Question: I need help finding what is the amount reported as a liability for its leases combined? Entire question is in the attachment. Thank you for
I need help finding what is the amount reported as a liability for its leases combined?
Entire question is in the attachment.
Thank you for your help.
Here is the LINK for full financial statement:
https://corporate.target.com/annual-reports/pdf-viewer-2017?cover=30827&parts=30826
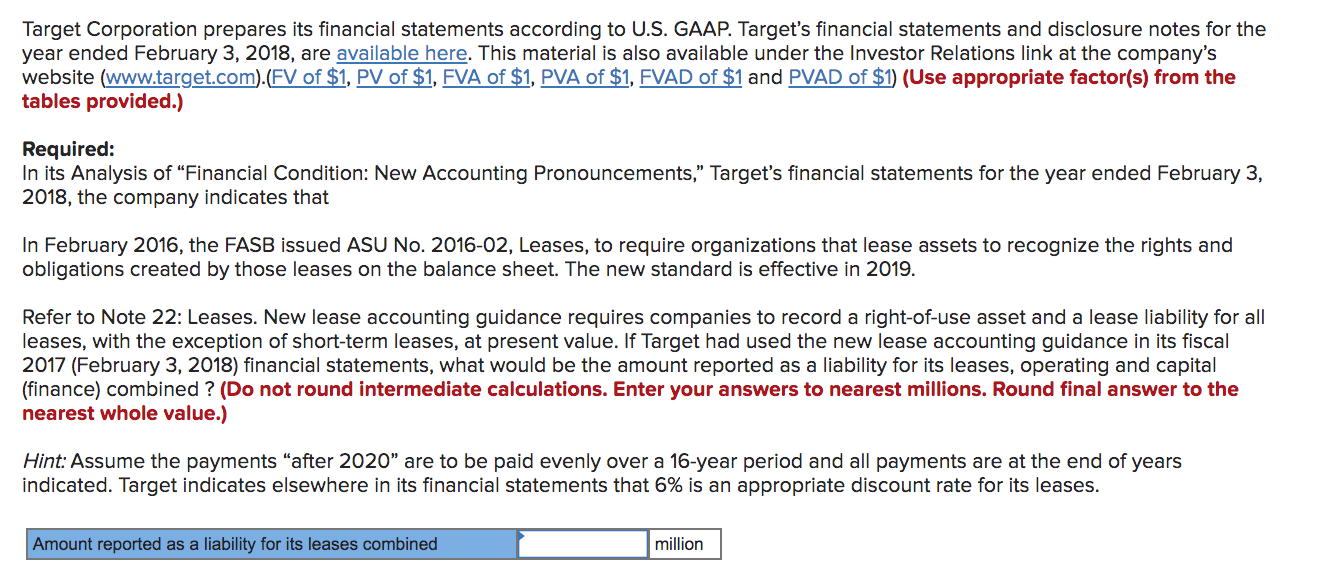
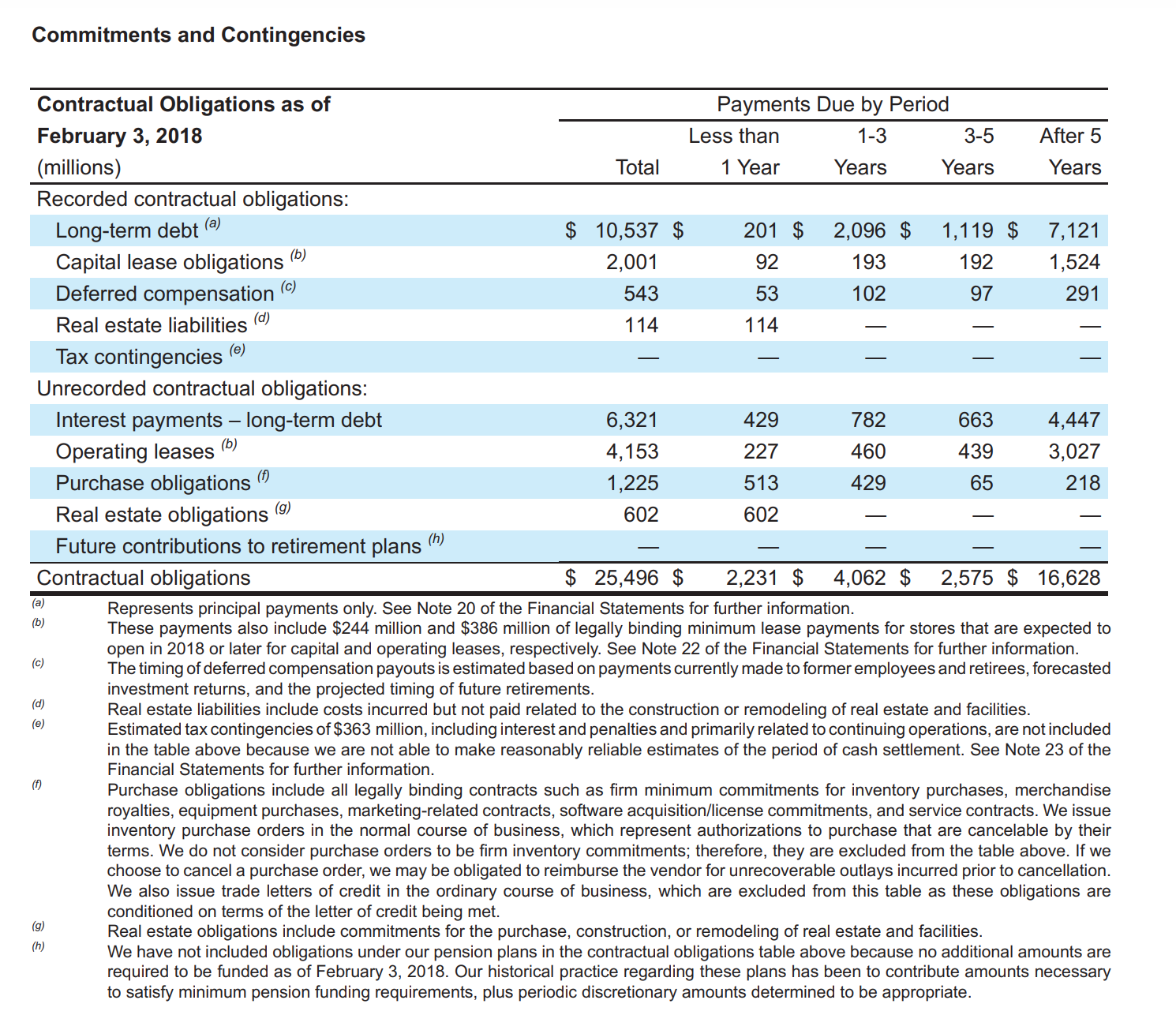
Target Corporation prepares its financial statements according to U.S. GAAP. Target's financial statements and disclosure notes for the year ended February 3, 2018, are available here. This material is also available under the Investor Relations link at the company's website (www.target.com).(FV of $1, PV of $1, EVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: In its Analysis of "Financial Condition: New Accounting Pronouncements," Target's financial statements for the year ended February 3, 2018, the company indicates that In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases, to require organizations that lease assets to recognize the rights and obligations created by those leases on the balance sheet. The new standard is effective in 2019. Refer to Note 22: Leases. New lease accounting guidance requires companies to record a right-of-use asset and a lease liability for all leases, with the exception of short-term leases, at present value. If Target had used the new lease accounting guidance in its fiscal 2017 (February 3, 2018) financial statements, what would be the amount reported as a liability for its leases, operating and capital (finance) combined ? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers to nearest millions. Round final answer to the nearest whole value.) Hint: Assume the payments "after 2020" are to be paid evenly over a 16-year period and all payments are at the end of years indicated. Target indicates elsewhere in its financial statements that 6% is an appropriate discount rate for its leases. Amount reported as a liability for its leases combined millionCommitments and Contingencies Contractual Obligations as of Payments Due by Period February 3, 2018 Less than 1-3 3-5 After 5 (millions) Total 1 Year Years Years Years Recorded contractual obligations: Long-term debt (at $ 10,537 $ 201 $ 2,096 $ 1,119 $ 7,121 Capital lease obligations 'b' 2,001 92 193 192 1,524 Deferred compensation '6' 543 53 102 97 291 Real estate liabilities 'd' 114 114 Tax contingencies (a) _ _ _ _ Unrecorded contractual obligations: Interest payments long-term debt 6,321 429 782 663 