Question: I. Introduction ---> Python An instance of the N-puzzle game consists of a board holding N = m^2 1 (m = 3, 4, 5, ...)
I. Introduction ---> Python An instance of the N-puzzle game consists of a board holding N = m^2 1 (m = 3, 4, 5, ...) distinct movable tiles, plus an empty space. The tiles are numbers from the set {1, ..., m^2 1}. For any such board, the empty space may be legally swapped with any tile horizontally or vertically adjacent to it. In this practice, we will represent the blank space with the number 0 and focus on the m = 3 case (8-puzzle).
Given an initial state of the board, the combinatorial search problem is to find a sequence of moves that transitions this state to the goal state; that is, the configuration with all tiles arranged in ascending order 0, 1,..., m^2 1. The search space is the set of all possible states reachable from the initial state.
The blank space may be swapped with a component in one of the four directions {Up, Down, Left, Right}, one move at a time. The cost of moving from one configuration of the board to another is the same and equal to one. Thus, the total cost of path is equal to the number of moves made from the initial state to the goal state.
II. Algorithm Review Recall from the lectures that search begins by visiting the root node of the search tree, given by the initial state. Among other book-keeping details, three major things happen in sequence in order to visit a node: First, we remove a node from the frontier set. Second, we check the state against the goal state to determine if a solution has been found. Finally, if the result of the check is negative, we then expand the node. To expand a given node, we generate successor nodes adjacent to the current node, and add them to the frontier set. Note that if these successor nodes are already in the frontier, or have already been visited, then they should not be added to the frontier again.
This describes the life cycle of a visit, and is the basic order of operations for search agents in this assignment(1) remove, (2) check, and (3) expand.
III. Write driver.py Write driver.py, which solves any 8-puzzle board when given an arbitrary starting configuration. The program will be executed as follows: $ python driver.py
The method argument will be one of the following. You need to implement all three of them: bfs (Breadth-First Search) dfs (Depth-First Search) ast (A-Star Search)
