Question: I need help in this case questions. Please do all the questions in MS-EXCEL and do them 100% and do not make any mistake. Please
I need help in this case questions. Please do all the questions in MS-EXCEL and do them 100% and do not make any mistake. Please I need to do it correctly, as i am not sure on my answers. Please show the formulas as well

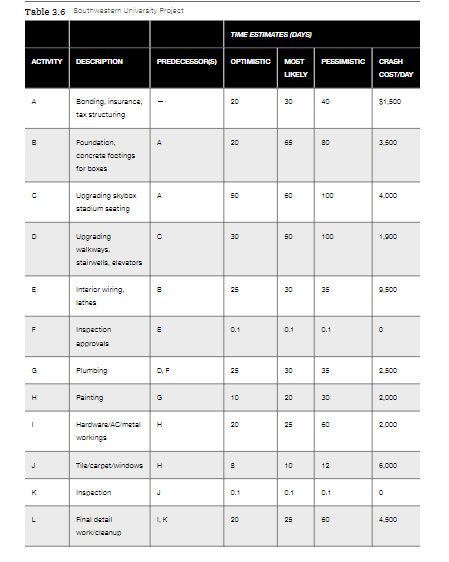
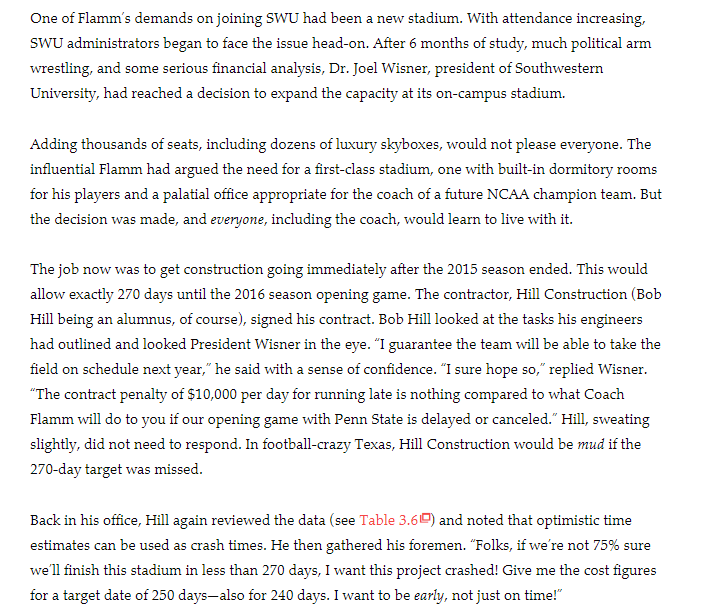

Southwestern University: (A)* Southwestern University (SWU), a large state college in Stephenville, Texas, 30 miles southwest of the Dallas/Fort Worth metroplex, enrolls close to 20,000 students. In a typical town-gown relationship, the school is a dominant force in the small city, with more students during fall and spring than permanent residents. A longtime football powerhouse, SWU is a member of the Big Eleven conference and is usually in the top 20 in college football rankings. To bolster its chances of reaching the elusive and long- desired number-one ranking, in 2009, SWU hired the legendary Phil Flamm as its head coach. Table 3.6 Southwestern Universty Project TIME ESTIMATESDAY ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION PREDECESSORES) OPTIMESTIC MOST PESIMISTIC PESMASTIC CRASH COST/DAY UMELY 20 30 40 $1.500 Bonding, insurance tax structuring B A ES 20 3.500 Foundation concrete footings for boxes c A 50 50 100 4.000 Uogracing skybox stadium seating D c 30 50 100 1.900 Uogracing walkways, stairwells, elevators Interior wiring, B 30 35 9.500 F 0.1 0.1 0.1 0 Inspection approvals G Plumbing DF 25 30 2.500 H Painting 10 20 30 2000 1 25 50 2000 Hardware/Ametal working J Tila carpet windows H B 10 12 6.000 Inspection 0.1 0.1 0 L Final detail LK 20 25 50 4.500 world cleanup One of Flamm's demands on joining SWU had been a new stadium. With attendance increasing, SWU administrators began to face the issue head-on. After 6 months of study, much political arm wrestling, and some serious financial analysis, Dr. Joel Wisner, president of Southwestern University, had reached a decision to expand the capacity at its on-campus stadium. Adding thousands of seats, including dozens of luxury skyboxes, would not please everyone. The influential Flamm had argued the need for a first-class stadium, one with built-in dormitory rooms for his players and a palatial office appropriate for the coach of a future NCAA champion team. But the decision was made, and everyone, including the coach, would learn to live with it. The job now was to get construction going immediately after the 2015 season ended. This would allow exactly 270 days until the 2016 season opening game. The contractor, Hill Construction (Bob Hill being an alumnus, of course), signed his contract. Bob Hill looked at the tasks his engineers had outlined and looked President Wisner in the eye. "I guarantee the team will be able to take the field on schedule next year," he said with a sense of confidence. "I sure hope so," replied Wisner. "The contract penalty of $10,000 per day for running late is nothing compared to what Coach Flamm will do to you if our opening game with Penn State is delayed or canceled. Hill, sweating slightly, did not need to respond. In football-crazy Texas, Hill Construction would be mud if the 270-day target was missed. Back in his office, Hill again reviewed the data (see Table 3.60) and noted that optimistic time estimates can be used as crash times. He then gathered his foremen. Folks, if we're not 75% sure we'll finish this stadium in less than 270 days, I want this project crashed! Give me the cost figures for a target date of 250 days-also for 240 days. I want to be early, not just on time!" 1. Draw the project network diagram. 2. Calculate the mean (expected activity time), standard deviation, and variance for each activity. Create a table to display the results. 3. Find the critical path. Utilize a forward and backward pass analysis. Create a table to display ES, EF, LS, LF, and slack Calculate the expected project completion time and the standard deviation of the critical path. Use the mean activity time in your calculations. 4. Find the probability of completing in 270 days. 5. Examine the possibility of crashing the project to 250 and 240 days, respectively, to answer the third discussion question. Clarification: use the optimistic time as the crash time you will need to calculate the total cost of crashing using the cost per day. You do not need to calculate cost per day for crashing as with some problems the cost is per day to crash the project down to the optimistic time. 6. Provide recommendations to managers of actions that should be pursued. Share your own insights that you discovered while solving the
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


