Question: I need help with part B of this problem, I have already figured out part 1. This question has multiple parts. Work all the parts
I need help with part B of this problem, I have already figured out part 1.
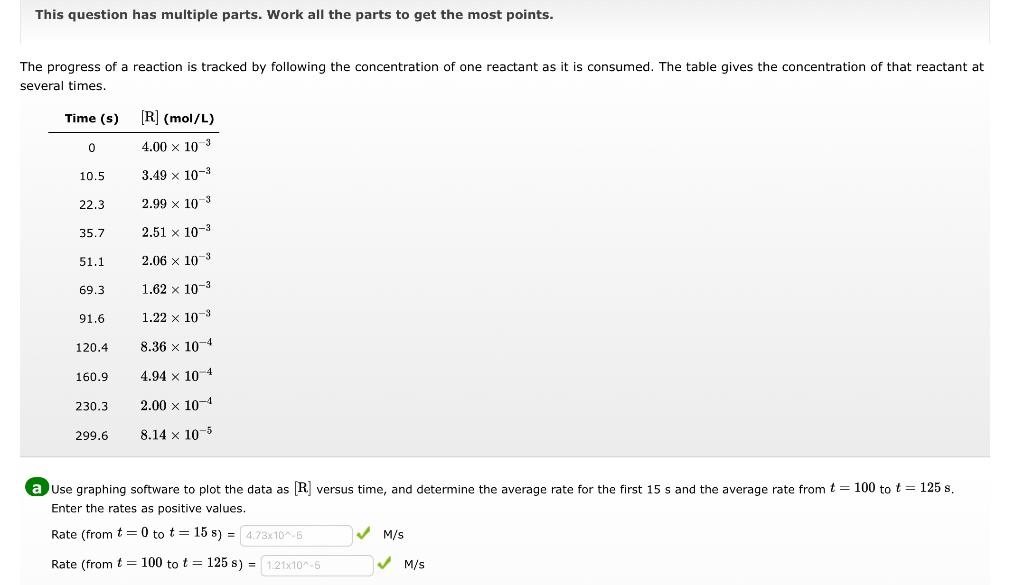
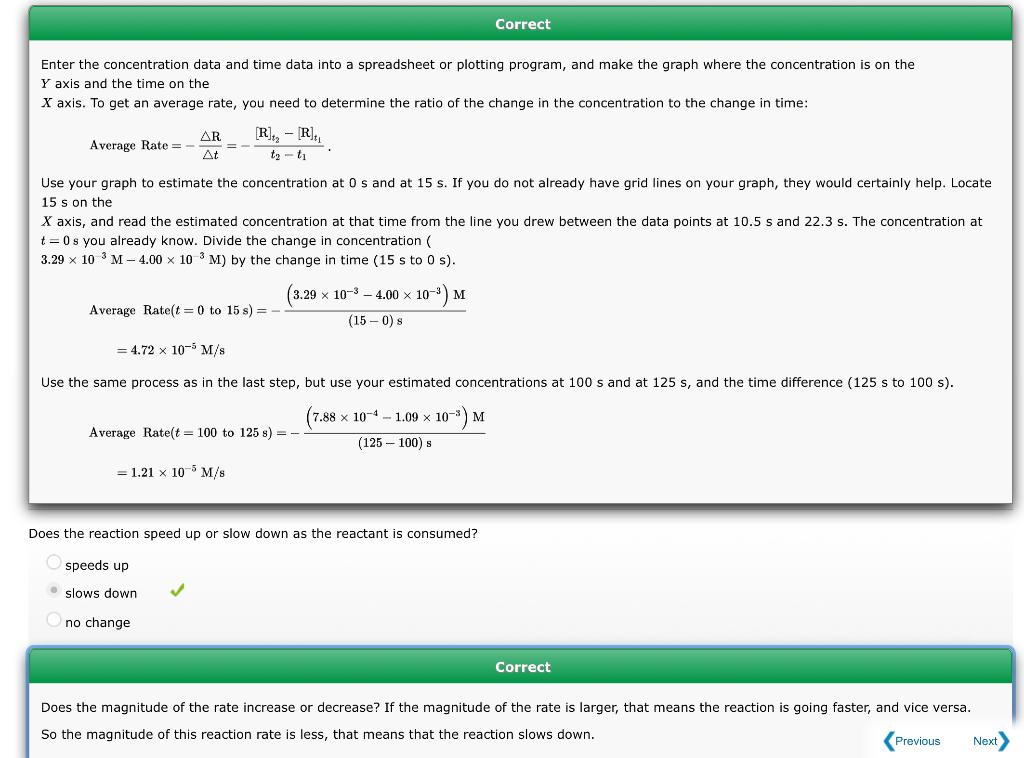

This question has multiple parts. Work all the parts to get the most points. The progress of a reaction is tracked by following the concentration of one reactant as it is consumed. The table gives the concentration of that react several times. a Use graphing software to plot the data as [R] versus time, and determine the average rate for the first 15s and the average rate from t=100 to t=125s. Enter the rates as positive values. Rate (from t=0 to t=15s ) = Rate (from t=100 to t=125s ) = M/s Enter the concentration data and time data into a spreadsheet or plotting program, and make the graph where the concentration is on the Y axis and the time on the X axis. To get an average rate, you need to determine the ratio of the change in the concentration to the change in time: AverageRate=tR=t2t1[R]t2[R]t1. Use your graph to estimate the concentration at 0 s and at 15 s. If you do not already have grid lines on your graph, they would certainly help. Locate 15 on the X axis, and read the estimated concentration at that time from the line you drew between the data points at 10.5s and 22.3s. The concentration at t=0s you already know. Divide the change in concentration ( 3.29103M4.00103M) by the change in time (15s to 0s). AverageRate(t=0to15s)=(150)s(3.291034.00103)M=4.72105M/s Use the same process as in the last step, but use your estimated concentrations at 100s and at 125s, and the time difference ( 125s to 100s ). AverageRate(t=100to125s)=(125100)s(7.881041.09103)M=1.21105M/s Does the reaction speed up or slow down as the reactant is consumed? speeds up slows down no change Correct Does the magnitude of the rate increase or decrease? If the magnitude of the rate is larger, that means the reaction is going faster, and vice versa. So the magnitude of this reaction rate is less, that means that the reaction slows down. b Use a graphical method to determine the reaction order with respect to the reactant and the value of the rate constant. What is the half-life of this reaction? Reaction order = Rate constant =s1 Half-life = s An error has been detected in your answer. Check for typos, miscalculations etc. before submitting your
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


