Question: (I need help with coding this. I keep ending up with too many errors, so if you can, please comment as much as you can.
(I need help with coding this. I keep ending up with too many errors, so if you can, please comment as much as you can. All the steps come together, and it needs to be coded in C++)

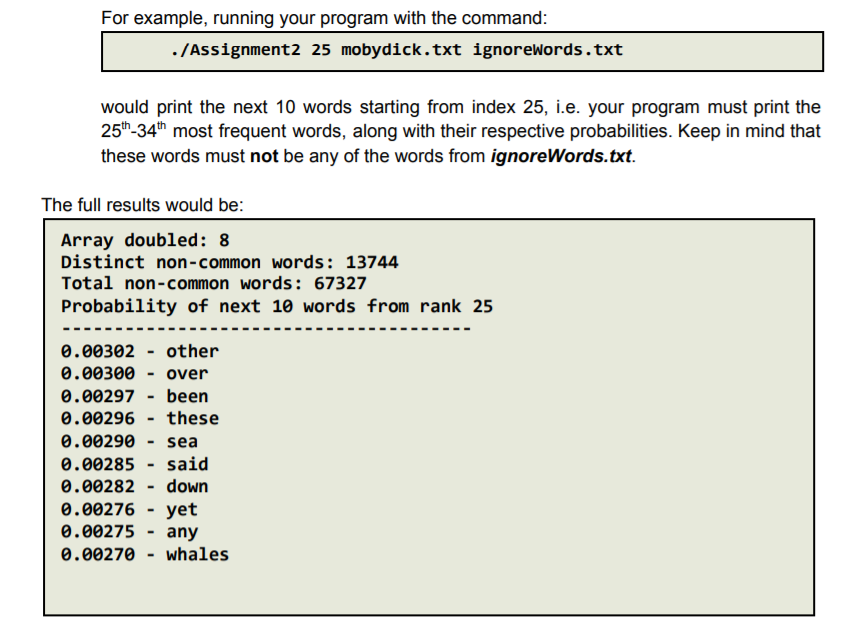



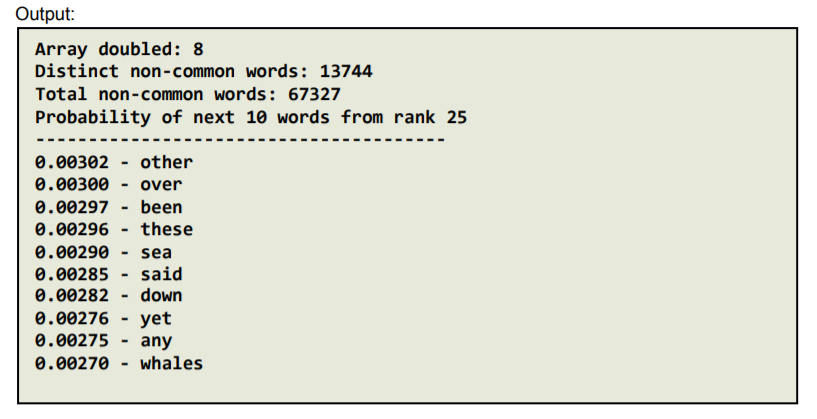
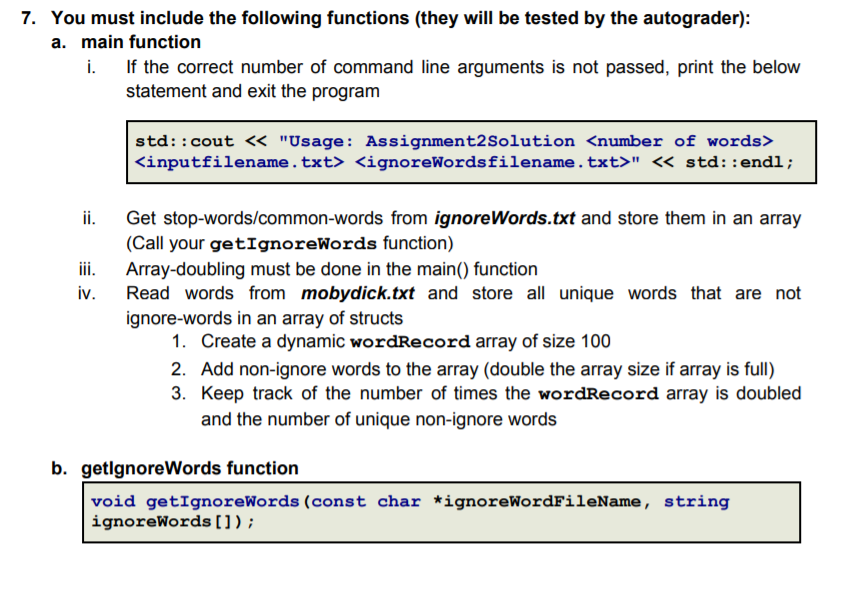

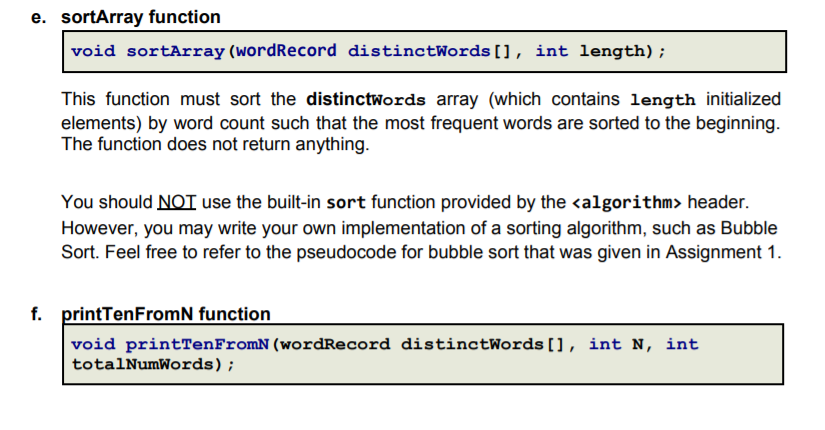
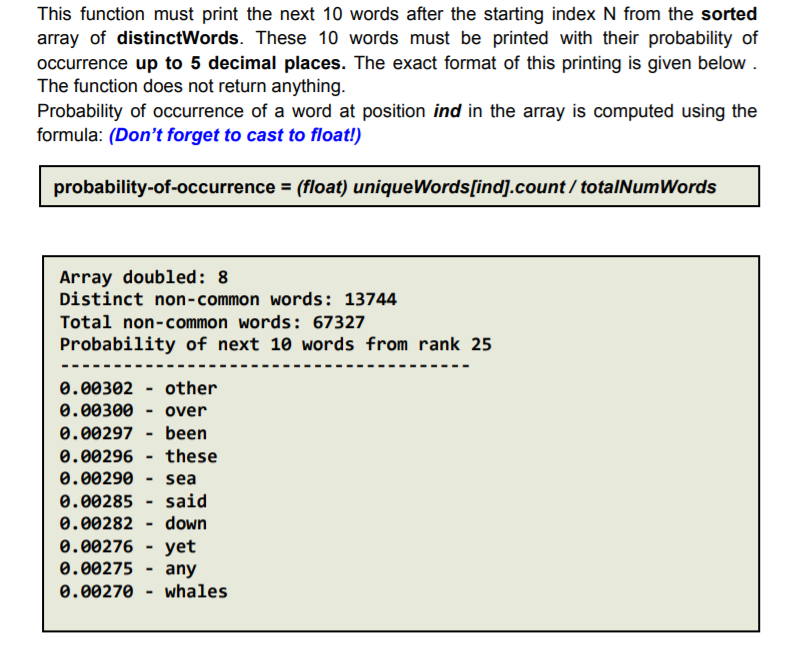
OBJECTIVES 1. Read a file with unknown size and store its contents in a dynamic array 2. Store, search and iterate through data in an array of structs 3. Use array doubling via dynamic memory to increase the size of the array Instructions In this assignment, we will write a program to analyze the word frequency of a document. As the number of words in the document may not be known a priori, we will implement a dynamically doubling array to store the information. Please read all the directions before writing code, as this write-up contains specific requirements for how the code must be written. Problem Overview: There are two files on Canvas. mobydick.txt - contains text to be read and analyzed by your program. The file contains the full text from Moby Dick. For your convenience, all the punctuation has been removed, words have been converted to lowercase, and the entire document can be read as if it were written on a single line. ignoreWords.txt contains the 50 of the most common words in the English language, which your program will ignore during analysis. Your program must take three command line arguments in the following order - a number N, the file name of the text to be read, and the file name containing the words to be ignored. It will read the text from the first file while ignoring the words from the second file and store all the unique words encountered in a dynamically doubling array. After necessary calculation, the program must print the following information: The number of times array doubling was required to store all the unique words The number of unique non-ignore words in the file The total word count of the file (excluding the ignore words) After calculating the probability of occurrence of each word and storing it in an array in the decreasing order of probability, starting from index N of the array, print the 10 most frequent words along with their probability (up to 5 decimal places) For example, running your program with the command: ./Assignment2 25 mobydick.txt ignorewords.txt would print the next 10 words starting from index 25, i.e. your program must print the 25th-34th most frequent words, along with their respective probabilities. Keep in mind that these words must not be any of the words from ignoreWords.txt. The full results would be: Array doubled: 8 Distinct non-common words: 13744 Total non-common words: 67327 Probability of next 10 words from rank 25 0.00302 other 0.00300 - over 0.00297 been 0.00296 these 0.00290 sea 0.00285 said 0.00282 down 0.00276 yet 0.00275 - any 0.00270 - whales Specifications: 1. Use an array of structs to store the words and their counts You will store each unique word and its count (the number of times it occurs in the document) in an array of structs. As the number of unique words is not known ahead of time, the array of structs must be dynamically sized. The struct must be defined as follows: struct wordRecord { string word; int count; }; 2. Use the array-doubling algorithm to increase the size of your array Your array will need to grow to fit the number of words in the file. Start with an array size of 100, and double the size whenever the array runs out of free space. You will need to allocate CSCI 2270 Data Structures Spring 2021 Instructors: Trivedi, Zagrodzki your array dynamically and copy values from the old array to the new array. (Array-doubling algorithm must be implemented in the main() function). Note: Don't use the built-in std::vector class. This will result in a loss of points. You're actually writing the code that the built-in vector uses behind-the-scenes! 