrival follows Bernoulli distribution with mean , and the file size is always equal to 1/u In a Geo/X/1 queue, the arrival follows Bernoulli distribution with mean , and the file size is equal to M with probability (1/H - 1)/(M-1), and 1 otherwise. In the simulation, please take
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


