Question: I need help shifting and rotating bits for a lab in C++. The specific requirements for the assignment are: This is the code I've made
I need help shifting and rotating bits for a lab in C++. The specific requirements for the assignment are:
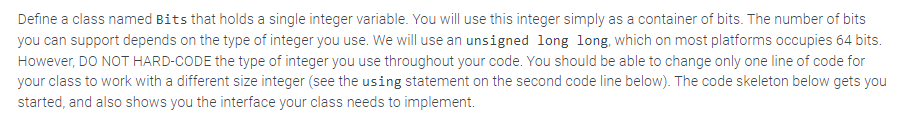
This is the code I've made so far. (That is, the shift and rotate methods are mine. Everything else was part of the skeleton.)
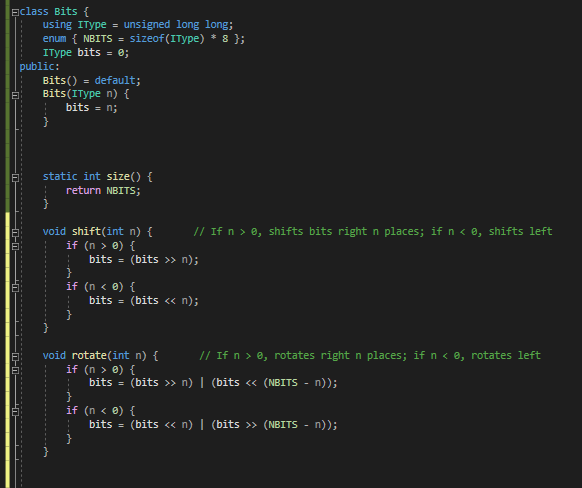
Define a class named Bits that holds a single integer variable. You will use this integer simply as a container of bits. The number of bits you can support depends on the type of integer you use. We will use an unsigned long long, which on most platforms occupies 64 bits. However, DO NOT HARD-CODE the type of integer you use throughout your code. You should be able to change only one line of code for your class to work with a different size integer (see the using statement on the second code line below). The code skeleton below gets you started, and also shows you the interface your class needs to implement. Ficlass Bits { using IType = unsigned long long; enum { NBITS = sizeof(IType) * 8 }; IType bits = m; public: Bits() default; Bits(IType n) { bits = n; } FI static int size() { return NBITS; } void shift(int n) { // If n > e, shifts bits right n places; if n 0) { bits = (bits >> n); if (n e, rotates right n places; if n
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