3. Ignore the top 50 most common words that are read from the ignore Words.txt file To get useful information about word frequency, we will be ignoring the 50 most common words in the English language as noted in ignoreWords.txt 4. Take three command line arguments Your program must take three command line arguments 1. a number N which tells your program the starting index to print the next 10 most frequent words 2. the name of the text file to be read and analyzed 3. The name of the text file with the words to be ignored. 5. Output the Next 10 most frequent words starting from index N Your program must print out the next 10 most frequent words - not including the common words - starting index N in the text where N is passed as a command line argument. If two words have the same frequency, list them alphabetically. 6. Format your final output this way: Array doubled: Distinct non-common words: Total non-common words: Probability of next 10 words from rank - - ... - For example, using the command: ./Assignment2 25 mobydick.txt ignoreWords.txt Output: Array doubled: 8 Distinct non-common words: 13744 Total non-common words: 67327 Probability of next 10 words from rank 25 - 0.00302 - other 0.00300 over 0.00297 been 0.00296 these 0.00290 - sea 0.00285 said 0.00282 - down 0.00276 yet 0.00275 any 0.00270 whales 7. You must include the following functions (they will be tested by the autograder): a. main function i. If the correct number of command line arguments is not passed, print the below statement and exit the program std::cout " std::endl; ii. iii. iv. Get stop-words/common-words from ignoreWords.txt and store them in an array (Call your getIgnoreWords function) Array-doubling must be done in the main() function Read words from mobydick.txt and store all unique words that are not ignore-words in an array of structs 1. Create a dynamic wordRecord array of size 100 2. Add non-ignore words to the array (double the array size if array is full) 3. Keep track of the number of times the wordRecord array is doubled and the number of unique non-ignore words b. getignoreWords function void getIgnoreWords (const char *ignoreWordFileName, string ignoreWords []); This function must read the stop words from the file with the name stored in ignoreWordFileName and store them in the ignorewords array. You can assume there will be exactly 50 stop words. There is no return value. In case the file fails to open, print an error message using the below cout statement: std::cout header. However, you may write your own implementation of a sorting algorithm, such as Bubble Sort. Feel free to refer to the pseudocode for bubble sort that was given in Assignment 1. f. printTenFromN function void printTenFromN (wordRecord distinctWords [], int n, int totalNumWords) ; This function must print the next 10 words after the starting index N from the sorted array of distinctWords. These 10 words must be printed with their probability of occurrence up to 5 decimal places. The exact format of this printing is given below. The function does not return anything. Probability of occurrence of a word at position ind in the array is computed using the formula: (Don't forget to cast to float!) probability-of-occurrence = (float) unique Words[ind].count/totalNumWords Array