Question: I just need help with part b. It says that the answer is not complete and some are wrong. So can you kindly fix it
I just need help with part b. It says that the answer is not complete and some are wrong. So can you kindly fix it for me and give me the full answers as it says the answer is "not complete". Thank you!
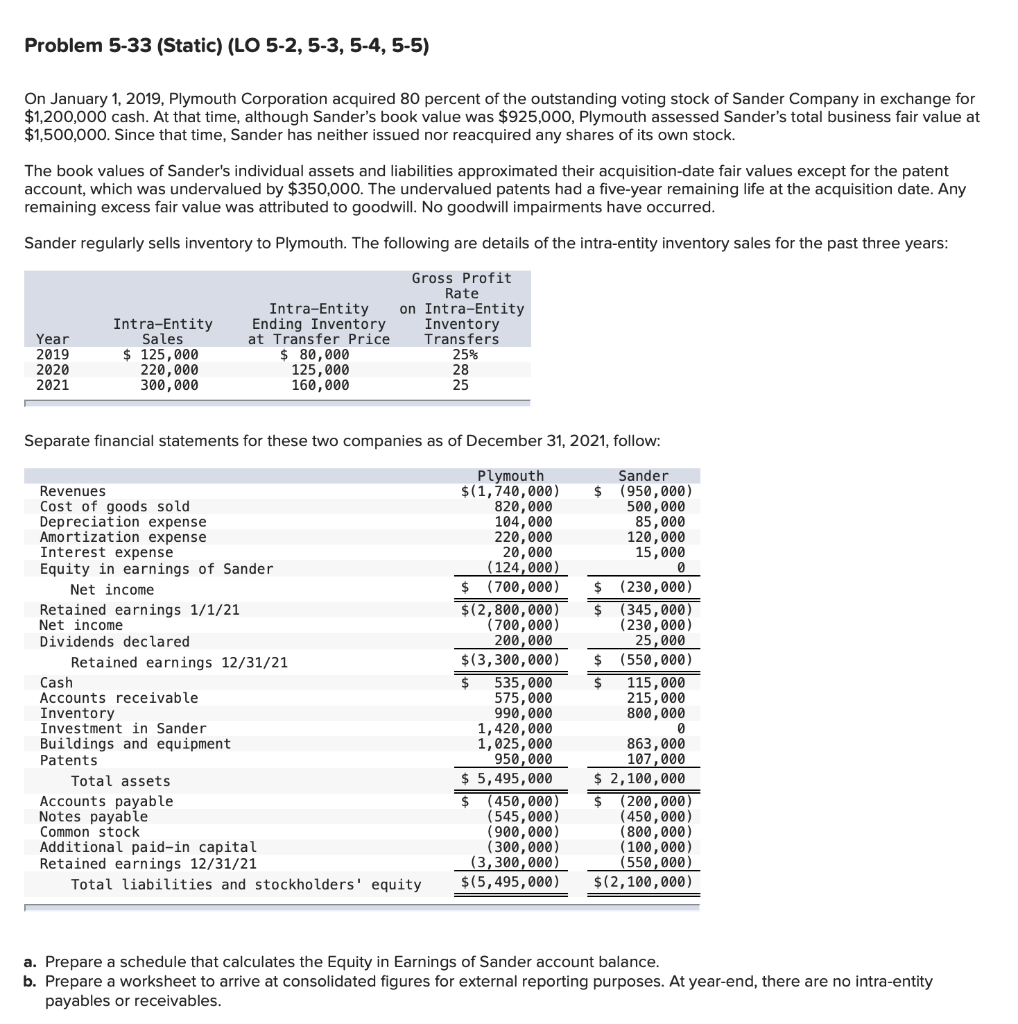
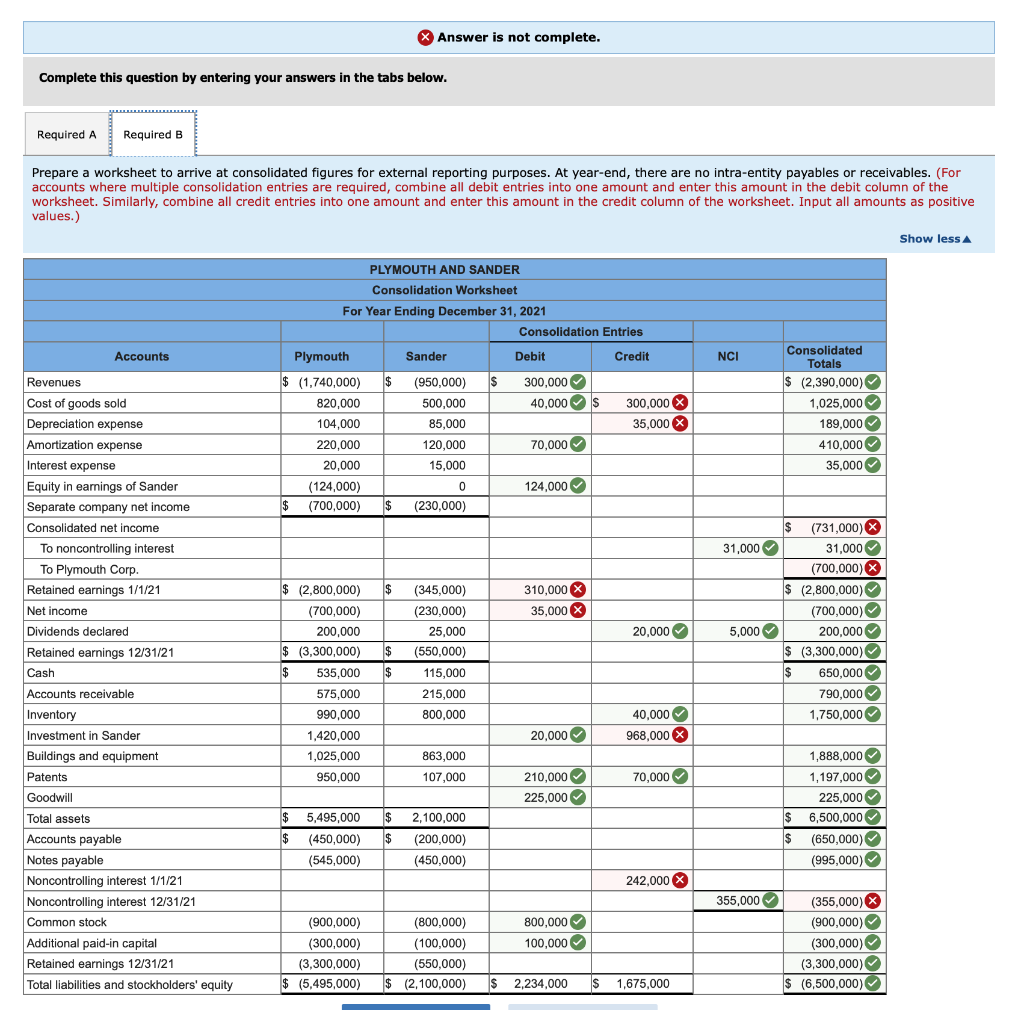
Problem 5-33 (Static) (LO 5-2,5-3,5-4,5-5) On January 1, 2019, Plymouth Corporation acquired 80 percent of the outstanding voting stock of Sander Company in exchange for $1,200,000 cash. At that time, although Sander's book value was $925,000, Plymouth assessed Sander's total business fair value at $1,500,000. Since that time, Sander has neither issued nor reacquired any shares of its own stock. The book values of Sander's individual assets and liabilities approximated their acquisition-date fair values except for the patent account, which was undervalued by $350,000. The undervalued patents had a five-year remaining life at the acquisition date. Any remaining excess fair value was attributed to goodwill. No goodwill impairments have occurred. Sander regularly sells inventory to Plymouth. The following are details of the intra-entity inventory sales for the past three years: Intra-Entity Sales $ 125,000 220,000 300,000 Year 2019 2020 2021 Gross Profit Rate on Intra-Entity Inventory Transfers 25% 28 25 Intra-Entity Ending Inventory at Transfer Price $ 80,000 125,000 160,000 Separate financial statements for these two companies as of December 31, 2021, follow: Revenues Cost of goods sold Depreciation expense Amortization expense Interest expense Equity in earnings of Sander Net income