Question: I need help on Question 2 QUESTION 1 10 points Saved For this question and the two following questions, assume that addresses are 14 bits
 I need help on Question 2
I need help on Question 2
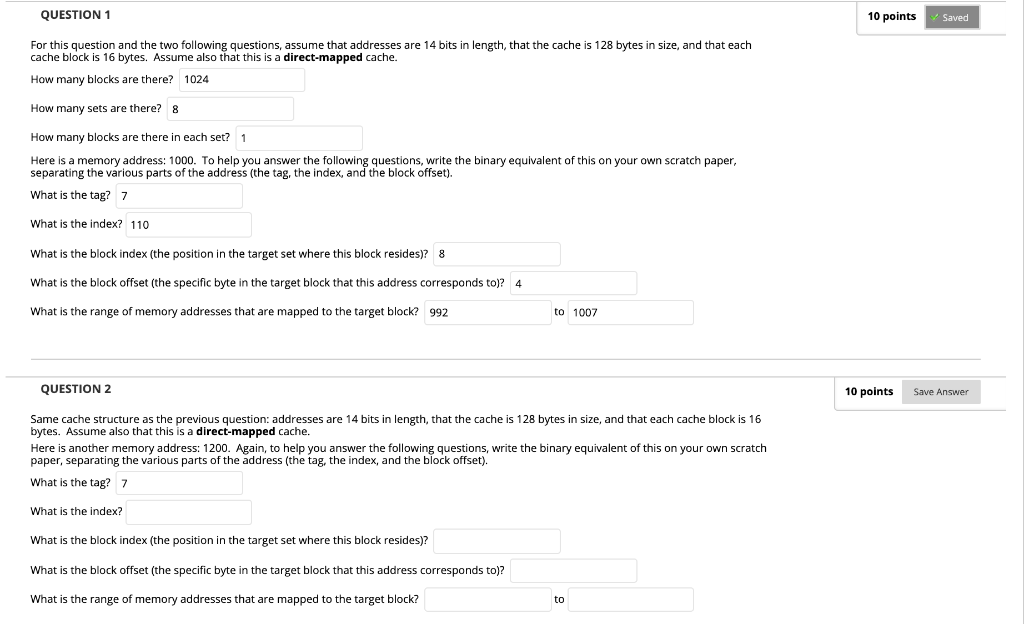
QUESTION 1 10 points Saved For this question and the two following questions, assume that addresses are 14 bits in length, that the cache is 128 bytes in size, and that each cache block is 16 bytes. Assume also that this is a direct-mapped cache. How many blocks are there? 1024 How many sets are there? 8 How many blocks are there in each set? 1 Here is a memory address: 1000. To help you answer the following questions, write the binary equivalent of this on your own scratch paper, separating the various parts of the address (the tag, the index, and the block offset). What is the tag? 7 What is the index? 110 What is the block index (the position in the target set where this block resides)? 8 What is the block offset (the specific byte in the target block that this address corresponds to)? 4 What is the range of memory addresses that are mapped to the target block? 992 to 1007 QUESTION 2 10 points Save Answer Same cache structure as the previous question: addresses are 14 bits in length, that the cache is 128 bytes in size, and that each cache block is 16 bytes. Assume also that this is a direct-mapped cache. Here is another memory address: 1200. Again, to help you answer the following questions, write the binary equivalent of this on your own scratch paper, separating the various parts of the address (the tag, the index, and the block offset). What is the tag? 7 What is the index? What is the block index (the position in the target set where this block resides)? What is the block offset (the specific byte in the target block that this address corresponds to)? What is the range of memory addresses that are mapped to the target block? to
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