doubled: 8 Distinct non-common words: 13744 Total non-common words: 67327 Probability of next 10 words from rank 25 0.00302 - other 0.00300 over 0.00297 been 0.00296 these 0.00290 sea 0.00285 - said 0.00282 down 0.00276 yet 0.00275 any 0.00270 whales OBJECTIVES 1. Read a file with unknown size and store its contents in a dynamic array 2. Store, search and iterate through data in an array of structs 3. Use array doubling via dynamic memory to increase the size of the array Instructions In this assignment, we will write a program to analyze the word frequency of a document. As the number of words in the document may not be known a priori, we will implement a dynamically doubling array to store the information. Please read all the directions before writing code, as this write-up contains specific requirements for how the code must be written. Problem Overview: There are two files on Canvas. mobydick.txt - contains text to be read and analyzed by your program. The file contains the full text from Moby Dick. For your convenience, all the punctuation has been removed, words have been converted to lowercase, and the entire document can be read as if it were written on a single line. ignoreWords.txt contains the 50 of the most common words in the English language, which your program will ignore during analysis. Your program must take three command line arguments in the following order - a number N, the file name of the text to be read, and the file name containing the words to be ignored. It will read the text from the first file while ignoring the words from the second file and store all the unique words encountered in a dynamically doubling array. After necessary calculation, the program must print the following information: The number of times array doubling was required to store all the unique words The number of unique non-ignore words in the file The total word count of the file (excluding the ignore words) After calculating the probability of occurrence of each word and storing it in an array in the decreasing order of probability, starting from index N of the array, print the 10 most frequent words along with their probability (up to 5 decimal places) For example, running your program with the command: ./Assignment2 25 mobydick.txt ignorewords.txt would print the next 10 words starting from index 25, i.e. your program must print the 25th-34th most frequent words, along with their respective probabilities. Keep in mind that these words must not be any of the words from ignoreWords.txt. The full results would be: Array doubled: 8 Distinct non-common words: 13744 Total non-common words: 67327 Probability of next 10 words from rank 25 0.00302 other 0.00300 - over 0.00297 been 0.00296 these 0.00290 sea 0.00285 said 0.00282 down 0.00276 yet 0.00275 - any 0.00270 - whales Specifications: 1. Use an array of structs to store the words and their counts You will store each unique word and its count (the number of times it occurs in the document) in an array of structs. As the number of unique words is not known ahead of time, the array of structs must be dynamically sized. The struct must be defined as follows: struct wordRecord { string word; int count; }; 2. Use the array-doubling algorithm to increase the size of your array Your array will need to grow to fit the number of words in the file. Start with an array size of 100, and double the size whenever the array runs out of free space. You will need to allocate CSCI 2270 Data Structures Spring 2021 Instructors: Trivedi, Zagrodzki your array dynamically and copy values from the old array to the new array. (Array-doubling algorithm must be implemented in the main() function). Note: Don't use the built-in std::vector class. This will result in a loss of points. You're actually writing the code that the built-in vector uses behind-the-scenes! 