Question: I need help with 3. Duopoly: Use the same market system as in question 2. Assume that two firms made an agreement to restrict their
I need help with 3. Duopoly: Use the same market system as in question 2. Assume that two firms made an agreement to restrict their output - splitting equally the monopolist's quantity. Firm 1 holds to the agreement but firm 2 defects and chooses it's own profit maximizing output. What are the two firms outputs and profits. What is the consumer.
Can you show me how to work it and include the graphs?
Chris

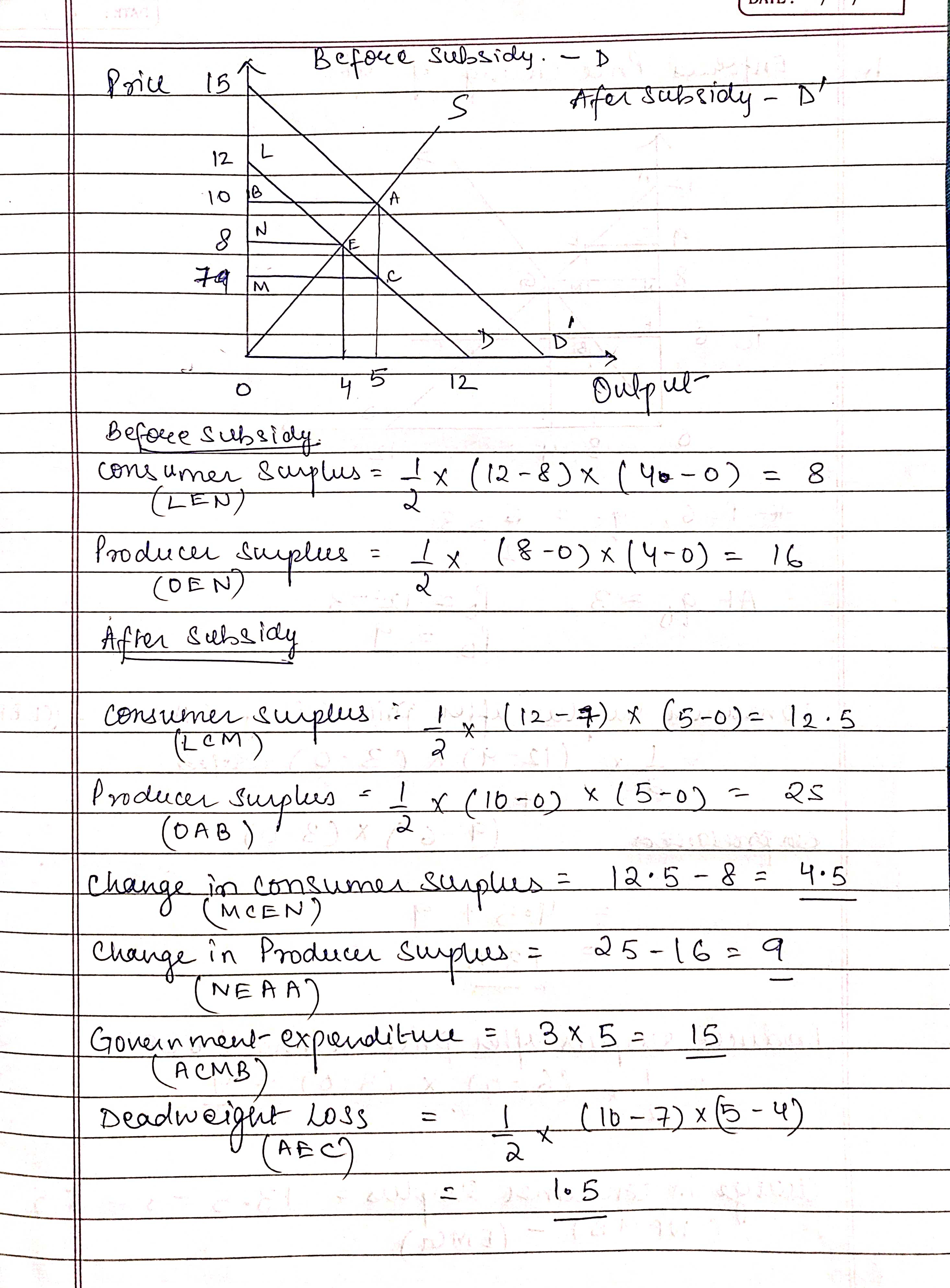
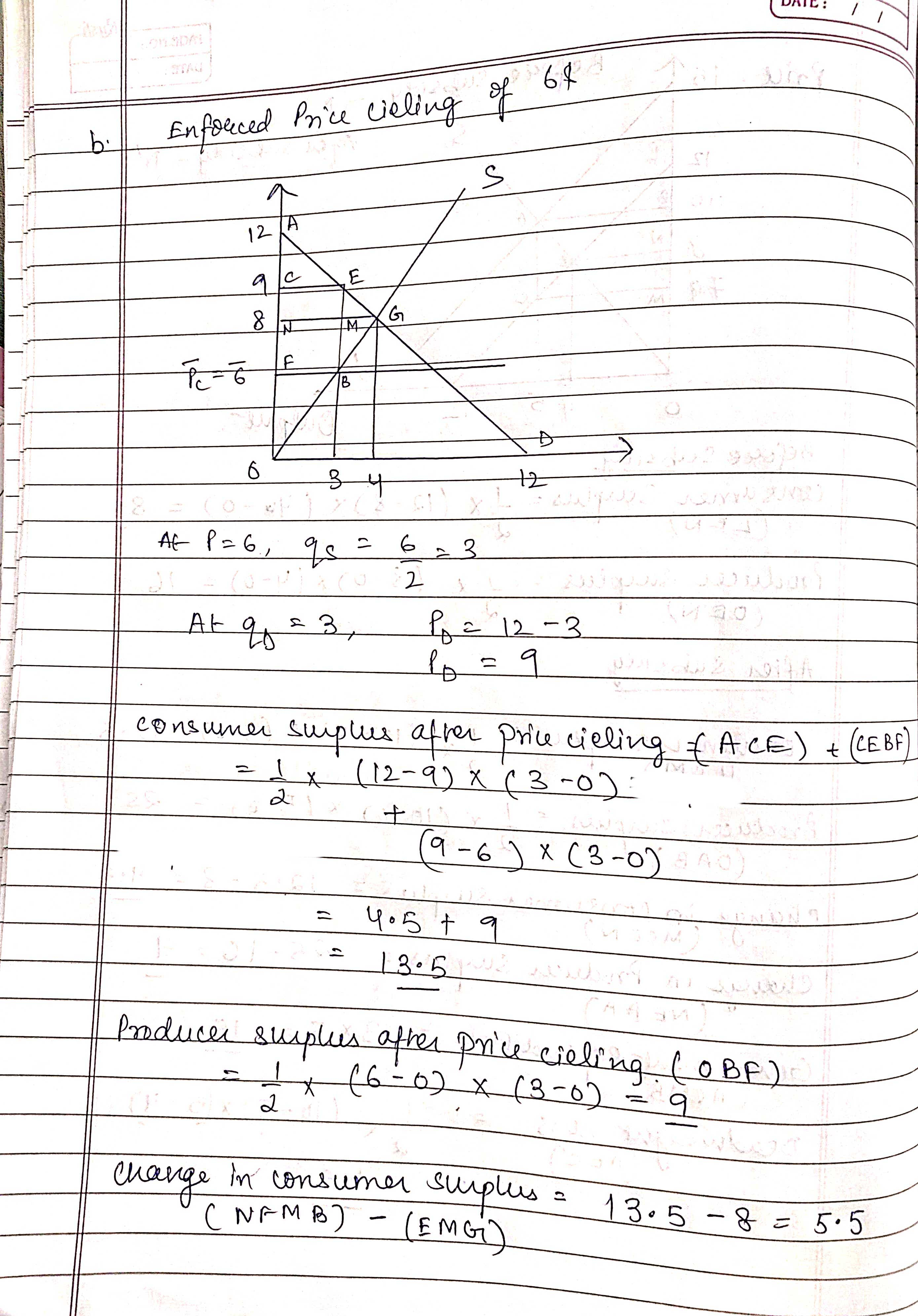


PAGE NO.: .On 20:0 DATE : I I and Is = 29 Ans PD = 12 - 9 in equilibrium In = f 12 - 9 = 29 39 = 12 and PT. 8 A Subsidy to consumers of 38 per unit - This means consumers Day a lower price for each good . Thees . PD = 12 - 9 912 12 - P 9= 12 - ( 1 : 3 ) 90 = 15 - P and 2 At equilibrium 15 - P = P 30 - 2P = P 3p = 30 P = 10 and q* = 5Price 152 Before subsidy. - D S Afer Subsidy - D 12 10 B A 8 IN 74 M . C 4 5 72 Before subsidy Consumer surplus = 1 x ( 12 - 8) x ( 40 - 0) = 8 ( LEN ) Producer Surplus = 1 x (8 - 0 ) x ( 4 - 0 ) = 16 (DEN ) After subsidy consumer surplus . ? 