Question: I need help. (b) Delete the first row and the first column of L and compute the determinant of the resulting 3 x 3 matrix.
I need help.

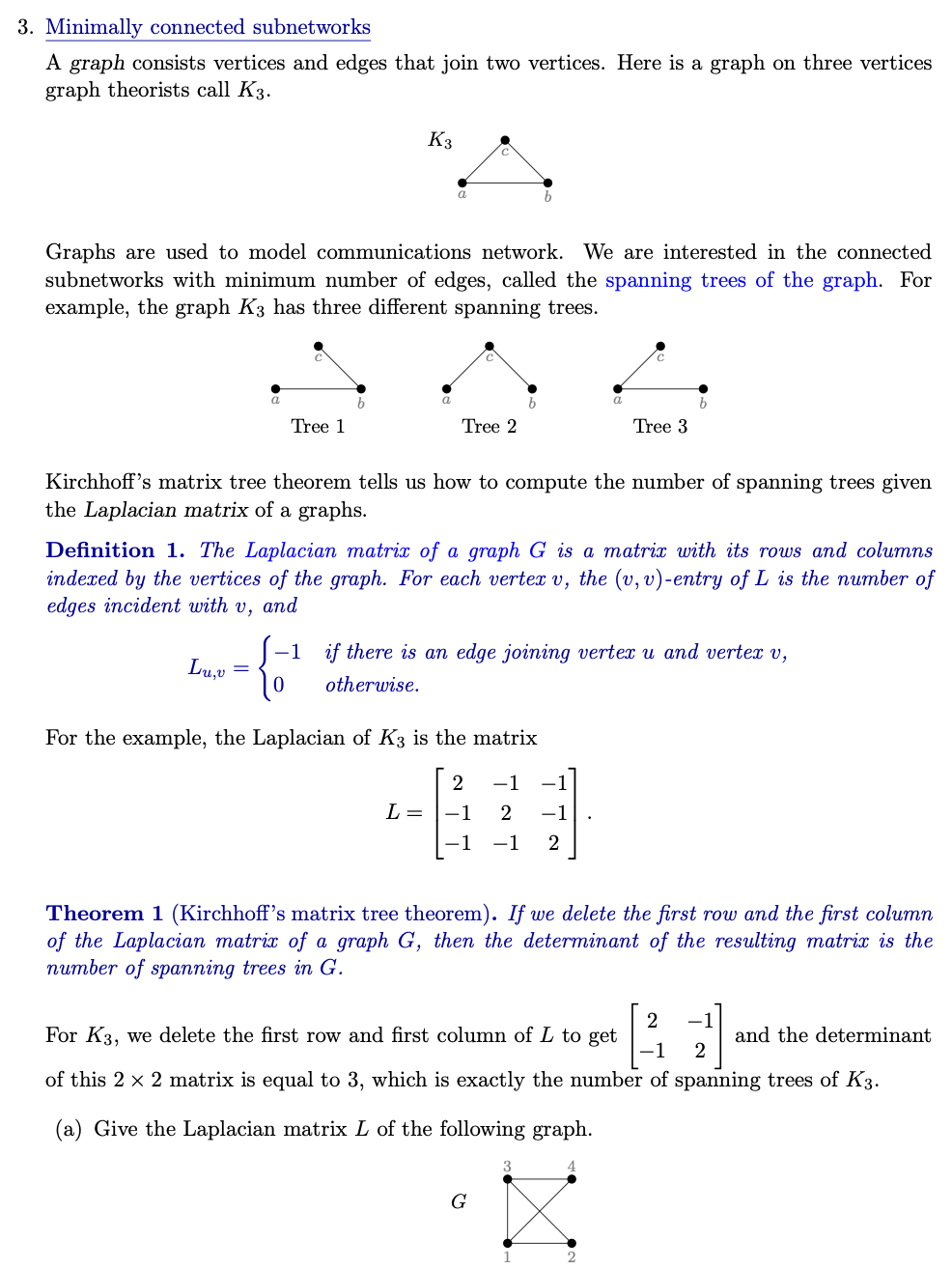
(b) Delete the first row and the first column of L and compute the determinant of the resulting 3 x 3 matrix. (c) Draw all spanning trees of G.3. Minimally connected subnetworks A graph consists vertices and edges that join two vertices. Here is a graph on three vertices graph theorists call K3. K3 Graphs are used to model communications network. We are interested in the connected subnetworks with minimum number of edges, called the spanning trees of the graph. For example, the graph K3 has three different spanning trees. Tree 1 Tree 2 Tree 3 Kirchhoff's matrix tree theorem tells us how to compute the number of spanning trees given the Laplacian matrix of a graphs. Definition 1. The Laplacian matrix of a graph G is a matrix with its rows and columns indexed by the vertices of the graph. For each vertex v, the (v, v)-entry of L is the number of edges incident with v, and Lu,v = -1 if there is an edge joining vertex u and vertex v, otherwise. For the example, the Laplacian of K3 is the matrix N -1 L = 2 -1 2 Theorem 1 (Kirchhoff's matrix tree theorem). If we delete the first row and the first column of the Laplacian matrix of a graph G, then the determinant of the resulting matrix is the number of spanning trees in G. For K3, we delete the first row and first column of L to get 2 and the determinant of this 2 x 2 matrix is equal to 3, which is exactly the number of spanning trees of K3. (a) Give the Laplacian matrix L of the following graph. G
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