Retained earnings 1/1/21 Net income Dividends declared Retained earnings 12/31/21 Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Investment in Sander Buildings and equipment Patents Total assets Accounts payable Notes payable Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings 12/31/21 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity Plymouth $(1,740,000) 820,000 104,000 220,000 20,000 (124, 000) $ (700,000) $(2,800,000) (700,000) 200,000 $(3,300,000) $ 535,000 575,000 990,000 1,420,000 1,025,000 950,000 $ 5,495,000 $ (450,000) (545, 000) (900,000) (300,000) (3,300,000) $(5,495,000) Sander $ (950,000) 500,000 85,000 120,000 15,000 0 $ (230,000) (345,000) (230,000) 25,000 $ (550,000) $ 115,000 215,000 800,000 0 863,000 107,000 $ 2,100,000 $ (200,000) (450,000) (800,000) (100,000) (550,000 $(2,100,000) a. Prepare a schedule that calculates the Equity in Earnings of Sander account balance. b. Prepare a worksheet to arrive at consolidated figures for external reporting purposes. At year-end, there are no intra-entity payables or receivables. Answer is not complete. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Prepare a worksheet to arrive at consolidated figures for external reporting purposes. At year-end, there are no intra-entity payables or receivables. (For accounts where multiple consolidation entries are required, combine all debit entries into one amount and enter this amount in the debit column of the worksheet. Similarly, combine all credit entries into one amount and enter this amount in the credit column of the worksheet. Input all amounts as positive values.) Show less PLYMOUTH AND SANDER Consolidation Worksheet For Year Ending December 31, 2021 