4,447 Operating leases ('0 4,153 227 460 439 3,027 Purchase obligations m 1,225 513 429 65 218 Real estate obligations (9) 602 602 Future contributions to retirement plans (h) Contractual obligations $ 25,496 $ 2,231 $ 4,062 $ 2.575 $ 16.628 (a) (h) (B) (d) (9) {f} (g) (h) Represents principal payments only. See Note 20 of the Financial Statements for further information. These payments also include $244 million and $386 million of legally binding minimum lease payments for stores that are expected to open in 2018 or later for capital and operating leases, respectively. See Note 22 of the Financial Statements for further information. The timing of deferred compensation payouts is estimated based on payments currently made to fom'ier employees and retirees, forecasted investment returns, and the projected timing of future retirements. Real estate liabilities include costs incurred but not paid related to the construction or remodeling of real estate and facilities. Estimated tax contingencies of $363 million, including interestand penalties and primarily related to continuing operations, are not included in the table above because we are not able to make reasonably reliable estimates ofthe period of cash settlement. See Note 23 of the Financial Statements for further information. Purchase obligations include all legally binding contracts such as rm minimum commitments for inventory purchases, merchandise royalties, equipment purchases, marketing-related contracts, software acquisition/license commitments, and service contracts. We issue inventory purchase orders in the normal course of business, which represent authorizations to purchase that are cancelable by their terms. We do not consider purchase orders to be rm inventory commitments; therefore, they are excluded from the table above. If we choose to cancel a purchase order, we may be obligated to reimburse the vendor for unrecoverable outlays incurred prior to cancellation. We also issue trade letters of credit in the ordinary course of business, which are excluded from this table as these obligations are conditioned on terms of the letter of credit being met. Real estate obligations include commitments for the purchase, construction, or remodeling of real estate and facilities. We have not included obligations under our pension plans in the contractual obligations table above because no additional amounts are required to be funded as of February 3, 2018. Our historical practice regarding these plans has been to contribute amounts necessary to satisfy minimum pension funding requirements, plus periodic discretionary amounts determined to be appropriate