Question: I need help solving this problem, thank you in advance! 24 MN Strain Positive Negative 9 2 6 26 15 Unvaccinated Vaccinated Totals Patient Group
I need help solving this problem, thank you in advance! 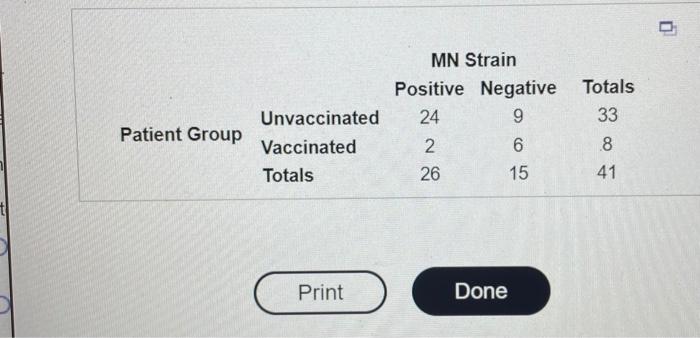


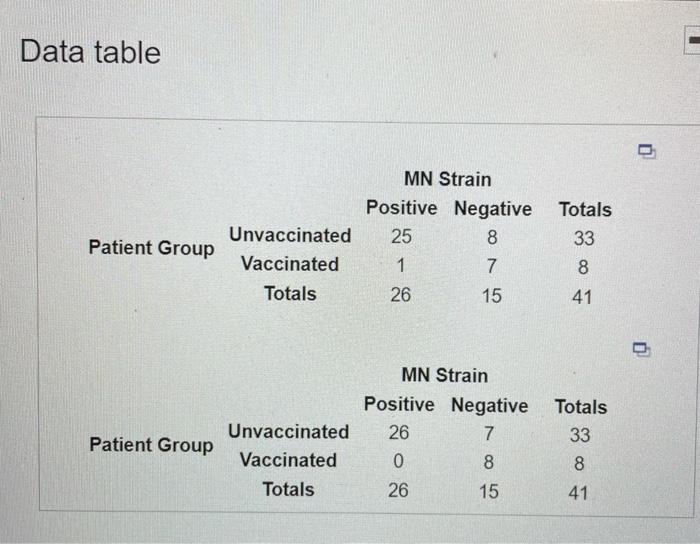

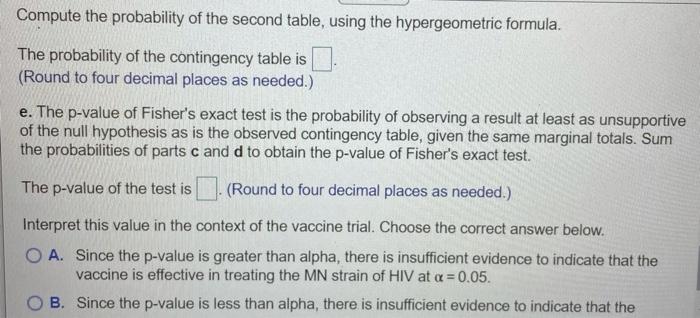
24 MN Strain Positive Negative 9 2 6 26 15 Unvaccinated Vaccinated Totals Patient Group Totals 33 .8 41 Print Done A statistician demonstrated how to test the efficacy of an HIV vaccine. He reported the results in the 2x2 table shown below. The trial consisted of 8 AIDS patients vaccinated with the new drug and 33 AIDS patients who were treated with a placebo (no vaccination). The table shows the number of patients who tested positive and negative for the MN strain in the trial follow-up period. Complete parts a through e. Click the icon to view the table. a. Conduct a test to determine whether the vaccine is effective in treating the MN strain of HIV. Use a=0.05. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: The unvaccinated and vaccinated groups are independent of each other Ha: The unvaccinated and vaccinated groups depend on each other OB. Ho: Positive and negative tested groups of patients are independent of each other He: Positive and negative tested groups of patients depend on each other OC. Ho: Vaccine and MN strain are independent Ha: Vaccine and MN strain are dependent Find the test statistic. x2 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) A statistician demonstrated how to test the efficacy of an HIV vaccine. He reported the results in the 2x2 table shown below. The trial consisted of 8 AIDS patients vaccinated with the new drug and 3 AIDS patients who were treated with a placebo (no vaccination). The table shows the number of patients who tested positive and negative for the MN strain in the trial follow-up period. Complete pa a through e. Click the icon to view the table. ... 8 33 2. 24 c. In the case of a 2x2 contingency table, R. A. Fisher developed a procedure for computing the exact p-value for the test. The method utilizes the hypergeometric probability distribution. Consider the hypergeometric probability shown on the right which represents the probability that 2 out of 8 vaccinated AIDS patients test positive and 24 out of 33 unvaccinated patients test positivethat is, the probability of the result shown in table, given that the null hypothesis of independence is true. Compute this probability. The probability is p= (Round to four decimal places as needed.) 41 26 Data table Patient Group Unvaccinated Vaccinated Totals MN Strain Positive Negative 25 8 1 7 26 15 Totals 33 8 41 MN Strain Positive Negative Totals 26 7 33 0 8 8 26 15 Unvaccinated Vaccinated Totals Patient Group 2 41 d. Refer to part c. Two contingency tables that are more unsupportive of the null hypothesis of independence than the observed table are shown in the accompanying table. Explain why these tables provide more evidence to reject He than the original table does. E! Click the icon to view the contingency tables. If vaccine and MN strain are independent, then the proportion of positive results should be relatively the same for both patient groups. In the two tables presented, the proportion of positive results for the vaccinated group is smaller than the proportion for the original table. Compute the probability of the first table, using the hypergeometric formula, The probability of the contingency table is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Compute the probability of the second table, using the hypergeometric formula. Compute the probability of the second table, using the hypergeometric formula The probability of the contingency table is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) e. The p-value of Fisher's exact test is the probability of observing a result at least as unsupportive of the null hypothesis as is the observed contingency table, given the same marginal totals. Sum the probabilities of parts c and d to obtain the p-value of Fisher's exact test. The p-value of the test is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Interpret this value in the context of the vaccine trial. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Since the p-value is greater than alpha, there is insufficient evidence to indicate that the vaccine is effective in treating the MN strain of HIV at a = 0.05. B. Since the p-value is less than alpha, there is insufficient evidence to indicate that the 





Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


