Question: I need help on part a b c pls 9.9 Shared Pain and Bonding. Although painful experiences are involved in social rituals in many parts


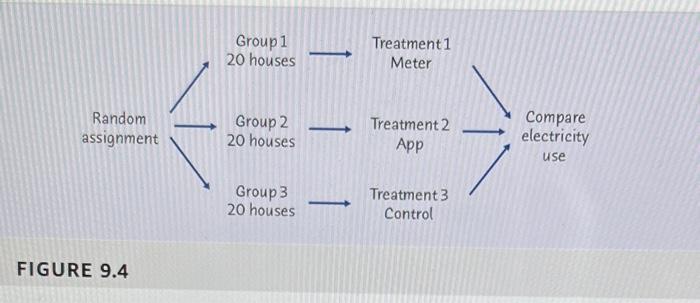

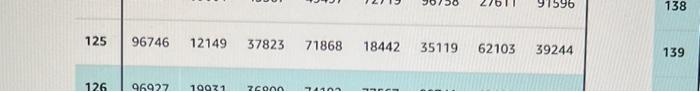
9.9 Shared Pain and Bonding. Although painful experiences are involved in social rituals in many parts of the world, little is known about the social effects of pain. Will sharing painful experiences in a small group lead to greater bonding of group members than sharing a similar nonpainful experience? Twenty- seven of 54 university students in New South Wales, Australia, were assigned at random into a pain group, with the remaining students in the no-pain group. Pain was induced by two tasks. In the first task, students submerged their hands in freezing water for as long as possible, moving metal balls at the bottom of the vessel into a submerged container; in the second task, students performed a standing wall squat with back straight and knees at 90 degrees for as long as possible. The no-pain group completed the first task using room temperature water for 90 seconds, and the second task by balancing on one foot for 60 seconds, changing feet if necessary. In both the pain and no-pain settings, the students completed the tasks in small groups, which typically consisted of four students and contained similar levels of group interaction. Afterward, each student completed a questionnaire to create a bonding score based on answers to questions such as I feel the participants in this study have a lot in common" or "I feel I can trust the other participants."12 a. Outline the design of the experiment, following the model of Figure 9.4. b. Explain how you will randomly assign the subjects at random to the two groups and then carry out this randomization using software, Group 1 20 houses Treatment1 Meter Random assignment Group 2 20 houses Treatment 2 App Compare electricity use Group 3 20 houses Treatment 3 Control FIGURE 9.4 the Simple Random Sample applet, or Table B, beginning at line 125. c. Why do you think the experimenter had students in the no-pain group complete similar pain-free tasks in small groups? Do you think this is important for the type of conclusion that can be reached? Explain. 91596 138 125 96746 12149 37823 71868 18442 35119 62103 39244 139 126 96927 10071 con TA
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


