Question: I. Introduction: Determining the density, specific gravity and API is required to classify the petroleum product. API Gravity, or The American Petroleum Institute gravity,



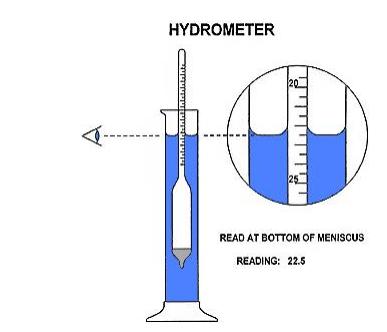


I. Introduction: Determining the density, specific gravity and API is required to classify the petroleum product. API Gravity, or The American Petroleum Institute gravity, is a measure of how light or heavy a petroleum liquid is compared to water. If a product has an API gravity of less than 10, it sinks. If the product has an API gravity greater than 10, it floats. The lower the API gravity of a sample, the higher viscosity and carbon residue content. The higher the API gravity of a sample, the lower the viscosity, carbon residue content, and the greater the heat of combustion. The API gravity is used to classify oils as light, medium, heavy, or extra heavy. As the "weight" of an oil is the largest determinant of its market value, API gravity is exceptionally important. The API values for each "weight" are as follows: Light - API > 31.1 Medium - API between 22.3 and 31.1 Heavy - API < 22.3 Extra Heavy and bitumen - API < 10.0 II. Aim Determination of Specific Gravity, Density, and API for petroleum products. III. Tools/Equipment Density by Pycnometer test: The pycnometer (from the Greek puknos, meaning "density", also called pyknometer or specific gravity bottle), is a flask with a close-fitting ground glass stopper with a fine hole through it, so that a given volume can be accurately obtained. This enables the density of a fluid to be measured accurately using an analytical balance. 154 (50) The pycnometer is used in ISO standard: ISO 1183-1:2004, and ASTM standard: ASTM D854: Specific Gravity by Hydrometer test: A hydrometer is usually made of glass, and consists of a cylindrical stem and a bulb weighted with mercury or lead shot to make it float upright. HYDROMETER Jalalalalalalalalalalalalalalate. 20 READ AT BOTTOM OF MENISCUS READING: 22.5 A hydrometer or areometer is an instrument that measures the specific gravity (relative density) of liquids-the ratio of the density of the liquid to the density of water. The hydrometer makes use of Archimedes' principle: a solid suspended in a fluid is buoyed by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the submerged part of the suspended solid. The lower the density of the fluid, the deeper a hydrometer of a given weight sinks; the stem is calibrated to give a numerical reading. IV. Procedure Density by Pycnometer Test: 1. The pycnometer is delicate and expensive; exercise care when handling it. 2. The bulb and stopper of the pycnometer are both engraved with the same number. Be sure that you do not inadvertently switch stoppers with someone else; check the numbers occasionally. 3. The pycnometer must be clean and DRY before the initial weighing. 4. To fill the pycnometer with liquid, use a Pasteur pipet to fill the bulb to about halfway up the neck (there is usually a white mark). Then slowly insert the capillary stopper. 5. When full, there should be NO air bubbles in the bulb or capillary of the pycnometer, and no air space at the top of the capillary. Before weighing the full pycnometer, the outside should be perfectly dry. Hydrometer Test: The liquid to test is poured into a tall container, often a graduated cylinder, and the hydrometer is gently lowered into the liquid until it floats freely. The point at which the surface of the liquid touches the stem of the hydrometer correlates to specific gravity. Hydrometers usually contain a scale inside the stem, so that the person using it can read specific gravity. A variety of scales exist for different contexts. API Gravity: API gravity is calculated using the specific gravity of an oil, which is nothing more than the ratio of its density to that of water (density of the oil/density of water). Specific gravity for API calculations is always determined at 60 degrees Fahrenheit. API gravity is found as follows: API gravity = (141.5/Specific Gravity) - 131.5 Though API values do not have units, they are often referred to as degrees. So the API gravity of West Texas Intermediate is said to be 39.6 degrees. API gravity moves inversely to density, which means the denser an oil is, the lower its API gravity will be. An API of 10 is equivalent to water, which means any oil with an API above 10 will float on water while any with an API below 10 will sink Solve the following question: V. Results/Discussion The density of sample is Specific gravity of sample is The API gravity of sample is The sample of oil is classified as
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Answer API Gravity and Classification API Gravity is a measure of how light or heavy a petroleum liq... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