The board argument will be a comma-separated list of integers containing no spaces. For example, to use the bread-first search strategy to solve the input board given by the starting configuration {0,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1}, the program will be executed like so (with no spaces between commas): $ python driver.py bfs 0,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1
IV. What Your Program Outputs When executed, your program will create / write to a file called output.txt, containing the following statistics: path_to_goal: the sequence of moves taken to reach the goal cost_of_path: the number of moves taken to reach the goal nodes_expanded: the number of nodes that have been expanded search_depth: the depth within the search tree when the goal node is found max_search_depth: the maximum depth of the search tree in the lifetime of the algorithm running_time: the total running time of the search instance, reported in seconds max_ram_usage: the maximum RAM usage in the lifetime of the process as measured by the ru_maxrss attribute in the resource module, reported in megabytes
Example #1: Breadth-First Search Suppose the program is executed for breadth-first search as follows: $ python driver.py bfs 1,2,5,3,4,0,6,7,8 Which should lead to the following solution to the input board:
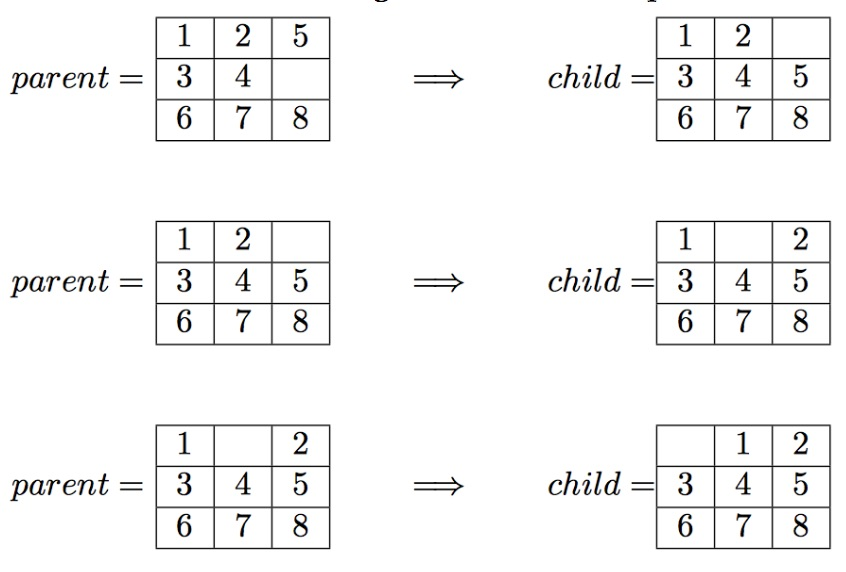 The output file will contain exactly the following lines: path_to_goal: ['Up', 'Left', 'Left'] cost_of_path: 3 nodes_expanded: 10 search_depth: 3 max_search_depth: 4 running_time: 0.00188088 max_ram_usage: 0.07812500
The output file will contain exactly the following lines: path_to_goal: ['Up', 'Left', 'Left'] cost_of_path: 3 nodes_expanded: 10 search_depth: 3 max_search_depth: 4 running_time: 0.00188088 max_ram_usage: 0.07812500
Example #2: Depth-First Search Suppose the program is executed for depth-first search as follows: $ python driver.py dfs 1,2,5,3,4,0,6,7,8 Which should lead to the following solution to the input board:
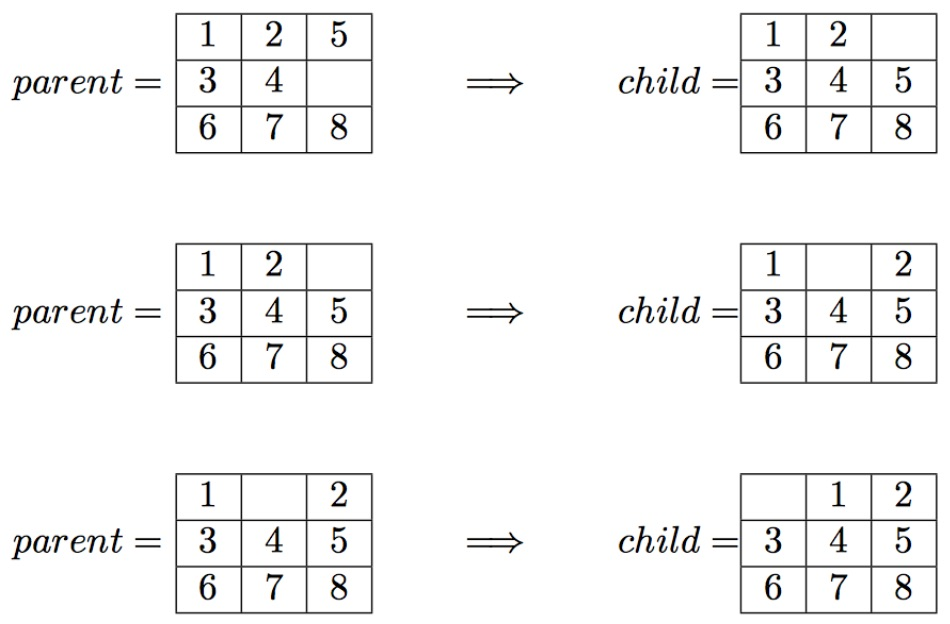 The output file will contain exactly the following lines: path_to_goal: ['Up', 'Left', 'Left'] cost_of_path: 3 nodes_expanded: 181437 search_depth: 3 max_search_depth: 66125 running_time: 5.01608433 max_ram_usage: 4.23940217
The output file will contain exactly the following lines: path_to_goal: ['Up', 'Left', 'Left'] cost_of_path: 3 nodes_expanded: 181437 search_depth: 3 max_search_depth: 66125 running_time: 5.01608433 max_ram_usage: 4.23940217
1 2 5 parent 3 4 6 7 8 1 2 parent 3 4 5 6 7 8 parent 3 4 5 6 8 1 2 child 3 4 5 6 7 8 child 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 child 3 4 5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


