Question: I need help with a 2-part (related) Cryptology problem using Python: Breaking the shift cipher. For this exercise (as for all programming problems) include your
I need help with a 2-part (related) Cryptology problem using Python:
Breaking the shift cipher. For this exercise (as for all programming problems) include your program and screenshots of test-runs.
a) Write a program that automatically breaks a shift cipher using the following simple heuristic: the letter that occurs most frequently in the ciphertext corresponds to plaintext 'e' (which, at 12.5% is the most frequent letter in English). Write a function simpleshiftbreak(ct) that given ciphertext ct, returns the key suggested by this heuristic. You can make use of the shift-cipher program shift.py provided below:
Shift.py:

b) Test your program with texts of various lengths and prepare a statistic. More specifically, write a function testsimple(a,b) which for each text-length between a and b creates random plaintexts, encrypts them by shifting them with a randomly chosen key, and then uses your program from part a) to find the decryption key. Output should be similar to
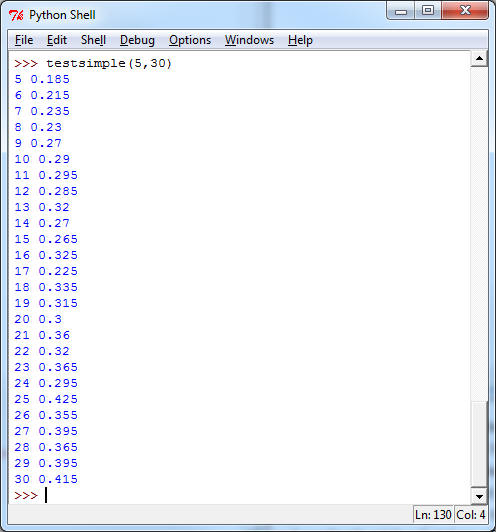
This output means that my shift-breaking algorithm breaks 18.5% of the 5-letters sentences correctly (ie. I fed 100 randomly encrypted plaintexts of length 5 to it, and it determined the correct key in 18.5 % of the cases), etc. all the way up to 41.5% of the 30 letter sentences. To generate testing material I took a long text (actually Mark Twain's Innocents Abroad) and randomly picked substrings of that text (it's ok if the text starts in the middle of a word). You want to preprocess pieces of text you pick like that by removing punctuation, spaces, etc. Here is what I use:
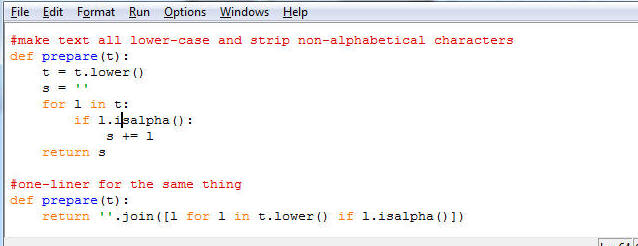
The length of the text is the test after you've removed all the non-alphabetic symbols. You may find Python dictionaries (really hash tables) useful in storing results. My code tests roughly 200 pieces of text for each length. Reading text in Python is very simple, you can read the whole text into a single string (called text below):
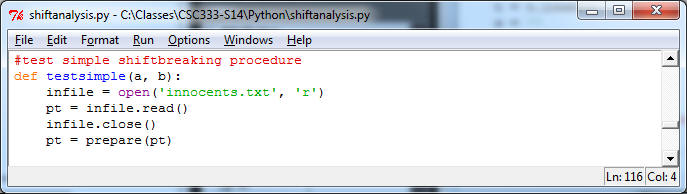
If you're on a Mac, you may need to use special codecs to read/write input. In that case, use "import codecs" at top of program, and then read the file using codecs.open('innocents.txt', 'utf-8').
#turn text into list of numbers (ASCII values) def encode (text) text text lower 01 lst (ord (letter) ord ('a') for letter in text if letter .isalpha return lst turn list of ASCII values into text def decode (lst) text join ([chr (ord ('a') +code) for code in lst]) return text def shift (pt, k plaintext pt shift k ptlst encode (pt) ctlst (x+k) 26 for x in ptlstj return decode (ctlst) #turn text into list of numbers (ASCII values) def encode (text) text text lower 01 lst (ord (letter) ord ('a') for letter in text if letter .isalpha return lst turn list of ASCII values into text def decode (lst) text join ([chr (ord ('a') +code) for code in lst]) return text def shift (pt, k plaintext pt shift k ptlst encode (pt) ctlst (x+k) 26 for x in ptlstj return decode (ctlst)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