3. Ignore the top 50 most common words that are read from the ignore Words.txt file To get useful information about word frequency, we will be ignoring the 50 most common words in the English language as noted in ignoreWords.txt 4. Take three command line arguments Your program must take three command line arguments 1. a number N which tells your program the starting index to print the next 10 most frequent words 2. the name of the text file to be read and analyzed 3. The name of the text file with the words to be ignored. 5. Output the Next 10 most frequent words starting from index N Your program must print out the next 10 most frequent words - not including the common words - starting index N in the text where N is passed as a command line argument. If two words have the same frequency, list them alphabetically. 6. Format your final output this way: Array doubled: Distinct non-common words: Total non-common words: Probability of next 10 words from rank - - ... - For example, using the command: ./Assignment2 25 mobydick.txt ignoreWords.txt Output: Array doubled: 8 Distinct non-common words: 13744 Total non-common words: 67327 Probability of next 10 words from rank 25 - 0.00302 - other 0.00300 over 0.00297 been 0.00296 these 0.00290 - sea 0.00285 said 0.00282 - down 0.00276 yet 0.00275 any 0.00270 whales 7. You must include the following functions (they will be tested by the autograder): a. main function i. If the correct number of command line arguments is not passed, print the below statement and exit the program std::cout " std::endl; ii. iii. iv. Get stop-words/common-words from ignoreWords.txt and store them in an array (Call your getIgnoreWords function) Array-doubling must be done in the main() function Read words from mobydick.txt and store all unique words that are not ignore-words in an array of structs 1. Create a dynamic wordRecord array of size 100 2. Add non-ignore words to the array (double the array size if array is full) 3. Keep track of the number of times the wordRecord array is doubled and the number of unique non-ignore words b. getignoreWords function void getIgnoreWords (const char *ignoreWordFileName, string ignoreWords []); This function must read the stop words from the file with the name stored in ignoreWordFileName and store them in the ignorewords array. You can assume there will be exactly 50 stop words. There is no return value. In case the file fails to open, print an error message using the below cout statement: std::cout header. However, you may write your own implementation of a sorting algorithm, such as Bubble Sort. Feel free to refer to the pseudocode for bubble sort that was given in Assignment 1. f. printTenFromN function void printTenFromN (wordRecord distinctWords [], int n, int totalNumWords) ; This function must print the next 10 words after the starting index N from the sorted array of distinctWords. These 10 words must be printed with their probability of occurrence up to 5 decimal places. The exact format of this printing is given below. The function does not return anything. Probability of occurrence of a word at position ind in the array is computed using the formula: (Don't forget to cast to float!) probability-of-occurrence = (float) unique Words[ind].count/totalNumWords Array doubled: 8 Distinct non-common words: 13744 Total non-common words: 67327 Probability of next 10 words from rank 25 0.00302 - other 0.00300 over 0.00297 been 0.00296 these 0.00290 sea 0.00285 - said 0.00282 down 0.00276 yet 0.00275 any 0.00270 whales | |













