Question: I know the code runs here is the assignment my professor said we have to change it. He gave us the code. You may need
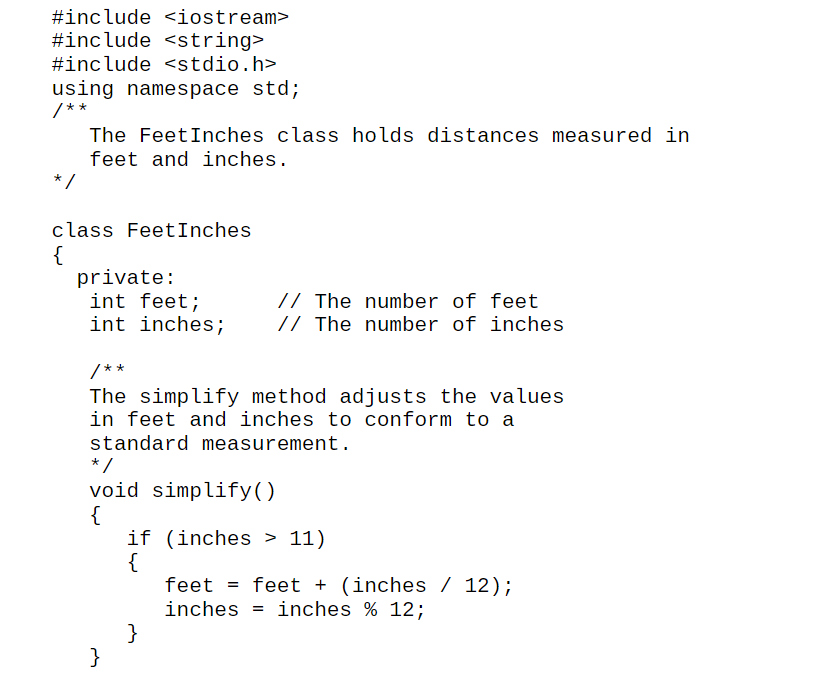
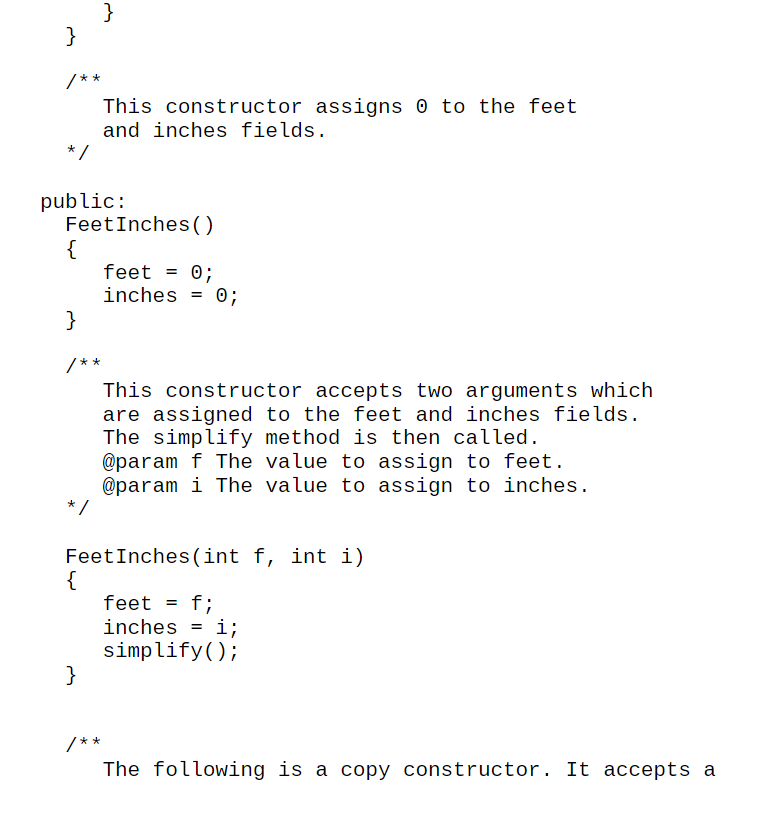



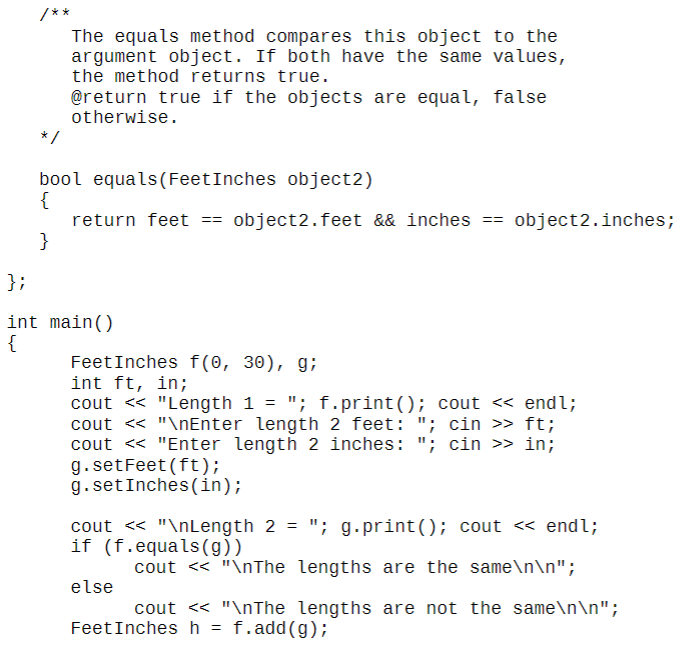

I know the code runs here is the assignment my professor said we have to change it. He gave us the code.