1 ( 12 - 4 ) x ( 5 - 0 ) = 12 . 5 ( LCM ) Producer surplus = 1 x ( 10-09 x (5 -0) - 25 ( DAB ) ' change in consumer surplus = 12 . 5 - 8 = 4.5 (MCEN) Change in Producer Surplus . = 25 - 16 = 9 NEAAJ Government- expenditure = 1 3 x 5 = 15 (ACMB Deadweight LOSS = AFC ) 2 * ( 10 - 7 ) x 5 - 4)\fchange in producer surplus . = ] - 16 = - 7 ( N F GB ) Dead weight loss ( EBG ) 1 x ( 9 - 6 ) x ( 4 - 3 ) 2 105 C. The reduction in economic s up lue / deadweight loes ) from price cieling is likely to be an under estimate because . The consumers who recieve the products are not - the consumers who value it the most . Consumers take costly actions to enhance their chances of being servedx 50 c. Explain why, according to Glaeser and Luttener's, The Misallocation of Housing Under Rent Control, 2003, the figure for dead weight loss in b. is likely an underestimate of the actual losses. See the "Empirical Studies of Market Interventions" folder in Blackboard Links for a copy of the paper. . 2. Steineman Chapter 8 #1 (Monopoly) 1. Disco, Inc., has a monopoly over the production of jukeboxes, with the follow- ing cost and revenue characteristics, where Q = the number of jukeboxes pro- duced per week:" Marginal revenue = 1,000 - 20.Q Total revenue = 1,000Q - 10Q Marginal cost = 100 + 100 What would be the price and quantity of jukeboxes sold under the following conditions? a) The firm behaved as a monopoly. b) The firm behaved as if the market were perfectly competitive. c) What is the producer and consumer surplus under monopoly and in the perfectly competitive outcome? 3. Duopoly: Use the same market system as in Question 2. Assume that two firms made an agreement to restrict their output - splitting equally the monopolist's quantity. . Firm 1 holds to the agreement but Firm.2 'defects' and chooses its own profit maximizing output. What are the two firms' outputs, and profits. What is the consumer surplus? Note: the reaction function determining firm 2's optimal response to firm I's choice is given by: R2 ( 91 ) = 90-1091 30 Extra credit: (5 points) derive the reaction function. 4. Steinemann Chapter 8.#5.. 5. One approach to regulating a natural monopoly is to let it determine its profit- maximizing point, then tax its profits and distribute them to consumers who pur- chase the good. Would this approach be preferable, from a societal perspective, to average cost pricing? JA 100.25% 1 of 1 DIC
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