Consolidation Entries Accounts Sander Debit Credit NCI $ 300,000 40,000 $ Plymouth $ (1,740,000) 820,000 104,000 220,000 20,000 (124,000) $ (700,000) $ (950,000) 500,000 85,000 120,000 15,000 300,000 x 35,000 X Consolidated Totals $ (2,390,000) 1,025,000 189,000 410,000 35,000 70.000 124,000 0 (230,000) $ 31,000 $ 310,000 X 35,000 X 20,000 $ (731,000) X 31,000 (700,000) $ (2,800,000) (700,000) 200,000 $ (3,300,000) $ 650,000 790,000 1,750,000 OOOOOO 5,000 $ $ (2,800,000) (700,000) 200,000 $ (3,300,000) 19 535,000 575,000 990,000 1,420,000 1,025,000 Revenues Cost of goods sold Depreciation expense Amortization expense Interest expense Equity in earnings of Sander Separate company net income Consolidated net income To noncontrolling interest To Plymouth Corp. Retained earnings 1/1/21 Net income Dividends declared Retained earnings 12/31/21 Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Investment in Sander Buildings and equipment Patents Goodwill Total assets Accounts payable Notes payable Noncontrolling interest 1/1/21 Noncontrolling interest 12/31/21 Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings 12/31/21 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity (345,000) (230,000) 25,000 (550,000) 115,000 215,000 800,000 $ 40,000 968,000 X 20,000 863,000 107,000 950,000 70,000 210,000 225,000 1,888,000 1,197,000 225,000 $ 6,500,000 $ (650,000) (995,000) $ $ $ 5,495,000 (450,000) (545,000) $ 2,100,000 (200,000) (450,000) 242,000 X 355,000 800,000 100,000 (900,000) (300,000) (3,300,000) $ (5,495,000) (800,000) (100,000) (550,000) $ (2,100,000) (355,000) X (900,000) (300,000) (3,300,000) $ (6,500,000) $ 2,234,000 1,675,000
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