You may need to remove the system("pause"); statement to run it in a different environment.
The assignment is to modify the class implementation without changing the functionality.
Remove the feet and inches data members and replace them with one data member named total_inches. Re-implement all the class methods so they have he same functionality as originally. This means that any program written using the public members of the new class must produce exactly the same results as the original implementation.
#include #include #include using namespace std; /** The Feet Inches class holds distances measured in feet and inches. */ class FeetInches private: int feet; int inches; // The number of feet // The number of inches /** The simplify method adjusts the values in feet and inches to conform to a standard measurement. */ void simplify(). if (inches > 11) feet = feet + (inches / 12); inches = inches % 12; w This constructor assigns o to the feet and inches fields. public: Feet Inches feet = 0; inches = 0; This constructor accepts two arguments which are assigned to the feet and inches fields. The simplify method is then called. @param f The value to assign to feet. @param i The value to assign to inches. Feet Inches(int f, int i) feet = f; inches = i; simplify(); The following is a copy constructor. It accepts a reference to another Feet Inches object. The feet and inches fields are set to the same values as those in the argument object. @param object2 The object to copy. */ Feet Inches (const Feet Inches& object2) feet = object2. feet; inches = object2.inches; /** The setFeet method assigns a value to the feet field. @param f The value to assign to feet. void setFeet(int f) { feet = f; The set Inches method assigns a value to the inches field. @param i The value to assign to inches. */ void setInches(int i) inches = i; simplify(); getFeet method @return the value in the feet field. int getFeet() return feet; getInches method return the value in the inches field. int getInches() return inches; print method prints the distance as feet/inches getFeet method @return the value in the feet field. int getFeet() return feet; getInches method return the value in the inches field. int getInches() return inches; print method prints the distance as feet/inches The equals method compares this object to the argument object. If both have the same values, the method returns true. @return true if the objects are equal, false otherwise. bool equals(Feet Inches object2) { return feet == object2.feet && inches == object2.inches; }; int main Feet Inches f(0, 30), g; int ft, in; cout > ft; cout > in; g. setFeet(ft); g.setInches (in); cout #include #include using namespace std; /** The Feet Inches class holds distances measured in feet and inches. */ class FeetInches private: int feet; int inches; // The number of feet // The number of inches /** The simplify method adjusts the values in feet and inches to conform to a standard measurement. */ void simplify(). if (inches > 11) feet = feet + (inches / 12); inches = inches % 12; w This constructor assigns o to the feet and inches fields. public: Feet Inches feet = 0; inches = 0; This constructor accepts two arguments which are assigned to the feet and inches fields. The simplify method is then called. @param f The value to assign to feet. @param i The value to assign to inches. Feet Inches(int f, int i) feet = f; inches = i; simplify(); The following is a copy constructor. It accepts a reference to another Feet Inches object. The feet and inches fields are set to the same values as those in the argument object. @param object2 The object to copy. */ Feet Inches (const Feet Inches& object2) feet = object2. feet; inches = object2.inches; /** The setFeet method assigns a value to the feet field. @param f The value to assign to feet. void setFeet(int f) { feet = f; The set Inches method assigns a value to the inches field. @param i The value to assign to inches. */ void setInches(int i) inches = i; simplify(); getFeet method @return the value in the feet field. int getFeet() return feet; getInches method return the value in the inches field. int getInches() return inches; print method prints the distance as feet/inches getFeet method @return the value in the feet field. int getFeet() return feet; getInches method return the value in the inches field. int getInches() return inches; print method prints the distance as feet/inches The equals method compares this object to the argument object. If both have the same values, the method returns true. @return true if the objects are equal, false otherwise. bool equals(Feet Inches object2) { return feet == object2.feet && inches == object2.inches; }; int main Feet Inches f(0, 30), g; int ft, in; cout > ft; cout > in; g. setFeet(ft); g.setInches (in); cout










